1 Volcano Eruption Styles and Case Examples
... pyroclastic flow of tephra at >700°C moving at 80 mph. The Plinian column rose to a height of about 24 km. The surge reached 20 km north of the volcano, leveling trees across a swath 30 km ...
... pyroclastic flow of tephra at >700°C moving at 80 mph. The Plinian column rose to a height of about 24 km. The surge reached 20 km north of the volcano, leveling trees across a swath 30 km ...
Volcano Webquest
... What happens to the finest ash particles that get ejected from the volcano during an eruption? ...
... What happens to the finest ash particles that get ejected from the volcano during an eruption? ...
Hazard map for volcanic ballistic impacts at El Chichón volcano
... case of a new eruption. The hazard map of El Chichón volcano (Macías et al., 2008) comprises pyroclastic flows, pyroclastic surges, lahars and ash fall but not ballistic projectiles, which represent an important threat to people, infrastructure and vegetation in the case of an eruption. In fact, the ...
... case of a new eruption. The hazard map of El Chichón volcano (Macías et al., 2008) comprises pyroclastic flows, pyroclastic surges, lahars and ash fall but not ballistic projectiles, which represent an important threat to people, infrastructure and vegetation in the case of an eruption. In fact, the ...
Introduction to Volcanism and Plate Tectonic Overview
... note that some calderas can be very large – ! the average is ~6 km but the range is from ~2-50 km! ...
... note that some calderas can be very large – ! the average is ~6 km but the range is from ~2-50 km! ...
Lithosphere L > E Heat flowing in Earth`s core below the lithosphere
... “old” magma that either remains below ground (for example, as an intrusion) or is rising toward the surface. In this case, gases may escape continuously into the atmosphere from the soil, volcanic vents, fumaroles, and hydrothermal systems. ...
... “old” magma that either remains below ground (for example, as an intrusion) or is rising toward the surface. In this case, gases may escape continuously into the atmosphere from the soil, volcanic vents, fumaroles, and hydrothermal systems. ...
Chapter 5 and 6 Test Study Guide
... An island arc forms where two oceanic plates collide (p218). 4. Give examples of hot spot volcanoes. Hawaiian Islands, Yellowstone National Park (p 219) New hot spot volcanoes form as the plate drifts over the hot spot. 5. What causes magma to erupt to the surface? The force of expanding gases pushe ...
... An island arc forms where two oceanic plates collide (p218). 4. Give examples of hot spot volcanoes. Hawaiian Islands, Yellowstone National Park (p 219) New hot spot volcanoes form as the plate drifts over the hot spot. 5. What causes magma to erupt to the surface? The force of expanding gases pushe ...
Chapter 13 Section 2 Review Page 330
... http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=3977416382972126736&q=mt+st+helens+eruption&hl=en ...
... http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=3977416382972126736&q=mt+st+helens+eruption&hl=en ...
Section 13
... http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=3977416382972126736&q=mt+st+helens+eruption&hl=en ...
... http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=3977416382972126736&q=mt+st+helens+eruption&hl=en ...
Section 13
... eruptions be more likely to increase the steepness of a volcanic cone? Explain your answer. Explosive eruption are more likely to increase volcano height, because the pyroclastic materials rise upward and fall close to the volcanic vent. ...
... eruptions be more likely to increase the steepness of a volcanic cone? Explain your answer. Explosive eruption are more likely to increase volcano height, because the pyroclastic materials rise upward and fall close to the volcanic vent. ...
Impact of Volcanoes
... If a volcano erupts under the ocean, it can cause a tsunami—not only from its blast, but from the earthquake it creates. Lava and ____________________ flows can set fire to homes, cars, or anything else that is combustible. A ___________ can spit out debris that blocks a river channel or causes a cr ...
... If a volcano erupts under the ocean, it can cause a tsunami—not only from its blast, but from the earthquake it creates. Lava and ____________________ flows can set fire to homes, cars, or anything else that is combustible. A ___________ can spit out debris that blocks a river channel or causes a cr ...
mount st helens presentation byme nd rachael welton
... • At the same time, ice, snow and several glaciers which were on the volcano melted forming a large series of lahars that reached as far as the Columbia River ( nearly 50 miles to the south west) ...
... • At the same time, ice, snow and several glaciers which were on the volcano melted forming a large series of lahars that reached as far as the Columbia River ( nearly 50 miles to the south west) ...
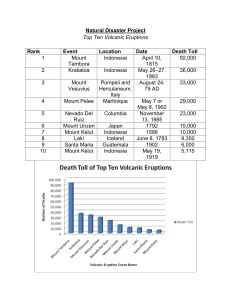
Natural Disaster Project Top Ten Volcanic Eruptions Rank Event
... city of Shimabaraon the island of Kyūshū, Japan’s southernmost main island.In 1792, the collapse of one of its several lava domes triggered a tsunami that killed about 15,000 people in Japan’s worst-ever volcanic-related disaster. The volcano was most recently active from 1990 to 1995, and a large e ...
... city of Shimabaraon the island of Kyūshū, Japan’s southernmost main island.In 1792, the collapse of one of its several lava domes triggered a tsunami that killed about 15,000 people in Japan’s worst-ever volcanic-related disaster. The volcano was most recently active from 1990 to 1995, and a large e ...
Force of Volcanoes
... ______________ volcanoes form from long, gradual lava flows, pouring out in all directions. The ___________ ______________ are short and built from these ejected materials, mainly ash and rocks that fall near the summit or crate of the volcano. ___________________ magma is a mixture of basaltic and ...
... ______________ volcanoes form from long, gradual lava flows, pouring out in all directions. The ___________ ______________ are short and built from these ejected materials, mainly ash and rocks that fall near the summit or crate of the volcano. ___________________ magma is a mixture of basaltic and ...
to start the Powerpoint presentation
... Draft volcano primer: Mt. Pinatubo and Taal volcanoes, the Philippines ...
... Draft volcano primer: Mt. Pinatubo and Taal volcanoes, the Philippines ...
Volcanic and Plutonic
... Tephra: a general term for materials of varying sizes ejected from a volcano during an explosive eruption. Tephra may range from fine ash to course pyroclasts or bombs. Volcanic Bombs: larger chucks of magma ejected during an eruption that cool rapidly in the air and land in various shapes. Volcanic ...
... Tephra: a general term for materials of varying sizes ejected from a volcano during an explosive eruption. Tephra may range from fine ash to course pyroclasts or bombs. Volcanic Bombs: larger chucks of magma ejected during an eruption that cool rapidly in the air and land in various shapes. Volcanic ...
The 1996 Surtseyan Type Eruption in Karymskoye Intracaldera Lake
... On January 2-3, 1996 a surtseyan type eruption with a discharge rate of basaltic magma of ~10 millions kg/s occurred in Karymskoe caldera lake. Initial water depth above the eruption vent was ~50 m. Characteristics of the deposits together with analyses of videotape of several explosions have allowe ...
... On January 2-3, 1996 a surtseyan type eruption with a discharge rate of basaltic magma of ~10 millions kg/s occurred in Karymskoe caldera lake. Initial water depth above the eruption vent was ~50 m. Characteristics of the deposits together with analyses of videotape of several explosions have allowe ...
EandV_Exam2_StudyGui..
... following: Is it extrusive or intrusive? What is its composition (mafic/intermediate/felsic) Which generally contains the most water? Is it high or low in silica? Is it more viscous or less viscous? ...
... following: Is it extrusive or intrusive? What is its composition (mafic/intermediate/felsic) Which generally contains the most water? Is it high or low in silica? Is it more viscous or less viscous? ...
volcanoreview
... composite cones, with explosive eruptions and erupted materials such as ash, bombs, and blocks. Mt St Helens ...
... composite cones, with explosive eruptions and erupted materials such as ash, bombs, and blocks. Mt St Helens ...
Chapter 5: Volcanoes
... from the magma chamber to the pipe until it flows or explodes out of the vent. ...
... from the magma chamber to the pipe until it flows or explodes out of the vent. ...
DISASTER EMERGENCY RESPONSE. Part VI.
... the 2nd largest terrestrial eruption of the 20th century, generated 200+ destructive lahars. ...
... the 2nd largest terrestrial eruption of the 20th century, generated 200+ destructive lahars. ...
Explosive and Non - Saint Peter School | Danbury, CT
... • Most of the rocks on the ocean floor come from these types of eruptions • Magma from these eruption have less silica • Magma is thinner and runnier Explosive • More destructive than a non-explosive Volcano • Produces hot ash and gas • Rock fragments shoot in the air • Ash from this type of eruptio ...
... • Most of the rocks on the ocean floor come from these types of eruptions • Magma from these eruption have less silica • Magma is thinner and runnier Explosive • More destructive than a non-explosive Volcano • Produces hot ash and gas • Rock fragments shoot in the air • Ash from this type of eruptio ...
Mount Kilauea, HI
... after the last known eruptive activity. This is the largest eruption that has occurred that anyone can remember and the second largest land eruption in the 20th century. Mount Pinatubo is a large, nearly symmetrical structure that is composed of layers of lava and pyroclastic deposits. Mount Pinatub ...
... after the last known eruptive activity. This is the largest eruption that has occurred that anyone can remember and the second largest land eruption in the 20th century. Mount Pinatubo is a large, nearly symmetrical structure that is composed of layers of lava and pyroclastic deposits. Mount Pinatub ...
Mount Pinatubo

Mount Pinatubo (Filipino: Bundok Pinatubo) is an active stratovolcano in the Cabusilan Mountains on the island of Luzon, near the tripoint of the Philippine provinces of Zambales, Tarlac, and Pampanga. Before the volcanic activities of 1991, its eruptive history was unknown to most people. It was heavily eroded, inconspicuous and obscured from view. It was covered with dense forest which supported a population of several thousand indigenous people, the Aetas, who fled to the mountains during the Spanish conquest of the Philippines.The volcano's Plinian / Ultra-Plinian eruption on 15 June 1991 produced the second largest terrestrial eruption of the 20th century after the 1912 eruption of Novarupta in the Alaska Peninsula.Complicating the eruption was the arrival of Typhoon Yunya (Diding), bringing a lethal mix of ash and rain to areas surrounding the volcano. Successful predictions at the onset of the climactic eruption led to the evacuation of tens of thousands of people from the surrounding areas, saving many lives, but the surrounding areas were severely damaged by pyroclastic flows, ash deposits, and subsequently, by the lahars caused by rainwaters re-mobilizing earlier volcanic deposits causing extensive destruction to infrastructure and changing the river systems months to years after the eruption.The effects of the eruption were felt worldwide. It ejected roughly 10,000,000,000 tonnes (1.1×1010 short tons) or 10 km3 (2.4 cu mi) of magma, and 20,000,000 tonnes (22,000,000 short tons) SO2, bringing vast quantities of minerals and metals to the surface environment. It injected more particulate into the stratosphere than any eruption since Krakatoa in 1883. Over the following months, the aerosols formed a global layer of sulfuric acid haze. Global temperatures dropped by about 0.5 °C (0.9 °F) in the years 1991-93, and ozone depletion temporarily increased substantially.