DNA - SchoolRack
... – Guanine bonds to Cytosine – Because of the complementary base pairing, adenine and thymine always exist in equal amounts; and guanine and cytosine always exist in equal amount. ...
... – Guanine bonds to Cytosine – Because of the complementary base pairing, adenine and thymine always exist in equal amounts; and guanine and cytosine always exist in equal amount. ...
Practise Final exam
... PCR involves denaturation of DNA followed by annealing primers and then synthesis from the primers using thermostable DNA polymerase. Generally each of these three steps is performed at a specific temperature. These temperatures are most often: A 95 C, 55 C, 72 C B 55 C, 72 C, 95 C C 72 C, 55 C, 95 ...
... PCR involves denaturation of DNA followed by annealing primers and then synthesis from the primers using thermostable DNA polymerase. Generally each of these three steps is performed at a specific temperature. These temperatures are most often: A 95 C, 55 C, 72 C B 55 C, 72 C, 95 C C 72 C, 55 C, 95 ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS: TRANSLATION AND
... mRNAs, are usually synthesized as significantly larger precursor molecules that are processed prior to export from the nucleus. Eukaryotic mRNA in the cytosol has several identifying characteristics. It is almost always monocistronic, that is, encoding a single polypeptide. The 59 end is capped with ...
... mRNAs, are usually synthesized as significantly larger precursor molecules that are processed prior to export from the nucleus. Eukaryotic mRNA in the cytosol has several identifying characteristics. It is almost always monocistronic, that is, encoding a single polypeptide. The 59 end is capped with ...
Coevolution of an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase with its tRNA substrates
... Microbiology and Center for Biocatalysis and Bioprocessing, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA 52242 ...
... Microbiology and Center for Biocatalysis and Bioprocessing, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA 52242 ...
Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics
... PCR involves denaturation of DNA followed by annealing primers and then synthesis from the primers using thermostable DNA polymerase. Generally each of these three steps is performed at a specific temperature. These temperatures are most often: A 95 C, 55 C, 72 C B 55 C, 72 C, 95 C C 72 C, 55 C, 95 ...
... PCR involves denaturation of DNA followed by annealing primers and then synthesis from the primers using thermostable DNA polymerase. Generally each of these three steps is performed at a specific temperature. These temperatures are most often: A 95 C, 55 C, 72 C B 55 C, 72 C, 95 C C 72 C, 55 C, 95 ...
Chapter 5 Gases - LCMR School District
... tRNA, and rRNA play during translation? • mRNA carries protein-building information; the bases in mRNA are “read” in sets of three during protein synthesis; most base triplets (codons) code for amino acids; the genetic code consists of all sixty-four codons • Ribosomes, which consist of two subunits ...
... tRNA, and rRNA play during translation? • mRNA carries protein-building information; the bases in mRNA are “read” in sets of three during protein synthesis; most base triplets (codons) code for amino acids; the genetic code consists of all sixty-four codons • Ribosomes, which consist of two subunits ...
Guided Exploration- (RI3) Learning Goal Three: Explain how DNA is
... DNA is the directions to build our bodies. The only problem is, DNA is locked inside the nucleus of a cell and can’t get out. To solve this problem, copies of the DNA are made in a form called mRNA. The process of making mRNA from DNA is called transcription. After transcription, the mRNA copies lea ...
... DNA is the directions to build our bodies. The only problem is, DNA is locked inside the nucleus of a cell and can’t get out. To solve this problem, copies of the DNA are made in a form called mRNA. The process of making mRNA from DNA is called transcription. After transcription, the mRNA copies lea ...
DNA REVIEW Name
... 10. What is the ultimate purpose of DNA?? ( what does it do for us??) DNA provides the codes for making all of our proteins 11. What are purines? Large double ringed bases Name the two bases which are purines. Adenine and Guanine 12. What are pyrimidines? Smaller single ringed bases Name the two bas ...
... 10. What is the ultimate purpose of DNA?? ( what does it do for us??) DNA provides the codes for making all of our proteins 11. What are purines? Large double ringed bases Name the two bases which are purines. Adenine and Guanine 12. What are pyrimidines? Smaller single ringed bases Name the two bas ...
Chapter 17- Transcription and Translation
... B) What region of the DNA do general transcription factors bind to? C) What is an activator protein (specific transcription factor)? D) What region of the DNA do the activator proteins bind to? E) How is the binding of transcription factors and activator proteins impacted by the how tightly DNA is b ...
... B) What region of the DNA do general transcription factors bind to? C) What is an activator protein (specific transcription factor)? D) What region of the DNA do the activator proteins bind to? E) How is the binding of transcription factors and activator proteins impacted by the how tightly DNA is b ...
Chapter 15
... • Necessary to get the RNA polymerase II enzyme to a promoter and to initiate gene expression • Interact with RNA polymerase to form initiation complex at promoter ...
... • Necessary to get the RNA polymerase II enzyme to a promoter and to initiate gene expression • Interact with RNA polymerase to form initiation complex at promoter ...
Protein Synthesis Review Guide
... Mutations are a change in the sequence of nucleotide bases. This can happen during Replication (DNA DNA) or during Transcription (DNA RNA). There are 3 major types of mutations: 1) Point Mutation: A mutation that involves a single nucleotide is called a POINT mutation (it happens at a single poi ...
... Mutations are a change in the sequence of nucleotide bases. This can happen during Replication (DNA DNA) or during Transcription (DNA RNA). There are 3 major types of mutations: 1) Point Mutation: A mutation that involves a single nucleotide is called a POINT mutation (it happens at a single poi ...
Transcription Translation Powerpoint
... 1. SWBAT discuss translation using pictures, words, models, and online animations. 2. SWBAT draw out translation in their notes. 3. SWBAT complete a conclusion activity using a worksheet. 4. SWBAT answer multiple choice and short answer questions about transcription and replication. ...
... 1. SWBAT discuss translation using pictures, words, models, and online animations. 2. SWBAT draw out translation in their notes. 3. SWBAT complete a conclusion activity using a worksheet. 4. SWBAT answer multiple choice and short answer questions about transcription and replication. ...
Biology Final Exam 2011 Review - Dallastown Area School District
... 4. Diagram a pyramid of energy and explain why a pyramid is a good representation of how energy passes through an ecosystem. 5. Explain how photosynthesis and Respiration interact with each other in terms of the effect on the amounts of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the air. 6. Diagram a strand of DN ...
... 4. Diagram a pyramid of energy and explain why a pyramid is a good representation of how energy passes through an ecosystem. 5. Explain how photosynthesis and Respiration interact with each other in terms of the effect on the amounts of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the air. 6. Diagram a strand of DN ...
BIOL562_Lecture_13
... attached to amino acid by aminoacylation; 5’ end is attached to mRNA by condon-anticodon interactions; wobble effect allows single tRNA read more than 1 codons. Bacterial ribosome has internal binding site for mRNA; eukaryote doesn’t; initiation is controlled by global or transcript-specific mechani ...
... attached to amino acid by aminoacylation; 5’ end is attached to mRNA by condon-anticodon interactions; wobble effect allows single tRNA read more than 1 codons. Bacterial ribosome has internal binding site for mRNA; eukaryote doesn’t; initiation is controlled by global or transcript-specific mechani ...
Lecture3 (1/22/08) "Nucleic Acids, RNA, and Proteins"
... Also, notice start & stop codons. Can tell on DNA where protein starts/stops. ...
... Also, notice start & stop codons. Can tell on DNA where protein starts/stops. ...
Slides - nanoHUB
... Also, notice start & stop codons. Can tell on DNA where protein starts/stops. ...
... Also, notice start & stop codons. Can tell on DNA where protein starts/stops. ...
Ch 18 - Bob Bruner`s Chemistry and Molecular Biology Resources
... You should understand the general idea of the wobble phenomenon, which allows one tRNA to “properly” read more than one codon. Inosine in the anticodon is an example of tRNA base modification. More about this in Ch 19. We have already seen how the (bacterial) initiator tRNA can use a variety of codo ...
... You should understand the general idea of the wobble phenomenon, which allows one tRNA to “properly” read more than one codon. Inosine in the anticodon is an example of tRNA base modification. More about this in Ch 19. We have already seen how the (bacterial) initiator tRNA can use a variety of codo ...
Chapter 8 Protein Synthesis Study Guide
... Specifically, a locus on the human X chromosome contains such a stretch of nucleotides in which the triplet CGG is repeated. This causes a constriction in the X chromosome, which makes it quite fragile. This type of mutation is: _________________________ 2. In sickle-cell anemia, the gene for beta g ...
... Specifically, a locus on the human X chromosome contains such a stretch of nucleotides in which the triplet CGG is repeated. This causes a constriction in the X chromosome, which makes it quite fragile. This type of mutation is: _________________________ 2. In sickle-cell anemia, the gene for beta g ...
TRANSLATION: How to make proteins?
... Aminoacyl-AMP + tRNA Aminoacyl-tRNA + AMP Is catalyzed by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases There are at least 20 aa-tRNA synthetases, one for each amino acid Aminoacylation accuracy is very important for translation fidelity ...
... Aminoacyl-AMP + tRNA Aminoacyl-tRNA + AMP Is catalyzed by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases There are at least 20 aa-tRNA synthetases, one for each amino acid Aminoacylation accuracy is very important for translation fidelity ...
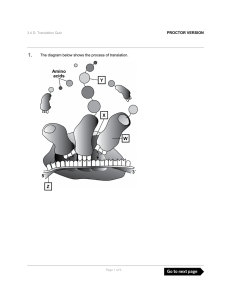
The diagram below shows the process of translation. PROCTOR
... (C) All of the amino acids after the first will be changed in the polypeptide, because the deletion will create a shift beginning with the second, and this will change all codons that follow. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that most deletions result in a frames ...
... (C) All of the amino acids after the first will be changed in the polypeptide, because the deletion will create a shift beginning with the second, and this will change all codons that follow. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that most deletions result in a frames ...
Molecular Biology
... from the nucleic acid base pair language to the amino acid language • Crick proposed that some type of adapter molecule was needed to provide the bridge for translation, perhaps a small RNA ...
... from the nucleic acid base pair language to the amino acid language • Crick proposed that some type of adapter molecule was needed to provide the bridge for translation, perhaps a small RNA ...
Life: The Science of Biology, 8e
... polypeptide. • tRNA - Transfer RNA: Brings amino acids to ribosomes during translation. • rRNA - Ribosomal RNA: With ribosomal proteins, makes up the ribosomes, the organelles that translate the mRNA. ...
... polypeptide. • tRNA - Transfer RNA: Brings amino acids to ribosomes during translation. • rRNA - Ribosomal RNA: With ribosomal proteins, makes up the ribosomes, the organelles that translate the mRNA. ...
Transfer RNA

A transfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA and archaically referred to as sRNA, for soluble RNA) is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length, that serves as the physical link between the mRNA and the amino acid sequence of proteins. It does this by carrying an amino acid to the protein synthetic machinery of a cell (ribosome) as directed by a three-nucleotide sequence (codon) in a messenger RNA (mRNA). As such, tRNAs are a necessary component of translation, the biological synthesis of new proteins according to the genetic code.The specific nucleotide sequence of an mRNA specifies which amino acids are incorporated into the protein product of the gene from which the mRNA is transcribed, and the role of tRNA is to specify which sequence from the genetic code corresponds to which amino acid. One end of the tRNA matches the genetic code in a three-nucleotide sequence called the anticodon. The anticodon forms three base pairs with a codon in mRNA during protein biosynthesis. The mRNA encodes a protein as a series of contiguous codons, each of which is recognized by a particular tRNA. On the other end of the tRNA is a covalent attachment to the amino acid that corresponds to the anticodon sequence. Each type of tRNA molecule can be attached to only one type of amino acid, so each organism has many types of tRNA (in fact, because the genetic code contains multiple codons that specify the same amino acid, there are several tRNA molecules bearing different anticodons which also carry the same amino acid).The covalent attachment to the tRNA 3’ end is catalyzed by enzymes called aminoacyl tRNA synthetases. During protein synthesis, tRNAs with attached amino acids are delivered to the ribosome by proteins called elongation factors (EF-Tu in bacteria, eEF-1 in eukaryotes), which aid in decoding the mRNA codon sequence. If the tRNA's anticodon matches the mRNA, another tRNA already bound to the ribosome transfers the growing polypeptide chain from its 3’ end to the amino acid attached to the 3’ end of the newly delivered tRNA, a reaction catalyzed by the ribosome.A large number of the individual nucleotides in a tRNA molecule may be chemically modified, often by methylation or deamidation. These unusual bases sometimes affect the tRNA's interaction with ribosomes and sometimes occur in the anticodon to alter base-pairing properties.