Simulation was carried out with the help of ns 2.29
... Mobile Ad-hoc networks (MANETs) consist of a set of mobile nodes operating without centralized administration communicating over a wireless interface. The field of mobile ad-hoc networking grew out of packet radio networks. In MANETs, the nodes are selforganized; they may move and join or leave the ...
... Mobile Ad-hoc networks (MANETs) consist of a set of mobile nodes operating without centralized administration communicating over a wireless interface. The field of mobile ad-hoc networking grew out of packet radio networks. In MANETs, the nodes are selforganized; they may move and join or leave the ...
Design Principles
... There are functions that can only be correctly implemented by the endpoints do not try to completely implement these at them elsewhere Can provide a partial form as performance enhancement Guideline not a law ...
... There are functions that can only be correctly implemented by the endpoints do not try to completely implement these at them elsewhere Can provide a partial form as performance enhancement Guideline not a law ...
lecture9
... (Part of the slides are based on Drs. Kurose & Ross’s slides for their Computer Networking book) ...
... (Part of the slides are based on Drs. Kurose & Ross’s slides for their Computer Networking book) ...
Chapter 15 Local Area Network Overview
... • Current standards for bridge protocols dictate no closed loops — Only one path between any two devices — Impossible in standards-based implementation to provide multiple paths through multiple switches between devices • Limits both performance and reliability. ...
... • Current standards for bridge protocols dictate no closed loops — Only one path between any two devices — Impossible in standards-based implementation to provide multiple paths through multiple switches between devices • Limits both performance and reliability. ...
chapter4-2007
... Flow Label: identify datagrams in same “flow.” (concept of“flow” not well defined). Next header: identify upper layer protocol for data ...
... Flow Label: identify datagrams in same “flow.” (concept of“flow” not well defined). Next header: identify upper layer protocol for data ...
INDUSTRONIC Glossary
... Group of events of which at least one event must occur to trigger an action. Events are detected by INDUSTRONIC systems as input conditions to trigger a certain action (e.g. activate a speaker or a flashing warning beacon). An event can also occur within the system (e.g. intercom station or line car ...
... Group of events of which at least one event must occur to trigger an action. Events are detected by INDUSTRONIC systems as input conditions to trigger a certain action (e.g. activate a speaker or a flashing warning beacon). An event can also occur within the system (e.g. intercom station or line car ...
Will the Internet be reliably bad enough to preserve PPVPNs?
... • multi-provider MPLS still an issue MPLScon ‘05 - 9 ...
... • multi-provider MPLS still an issue MPLScon ‘05 - 9 ...
A Framework for Group Key Management for Multicast Security
... – It sends the data to the trunk – There, the data are decrypted (leaf key) and again encrypted (trunk key). This is done by the KTs. – Before the trunk sends the data to the destination leaf, the KT decrypts (trunk key) and encrypts (leaf key) again. ...
... – It sends the data to the trunk – There, the data are decrypted (leaf key) and again encrypted (trunk key). This is done by the KTs. – Before the trunk sends the data to the destination leaf, the KT decrypts (trunk key) and encrypts (leaf key) again. ...
3rd Edition, Chapter 5
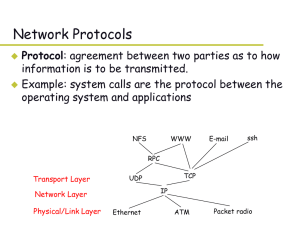
... framing, link access: encapsulate datagram into frame, adding header, trailer channel access if shared medium “MAC” addresses used in frame headers to identify source, dest • different from IP address! ...
... framing, link access: encapsulate datagram into frame, adding header, trailer channel access if shared medium “MAC” addresses used in frame headers to identify source, dest • different from IP address! ...
Multi-Segment Pseudowires : Recognising the Layer Network
... • We want to operate an integrated PSN • Network layers can be operated and planned independently • Dynamic integrated multi-layer networks are possible • Feedback loops between layers with appropriate policy controls and operator input • IP/Optical is the latest buzz in this area ...
... • We want to operate an integrated PSN • Network layers can be operated and planned independently • Dynamic integrated multi-layer networks are possible • Feedback loops between layers with appropriate policy controls and operator input • IP/Optical is the latest buzz in this area ...
MPLS networking at PSP Co Multi
... • Needed a single infrastructure that supports multitude of applications in a secure manner • Provide a highly scalable mechanism that was topology driven rather than flow driven • Load balance traffic to utilize network bandwidth efficiently • Allow core routers/networking devices to switch packets ...
... • Needed a single infrastructure that supports multitude of applications in a secure manner • Provide a highly scalable mechanism that was topology driven rather than flow driven • Load balance traffic to utilize network bandwidth efficiently • Allow core routers/networking devices to switch packets ...
No Slide Title
... station transmits at a time on the shared communication channel The protocol that determines who can transmit on a broadcast channel are called Medium Access Control (MAC) protocol The MAC protocol are implemented in the MAC sublayer which is the lower sublayer of the data link layer The higher port ...
... station transmits at a time on the shared communication channel The protocol that determines who can transmit on a broadcast channel are called Medium Access Control (MAC) protocol The MAC protocol are implemented in the MAC sublayer which is the lower sublayer of the data link layer The higher port ...
PDF
... identity of the endpoints. The protocol also embodies cryptographic commitments, join certificates, and disruption proofs to identify and exclude misbehaving hosts. The overall goals of CliqueNet, and the techniques used to achieve them, are: • Strong Anonymity: The system should provide strong, tha ...
... identity of the endpoints. The protocol also embodies cryptographic commitments, join certificates, and disruption proofs to identify and exclude misbehaving hosts. The overall goals of CliqueNet, and the techniques used to achieve them, are: • Strong Anonymity: The system should provide strong, tha ...
Sockets
... • myaddr is a pointer to address struct with: – port number and IP address – if port is 0, then host will pick ephemeral port + not usually for server (exception RPC port-map) ...
... • myaddr is a pointer to address struct with: – port number and IP address – if port is 0, then host will pick ephemeral port + not usually for server (exception RPC port-map) ...
An open source user space fast path TCP/IP stack
... An open source user space fast path TCP/IP stack ...
... An open source user space fast path TCP/IP stack ...
Document
... • An end-to-end function is best implemented at a higher level than at a lower level – End-to-end service requires all intermediate components to work properly – Higher-level better positioned to ensure correct operation ...
... • An end-to-end function is best implemented at a higher level than at a lower level – End-to-end service requires all intermediate components to work properly – Higher-level better positioned to ensure correct operation ...
Q1 on Ch09 TCPIP Protocol Suite and IP Addressing
... What steps must occur for devices to communicate between different physical network segments? (Choose two.) ...
... What steps must occur for devices to communicate between different physical network segments? (Choose two.) ...
Remote Access Service
... • Remote Access Service (RAS) is grouping of different hardware and software platforms to allow remote access to another computer or network device. • Originally used with dial-up services, Microsoft RAS has morphed into RRAS, or Routing and Remote Access Service. ...
... • Remote Access Service (RAS) is grouping of different hardware and software platforms to allow remote access to another computer or network device. • Originally used with dial-up services, Microsoft RAS has morphed into RRAS, or Routing and Remote Access Service. ...
The Internet: How It Works
... • Data is broken into small units called packets • Packets are sent over various routes to their destination • Packets are reassembled by the receiving computer • Packets contain – Destination/source addresses – Reassembling instructions – Data ...
... • Data is broken into small units called packets • Packets are sent over various routes to their destination • Packets are reassembled by the receiving computer • Packets contain – Destination/source addresses – Reassembling instructions – Data ...
hello world
... IEEE 802.15 (Bluetooth) for the Personal Area Network (PAN) IEEE 802.11 (Wi-Fi) for the Local Area Network (LAN) IEEE 802.16 (WiMax) for the Metropolitan Area Network ...
... IEEE 802.15 (Bluetooth) for the Personal Area Network (PAN) IEEE 802.11 (Wi-Fi) for the Local Area Network (LAN) IEEE 802.16 (WiMax) for the Metropolitan Area Network ...
lecture9
... datagrams: In-order datagram delivery Guaranteed minimum bandwidth to flow Restrictions on changes in inter-packet spacing No guarantee whatsoever ...
... datagrams: In-order datagram delivery Guaranteed minimum bandwidth to flow Restrictions on changes in inter-packet spacing No guarantee whatsoever ...
PPT
... – Network protocols are generally organized in layers – Replace one layer without replacing surrounding layers – Higher-level software does not have to know how to format an Ethernet packet … or even know that Ethernet is being used ...
... – Network protocols are generally organized in layers – Replace one layer without replacing surrounding layers – Higher-level software does not have to know how to format an Ethernet packet … or even know that Ethernet is being used ...
Selling an Idea or a Product
... log, sends a “yes” vote to the coordinator (site A) and crashes. – Site A crashes – Site B wakes up, checks its log and realizes that it had voted “yes” on the update. » It sends a message to site A, asking what happened. » At this point, B cannot change its mind and decide to abort, because the upd ...
... log, sends a “yes” vote to the coordinator (site A) and crashes. – Site A crashes – Site B wakes up, checks its log and realizes that it had voted “yes” on the update. » It sends a message to site A, asking what happened. » At this point, B cannot change its mind and decide to abort, because the upd ...
Internet protocol suite

The Internet protocol suite is the computer networking model and set of communications protocols used on the Internet and similar computer networks. It is commonly known as TCP/IP, because among many protocols, the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP) is the accepted and most widely used protocol in Internet. Often also called the Internet model, it was originally also known as the DoD model, because the development of the networking model was funded by DARPA, an agency of the United States Department of Defense.TCP/IP provides end-to-end connectivity specifying how data should be packetized, addressed, transmitted, routed and received at the destination. This functionality is organized into four abstraction layers which are used to sort all related protocols according to the scope of networking involved. From lowest to highest, the layers are the link layer, containing communication technologies for a single network segment (link); the internet layer, connecting hosts across independent networks, thus establishing internetworking; the transport layer handling host-to-host communication; and the application layer, which provides process-to-process application data exchange.The TCP/IP model and related protocol models are maintained by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).