Guided Reading Strategies 2.1
... riddles by writing the correct name or term in the space provided. 1. “Without me, people would not have been able to survive in Egypt.” 2. “We are rapids that broke up the flow of the world’s longest river.” 3. “Egyptians created me so they would not have to carve hieroglyphics into wood or stone.” ...
... riddles by writing the correct name or term in the space provided. 1. “Without me, people would not have been able to survive in Egypt.” 2. “We are rapids that broke up the flow of the world’s longest river.” 3. “Egyptians created me so they would not have to carve hieroglyphics into wood or stone.” ...
Chapter 5 Egypt Lesson 2 REVISED Outline KEY
... Chapter 5 Ancient Egypt and Kush Lesson 2 Life in Ancient Egypt A. Egypt’s Early Rulers 1. The Old Kingdom began in Egypt around 2600 BC. 2. It lasted about 400 years. During this time, the Egyptians built cities and expanded trade. 3. Their kings, or pharaohs, set up a government. 4. Egypt was a th ...
... Chapter 5 Ancient Egypt and Kush Lesson 2 Life in Ancient Egypt A. Egypt’s Early Rulers 1. The Old Kingdom began in Egypt around 2600 BC. 2. It lasted about 400 years. During this time, the Egyptians built cities and expanded trade. 3. Their kings, or pharaohs, set up a government. 4. Egypt was a th ...
Research Methodologies
... The Hyksos ruled with great force. They burned cities and destroyed temples. The Hyksos were cruel to many Egyptians. But such force didn’t work for long. The Egyptians fought back. They used chariots against the Hyksos. Around 1539 B. C., they drove out the Hyksos. Around 1539 B.C., they drove out ...
... The Hyksos ruled with great force. They burned cities and destroyed temples. The Hyksos were cruel to many Egyptians. But such force didn’t work for long. The Egyptians fought back. They used chariots against the Hyksos. Around 1539 B. C., they drove out the Hyksos. Around 1539 B.C., they drove out ...
Nile—Egypt
... centered around city-states as in Meso but more centralized; flooding of the Nile was predictable every July; more selfsufficient than Mesopotamia & had a more centralized gov’t. that controlled the economy Divided into three eras or kingdoms 1. Old Kingdom (2686 – 2181 BCE)-united around 3100 BCE u ...
... centered around city-states as in Meso but more centralized; flooding of the Nile was predictable every July; more selfsufficient than Mesopotamia & had a more centralized gov’t. that controlled the economy Divided into three eras or kingdoms 1. Old Kingdom (2686 – 2181 BCE)-united around 3100 BCE u ...
4th Grade Social Studies Semester 2 Review
... ___ 2. The movement of early people in the search for food resulted in: a. the melting of glaciers. b. the building of land bridges. c. specialization. d. the spread of people to almost every part of Earth. ___ 3. Why was specialization of tasks important in larger bands? It allowed: a. bands to mov ...
... ___ 2. The movement of early people in the search for food resulted in: a. the melting of glaciers. b. the building of land bridges. c. specialization. d. the spread of people to almost every part of Earth. ___ 3. Why was specialization of tasks important in larger bands? It allowed: a. bands to mov ...
What was the the Old Kingdom
... Stunning advances in architecture, art, and technology were made during the Old Kingdom, fueled by the increased agricultural productivity made possible by a well developed central administration. Under the direction of the vizier, state officials collected taxes, coordinated irrigation projects to ...
... Stunning advances in architecture, art, and technology were made during the Old Kingdom, fueled by the increased agricultural productivity made possible by a well developed central administration. Under the direction of the vizier, state officials collected taxes, coordinated irrigation projects to ...
GRAPES of Ancient Egypt Powerpoint
... Menes Unites Upper & Lower Egypt C. 3100 BCE: Pharaoh Narmer (aka Menes) King of Upper Egypt Led his armies north to conquer Lower Egypt ...
... Menes Unites Upper & Lower Egypt C. 3100 BCE: Pharaoh Narmer (aka Menes) King of Upper Egypt Led his armies north to conquer Lower Egypt ...
Floodplain Civilizations Overview
... The Old Kingdom was a period of great peace Pharaoh had no standing army – each local area had its own militia There was little to no slavery Most of the large pyramids were constructed during the Old Kingdom ...
... The Old Kingdom was a period of great peace Pharaoh had no standing army – each local area had its own militia There was little to no slavery Most of the large pyramids were constructed during the Old Kingdom ...
PPT - FLYPARSONS.org
... The Old Kingdom was a period of great peace Pharaoh had no standing army – each local area had its own militia There was little to no slavery Most of the large pyramids were constructed during the Old Kingdom ...
... The Old Kingdom was a period of great peace Pharaoh had no standing army – each local area had its own militia There was little to no slavery Most of the large pyramids were constructed during the Old Kingdom ...
Pharaohs - Mrs Dado
... Lake Moeris lies at end of branch of Nile is centre of oasis called Faiyum Irrigation from Nile made Faiyum the third ...
... Lake Moeris lies at end of branch of Nile is centre of oasis called Faiyum Irrigation from Nile made Faiyum the third ...
EGYPT
... • Kingship was a divine institution and pharaohs had absolute power – Belief that the pharaoh was a god in human form – Egypt was a theocracy, a state ruled by a religious figure • Surrounded by a well-established bureaucracy – Bureaucracy = a highly structured organization, often governmental, mana ...
... • Kingship was a divine institution and pharaohs had absolute power – Belief that the pharaoh was a god in human form – Egypt was a theocracy, a state ruled by a religious figure • Surrounded by a well-established bureaucracy – Bureaucracy = a highly structured organization, often governmental, mana ...
Lesson Plan Week of Sept 26
... -Academic Assistance is available after school on Thursdays until 5pm with signed permission slip. -Egypt Test Oct 4th Standards: SS.6.W.1.1: Use timelines to identify chronological order of historical events. SS.6.W.2.4: Compare the economic, political, social, and religious institutions of ancient ...
... -Academic Assistance is available after school on Thursdays until 5pm with signed permission slip. -Egypt Test Oct 4th Standards: SS.6.W.1.1: Use timelines to identify chronological order of historical events. SS.6.W.2.4: Compare the economic, political, social, and religious institutions of ancient ...
Essential Reading Lesson 2
... The Old Kingdom began in Egypt around 2600 B.C. It lasted about 400 years. During this time, the Egyptians built cities and expanded trade. Their kings, or pharaohs, set up a government. Egypt was a theocracy. That means that the pharaoh was both the political and religious leader. The pharaoh had t ...
... The Old Kingdom began in Egypt around 2600 B.C. It lasted about 400 years. During this time, the Egyptians built cities and expanded trade. Their kings, or pharaohs, set up a government. Egypt was a theocracy. That means that the pharaoh was both the political and religious leader. The pharaoh had t ...
The Third Intermediate Period The Kushites The Assyrians The 26th
... Egypt never again regained the glory it had known at its height. ...
... Egypt never again regained the glory it had known at its height. ...
Egypt was the
... • ideas about a “soul” • belief in a hopeful life after death • Book of the Dead – collection of spells and prayers that Egyptians studied to obtain life after death • concept of judgment ...
... • ideas about a “soul” • belief in a hopeful life after death • Book of the Dead – collection of spells and prayers that Egyptians studied to obtain life after death • concept of judgment ...
World History A Ancient Egypt Booklet
... King Menes chose the city Memphis to be the capital of his country. Memphis is surrounded by desert and the Mediterranean Sea. Some people believe that "Menes" of this legend may have been a real king, possibly Narmer . They also believe it wasn't King Menes who first wore the red and white crown, b ...
... King Menes chose the city Memphis to be the capital of his country. Memphis is surrounded by desert and the Mediterranean Sea. Some people believe that "Menes" of this legend may have been a real king, possibly Narmer . They also believe it wasn't King Menes who first wore the red and white crown, b ...
Ex. 18. Which statement about mummification in ancient Egypt is
... Egyptian ideal of royal majesty. All imperfections like scars or wrinkles have been eliminated in order to portray the couple as perfect. This was only appropriate for an Egyptian pharaoh, who was a god and was thus perfect by definition. About 2300 В. С. the pharaohs lost their claim to absolute au ...
... Egyptian ideal of royal majesty. All imperfections like scars or wrinkles have been eliminated in order to portray the couple as perfect. This was only appropriate for an Egyptian pharaoh, who was a god and was thus perfect by definition. About 2300 В. С. the pharaohs lost their claim to absolute au ...
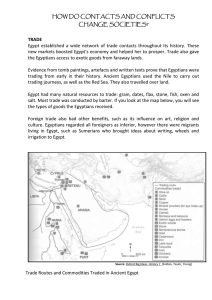
how do contacts and conflicts change societies? trade
... Some “trade” with other countries was more like an exchange of gifts. A less powerful nation (that probably feared Egypt) might give better goods than they received. This was a way foreign rulers showed respect to the pharaohs. At the height of its power, Egypt had vassal states. These were usually ...
... Some “trade” with other countries was more like an exchange of gifts. A less powerful nation (that probably feared Egypt) might give better goods than they received. This was a way foreign rulers showed respect to the pharaohs. At the height of its power, Egypt had vassal states. These were usually ...
Second Intermediate Period Old Kingdom Egypt
... Around 1786 BC some people we call the Hyksos invaded Egypt, ending the Middle Kingdom and starting the Second Intermediate Period. The Hyksos, who were invaders from West Asia, took over the eastern part of the Nile Delta (NorthEastern Egypt, the part closest to Asia), having their capital at Memph ...
... Around 1786 BC some people we call the Hyksos invaded Egypt, ending the Middle Kingdom and starting the Second Intermediate Period. The Hyksos, who were invaders from West Asia, took over the eastern part of the Nile Delta (NorthEastern Egypt, the part closest to Asia), having their capital at Memph ...
Class Lesson Plan
... Ancient History 7/8 Usborne Encyclopedia of World History 21. With what did the Egyptians link most of their gods and goddesses? ______________________________________________________________ 22. Where did the Egyptians believe their gods and goddesses lived? _______________________________________ ...
... Ancient History 7/8 Usborne Encyclopedia of World History 21. With what did the Egyptians link most of their gods and goddesses? ______________________________________________________________ 22. Where did the Egyptians believe their gods and goddesses lived? _______________________________________ ...
Egypt - Issaquah Connect
... Ruled by pharaohs – generational – family member Pharaohs in charge of trade Theocracy – ruled by one Three kingdoms (time periods) – Old, middle ,new Controlled both upper and lower Egypt Pharaoh’s thought of as a god – like a dictator Appointed bureaucrats and political leaders to carry out his or ...
... Ruled by pharaohs – generational – family member Pharaohs in charge of trade Theocracy – ruled by one Three kingdoms (time periods) – Old, middle ,new Controlled both upper and lower Egypt Pharaoh’s thought of as a god – like a dictator Appointed bureaucrats and political leaders to carry out his or ...
- erc
... on the east bank of the Nile River was built to honor the gods. Begun in the 1200s bc, it was added to by each succeeding dynasty. The use of colossal statues and obelisks was a standard for all Egyptian temples at that time. This temple was connected to the temple at Al Karnak by a street about 3.5 ...
... on the east bank of the Nile River was built to honor the gods. Begun in the 1200s bc, it was added to by each succeeding dynasty. The use of colossal statues and obelisks was a standard for all Egyptian temples at that time. This temple was connected to the temple at Al Karnak by a street about 3.5 ...
• Most Ancient Egyptian pyramids were built as tombs for pharaohs
... Most Ancient Egyptian pyramids were built as tombs for pharaohs (rulers of Ancient Egypt) and their families. To date, over 130 pyramids have been discovered in Egypt. The afterlife was incredibly important to the Egyptians. They believed that by preserving a dead person's body - which they did thro ...
... Most Ancient Egyptian pyramids were built as tombs for pharaohs (rulers of Ancient Egypt) and their families. To date, over 130 pyramids have been discovered in Egypt. The afterlife was incredibly important to the Egyptians. They believed that by preserving a dead person's body - which they did thro ...
Social Studies, 2nd 9 weeks
... Use multiple maps to understand the variety of maps available and I can use a variety of maps to understand geographic and historical how they serve as a resource to obtain geographic and historical information, including political maps, resource maps, product maps, information. Identify and define ...
... Use multiple maps to understand the variety of maps available and I can use a variety of maps to understand geographic and historical how they serve as a resource to obtain geographic and historical information, including political maps, resource maps, product maps, information. Identify and define ...
Nubia

Nubia is a region along the Nile river located in what is today northern Sudan and southern Egypt. One of the earliest civilizations of ancient Northeastern Africa, with a history that can be traced from at least 2000 B.C. onward through Nubian monuments and artifacts as well as written records from Egypt and Rome, it was home to one of the African empires. There were a number of large Nubian kingdoms throughout the Postclassical Era, the last of which collapsed in 1504, when Nubia became divided between Egypt and the Sennar sultanate resulting in the Arabization of much of the Nubian population. Nubia was again united within Ottoman Egypt in the 19th century, and within Anglo-Egyptian Sudan from 1899 to 1956.The name Nubia is derived from that of the Noba people, nomads who settled the area in the 4th century, with the collapse of the kingdom of Meroë. The Noba spoke a Nilo-Saharan language, ancestral to Old Nubian. Old Nubian was mostly used in religious texts dating from the 8th and 15th centuries AD. Before the 4th century, and throughout classical antiquity, Nubia was known as Kush, or, in Classical Greek usage, included under the name Ethiopia (Aithiopia).Historically, the people of Nubia spoke at least two varieties of the Nubian language group, a subfamily which includes Nobiin (the descendant of Old Nubian), Kenuzi-Dongola, Midob and several related varieties in the northern part of the Nuba Mountains in South Kordofan. Until at least 1970, the Birgid language was spoken north of Nyala in Darfur but is now extinct.