Connecting cortex to machines: recent advances in brain interfaces
... other animals to record its electrical activity, and thereby infer its function, or to modify its function by stimulating it electrically. Single-neuron recordings were already underway in humans1 and in behaving monkeys2 in the 1960s. Electrical stimulation has been used to influence brain function ...
... other animals to record its electrical activity, and thereby infer its function, or to modify its function by stimulating it electrically. Single-neuron recordings were already underway in humans1 and in behaving monkeys2 in the 1960s. Electrical stimulation has been used to influence brain function ...
CNS DEVELOPMENT - University of Kansas Medical Center
... membrane and will migrate past the ependymal cells to form a new outer layer of densely packed cells collectively called the: Mantle layer: Cells that make up the mantle layer are: NEUROBLASTS. Note that mantle layer is still covered by the external limiting membrane. ...
... membrane and will migrate past the ependymal cells to form a new outer layer of densely packed cells collectively called the: Mantle layer: Cells that make up the mantle layer are: NEUROBLASTS. Note that mantle layer is still covered by the external limiting membrane. ...
3680Lecture27
... Dorsal and Ventral Pathways • Different visual cortex regions contain cells with different tuning properties represent different features in the visual field • V5/MT is selectively responsive to motion ...
... Dorsal and Ventral Pathways • Different visual cortex regions contain cells with different tuning properties represent different features in the visual field • V5/MT is selectively responsive to motion ...
Motor “Binding:” Do Functional Assemblies in Primary Motor Cortex
... also branch to contact neurons in other motor neuron pools; their aggregate branching pattern yields a muscle field that describes the functional coupling, both facilitatory and suppressive, of a CM cell to a set of muscles. Commonly, a muscle field for a CM cell comprises motor neuron pools having ...
... also branch to contact neurons in other motor neuron pools; their aggregate branching pattern yields a muscle field that describes the functional coupling, both facilitatory and suppressive, of a CM cell to a set of muscles. Commonly, a muscle field for a CM cell comprises motor neuron pools having ...
Neurulation and Ectoderm
... During 1st year after birth, enough dendrites form to make 100,000 connections for each cortical neuron • Average cortical neuron connects to 10,000 other neural cells Axons • Long extension of cell body, carry impulse away from cell body • Forms as outgrowth of cell • Elongates along length due to ...
... During 1st year after birth, enough dendrites form to make 100,000 connections for each cortical neuron • Average cortical neuron connects to 10,000 other neural cells Axons • Long extension of cell body, carry impulse away from cell body • Forms as outgrowth of cell • Elongates along length due to ...
Of Toasters and Molecular Ticker Tapes
... are important for a given neuroscience question. As long as we cannot approach understanding the entire brain at the same time, it is highly useful to select what to stimulate and what to measure. (2) Get stimuli into the brain. To understand what neurons do, inputs need to be defined or known. (3) ...
... are important for a given neuroscience question. As long as we cannot approach understanding the entire brain at the same time, it is highly useful to select what to stimulate and what to measure. (2) Get stimuli into the brain. To understand what neurons do, inputs need to be defined or known. (3) ...
[pdf]
... been demonstrated, such as increases in baseline activity [1], increases in response gain of neurons that selectively respond to an attended feature or location [2,3], as well as shifts of neuronal tuning curves, for example, changes in preferred feature selectivity [4]. Although these studies have ...
... been demonstrated, such as increases in baseline activity [1], increases in response gain of neurons that selectively respond to an attended feature or location [2,3], as well as shifts of neuronal tuning curves, for example, changes in preferred feature selectivity [4]. Although these studies have ...
hebbRNN: A Reward-Modulated Hebbian Learning Rule for
... Software Archive: http://dx.doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.154745 ...
... Software Archive: http://dx.doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.154745 ...
Slides - Mathematics of Networks meetings
... Work started as an individual basic research project, motivated by a critical look at modeling biological neurons, rather than using popular connectionist models Biological characteristics of the model needed to include: - Action potential “Signals” in the form of spikes of fixed amplitude - Modelin ...
... Work started as an individual basic research project, motivated by a critical look at modeling biological neurons, rather than using popular connectionist models Biological characteristics of the model needed to include: - Action potential “Signals” in the form of spikes of fixed amplitude - Modelin ...
Understanding the brain by controlling neural activity
... development of more sophisticated methods for causal interference, such as nanostimulation and optogenetics, provide a more precise intervention with a greater flexibility. Nanostimulation permits activation of single brain cells in awake animals, facilitating the study of the importance of patterne ...
... development of more sophisticated methods for causal interference, such as nanostimulation and optogenetics, provide a more precise intervention with a greater flexibility. Nanostimulation permits activation of single brain cells in awake animals, facilitating the study of the importance of patterne ...
CNS DEVELOPMENT - University of Kansas Medical Center
... membrane and will migrate past the ependymal cells to form a new outer layer of densely packed cells collectively called the: Mantle layer: Cells that make up the mantle layer are: NEUROBLASTS. Note that mantle layer is still covered by the external limiting membrane. ...
... membrane and will migrate past the ependymal cells to form a new outer layer of densely packed cells collectively called the: Mantle layer: Cells that make up the mantle layer are: NEUROBLASTS. Note that mantle layer is still covered by the external limiting membrane. ...
as a PDF - University of Sussex
... patterns in the cortex related to visual processing. Jelinek and Elston [10] have shown that on a cellular level, processing complexity increases from V1 to prefrontal cortex, with layerIII pyramidal cell dendritic branching patterns becoming more complex and larger, thus requiring more energy. High ...
... patterns in the cortex related to visual processing. Jelinek and Elston [10] have shown that on a cellular level, processing complexity increases from V1 to prefrontal cortex, with layerIII pyramidal cell dendritic branching patterns becoming more complex and larger, thus requiring more energy. High ...
Oct2011_Computers_Brains_Extra_Mural
... Neural computing systems are trained on the principle that if a network can compute then it will learn to compute. Multi-net neural computing systems are trained on the principle that if two or more networks learn to compute simultaneously or sequentially , then the multi-net will learn to compute. ...
... Neural computing systems are trained on the principle that if a network can compute then it will learn to compute. Multi-net neural computing systems are trained on the principle that if two or more networks learn to compute simultaneously or sequentially , then the multi-net will learn to compute. ...
600 Kb PDF
... The goal of the Animat project is to create a neurallycontrolled artificial animal with which we can study learning in-vitro. This preliminary work has shown that it is possible to construct a system that can respond to and provide feedback in real-time to a living neural network. We do not yet know ...
... The goal of the Animat project is to create a neurallycontrolled artificial animal with which we can study learning in-vitro. This preliminary work has shown that it is possible to construct a system that can respond to and provide feedback in real-time to a living neural network. We do not yet know ...
Cellular Mechanisms of Learning and Memory
... in the target hippocampal neurons. This facilitation is called long-term potentiation (LTP). LTP can be studied in the intact animal, where it can last for days and even weeks. It can also be examined in slices of hippocampus and in cell culture for several hours. ...
... in the target hippocampal neurons. This facilitation is called long-term potentiation (LTP). LTP can be studied in the intact animal, where it can last for days and even weeks. It can also be examined in slices of hippocampus and in cell culture for several hours. ...
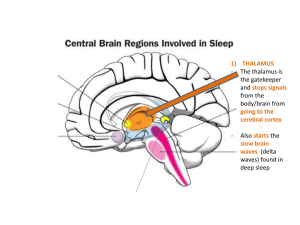
Sleep Brain Labelling
... - Damage to this area can cause a coma or death - Plays a central role in consciousness ...
... - Damage to this area can cause a coma or death - Plays a central role in consciousness ...
PDF version
... To stop it damaging neurons, the microdrive has been given a collision avoidance capability. “If the signal voltage starts rising very rapidly we know we are in danger of puncturing a neuron, so it backs off,†Burdick says. While the animal tests have shown that the microdrive can home in on the ...
... To stop it damaging neurons, the microdrive has been given a collision avoidance capability. “If the signal voltage starts rising very rapidly we know we are in danger of puncturing a neuron, so it backs off,†Burdick says. While the animal tests have shown that the microdrive can home in on the ...
Serotonin synaptic receptors in the mammalian central
... at sites that are not components of the presynaptic 5-HT system bu[ appear to be associated with synaptic 5-HT function. Under appropriate conditions[all] 5-HT binds saturab]y, reversibly and with high affinity (K, = 8 nM) to forebrain particulate preparations. In rat (6) and human (10) brain [3H]5- ...
... at sites that are not components of the presynaptic 5-HT system bu[ appear to be associated with synaptic 5-HT function. Under appropriate conditions[all] 5-HT binds saturab]y, reversibly and with high affinity (K, = 8 nM) to forebrain particulate preparations. In rat (6) and human (10) brain [3H]5- ...
Joint EuroSPIN/NeuroTime Meeting 2013, January 14
... Neuronal avalanches are a type of spontaneous activity first observed in vitro by recording local field potentials in cortical neural networks using slices of rat cortex as well as cultured networks. Propagation of spontaneous activity is balanced and shows a branching parameter close to 1. In addit ...
... Neuronal avalanches are a type of spontaneous activity first observed in vitro by recording local field potentials in cortical neural networks using slices of rat cortex as well as cultured networks. Propagation of spontaneous activity is balanced and shows a branching parameter close to 1. In addit ...
Exploring Artificial Neural Networks to discover Higgs at
... to Discover Higgs at LHC Outline: • What are Neural Networks and how do they work? • How can Neural Networks be used in bjet tagging to discover the Higgs boson? • What results have I obtained using Neural Networks to find b-jets? ...
... to Discover Higgs at LHC Outline: • What are Neural Networks and how do they work? • How can Neural Networks be used in bjet tagging to discover the Higgs boson? • What results have I obtained using Neural Networks to find b-jets? ...
Energy Saving Accounts for the Suppression of Sensory Detail
... complexity increases from V1 to prefrontal cortex, with layerIII pyramidal cell dendritic branching patterns becoming more complex and larger, thus requiring more energy. Higher visual processing areas deal more with conceptual phenomena by integrating simple bits of information from lower processin ...
... complexity increases from V1 to prefrontal cortex, with layerIII pyramidal cell dendritic branching patterns becoming more complex and larger, thus requiring more energy. Higher visual processing areas deal more with conceptual phenomena by integrating simple bits of information from lower processin ...
A true science of consciousness explains
... context in which they are presented. Even though the surfaces in A and B emit light with identical wavelengths, they have very different perceptual properties. Conversely, the apples seem to have the same color, whereas in fact apple B is much darker than apple A. During the Ponzo illusion (stimulus ...
... context in which they are presented. Even though the surfaces in A and B emit light with identical wavelengths, they have very different perceptual properties. Conversely, the apples seem to have the same color, whereas in fact apple B is much darker than apple A. During the Ponzo illusion (stimulus ...
Neurobiologically Inspired Robotics: Enhanced Autonomy through
... learning techniques. (Walter, Röhrbein, & Knoll, 2015). They further investigate how to program neuromorphic chips by means of learning, rather than programming. Final Thoughts. We hope you enjoy reading these articles that highlight the potential of neurobiologically inspired systems to advance the ...
... learning techniques. (Walter, Röhrbein, & Knoll, 2015). They further investigate how to program neuromorphic chips by means of learning, rather than programming. Final Thoughts. We hope you enjoy reading these articles that highlight the potential of neurobiologically inspired systems to advance the ...
Neural binding

Neural binding refers to the neuroscientific aspect of what is commonly known as the binding problem. The Binding Problem is an interdisciplinary term, named for the difficulty of creating a comprehensive and verifiable model for the unity of consciousness. ""Binding"" refers to the integration of highly diverse neural information in the forming of one's cohesive experience. The neural binding hypothesis states that neural signals are paired through synchronized oscillations of neuronal activity that combine and recombine to allow for a wide variety of responses to context-dependent stimuli. These dynamic neural networks are thought to account for the flexibility and nuanced response of the brain to various situations. The coupling of these networks is transient, on the order of milliseconds, and allows for rapid activity.A viable mechanism for this phenomenon must address (1) the difficulties of reconciling the global nature of the participating (exogenous) signals and their relevant (endogenous) associations, (2) the interface between lower perceptual processes and higher cognitive processes, (3) the identification of signals (sometimes referred to as “tagging”) as they are processed and routed throughout the brain, and (4) the emergence of a unity of consciousness.Proposed adaptive functions of neural binding have included the avoidance of hallucinatory phenomena generated by endogenous patterns alone as well as the avoidance of behavior driven by involuntary action alone.There are several difficulties that must be addressed in this model. First, it must provide a mechanism for the integration of signals across different brain regions (both cortical and subcortical). It must also be able to explain the simultaneous processing of unrelated signals that are held separate from one another and integrated signals that must be viewed as a whole.





![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008855303_1-42c5934975f83fadb4141440e1a86c3f-300x300.png)