Acute Hepatopathy in a Juvenile Canine - vmsg
... For the next several days after discharge, Oscar had waxing and waning episodes of lethargy, though overall he progressively improved and began to have the energy level of a puppy again. One week after discharge he was feeling well with complete resolution of his presenting clinical signs, and blood ...
... For the next several days after discharge, Oscar had waxing and waning episodes of lethargy, though overall he progressively improved and began to have the energy level of a puppy again. One week after discharge he was feeling well with complete resolution of his presenting clinical signs, and blood ...
Knowledge Level of Hepatitis B and its Prevalance in
... hepatitis B knowledge level according to age, sex, unit of working, and education level (p>0.05). ...
... hepatitis B knowledge level according to age, sex, unit of working, and education level (p>0.05). ...
Skills Lab 1
... Report incident to supervisor (2 purple tops & file incident report) Obtain history from the source patient (HIV, Hepatitis or risk factors) ...
... Report incident to supervisor (2 purple tops & file incident report) Obtain history from the source patient (HIV, Hepatitis or risk factors) ...
Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C: Whom to Test
... Principles of Long-Term Hepatitis B Management Provide patient with culturally and linguistically appropriate educational materials (see links below) Report case to local health department within seven days Vaccinate against hepatitis A unless immune Encourage patient’s sex partners, househo ...
... Principles of Long-Term Hepatitis B Management Provide patient with culturally and linguistically appropriate educational materials (see links below) Report case to local health department within seven days Vaccinate against hepatitis A unless immune Encourage patient’s sex partners, househo ...
Folie 1 - TWUC.NET
... • GGT = most common elevation, may be isolated – Sensitivity and specificity 50% • AST > ALT, AST: ALT >1 • MCV ↑↑. • Fatty liver on imaging (ultrasound, CT) – 100% , if alcohol consumption >60g/d • Carbohydrate deficient transferrin (CDT) ...
... • GGT = most common elevation, may be isolated – Sensitivity and specificity 50% • AST > ALT, AST: ALT >1 • MCV ↑↑. • Fatty liver on imaging (ultrasound, CT) – 100% , if alcohol consumption >60g/d • Carbohydrate deficient transferrin (CDT) ...
Liver Diseases
... • Alcoholic cirrhosis: micronodular type of cirrhosis!!! similar to other forms of cirrhosis: hypoproteinemia (globulins, albumin, and clotting factors) ...
... • Alcoholic cirrhosis: micronodular type of cirrhosis!!! similar to other forms of cirrhosis: hypoproteinemia (globulins, albumin, and clotting factors) ...
Viral hepatitis accompanying fever caused by non hepatitis viruses
... Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) shares the characteristic morphologic features of the herpesviridae family. The EBV genome consists of a linear DNA molecule that encodes nearly 100 viral proteins. After infecting B lymphocytes the linear EBV genome becomes circular, forming an episome, which usually remain ...
... Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) shares the characteristic morphologic features of the herpesviridae family. The EBV genome consists of a linear DNA molecule that encodes nearly 100 viral proteins. After infecting B lymphocytes the linear EBV genome becomes circular, forming an episome, which usually remain ...
Recent advances in micro/nanotechnologies for global control of
... and other viruses from ultra-low volume of blood, serum and plasma is realized. ...
... and other viruses from ultra-low volume of blood, serum and plasma is realized. ...
Vaccination - NUI Galway
... management. This includes follow-up boosters and other relevant measures for as long as the risk of exposure is thought likely. Where staff have received prior and adequate immunisation before the present risk assessment, the continued efficacy of immunisation will be assessed by a competent person ...
... management. This includes follow-up boosters and other relevant measures for as long as the risk of exposure is thought likely. Where staff have received prior and adequate immunisation before the present risk assessment, the continued efficacy of immunisation will be assessed by a competent person ...
Hepatitis A
... Infection transmitted from person to person in households and extended family settings - facilitated by asymptomatic infection among children Some groups at increased risk – specific factor varies – do not account for majority of cases ...
... Infection transmitted from person to person in households and extended family settings - facilitated by asymptomatic infection among children Some groups at increased risk – specific factor varies – do not account for majority of cases ...
Objectives of hepatitis C surveillance
... Infection transmitted from person to person in households and extended family settings - facilitated by asymptomatic infection among children Some groups at increased risk – specific factor varies – do not account for majority of cases ...
... Infection transmitted from person to person in households and extended family settings - facilitated by asymptomatic infection among children Some groups at increased risk – specific factor varies – do not account for majority of cases ...
Hepatitis B Fact Sheet
... This information is provided by the Hepatitis C Support Project a nonprofit organization for HCV education, support and advocacy. ©2015 Hepatitis C Support Project Reprint permission is granted and encouraged with credit to the Hepatitis C Support Project. ...
... This information is provided by the Hepatitis C Support Project a nonprofit organization for HCV education, support and advocacy. ©2015 Hepatitis C Support Project Reprint permission is granted and encouraged with credit to the Hepatitis C Support Project. ...
RESEARCH OPPORTUNITIES
... While you are working at your desk and you are moving around from the return area to the work area, always LOOK around before rolling. Check to see if a cord happens to get in the way before you move in order to avoid interrupting power to your station. Should you leave your desk at anytime, ALWAYS ...
... While you are working at your desk and you are moving around from the return area to the work area, always LOOK around before rolling. Check to see if a cord happens to get in the way before you move in order to avoid interrupting power to your station. Should you leave your desk at anytime, ALWAYS ...
Physical Assessment
... Note clinical venipuncture sites. Check for rashes, tattoos, body piercing, enlarged liver, needle track marks. Documentation of any of these findings may indicate viral hepatitis, AIDS or high risk behavior. ...
... Note clinical venipuncture sites. Check for rashes, tattoos, body piercing, enlarged liver, needle track marks. Documentation of any of these findings may indicate viral hepatitis, AIDS or high risk behavior. ...
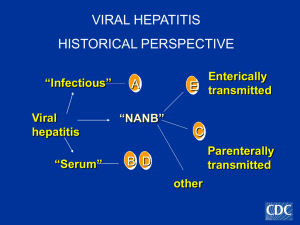
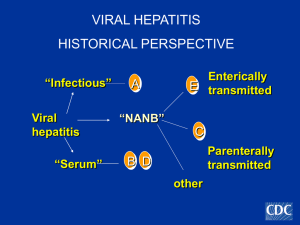
Epidemiology and Prevention of Viral Hepatitis A to E:
... Suspicion of HDV co-infection based on: • Risk factors (e.g., IVDA) • Clinical signs of severe hepatities Check anti-HDV ...
... Suspicion of HDV co-infection based on: • Risk factors (e.g., IVDA) • Clinical signs of severe hepatities Check anti-HDV ...
Unusual cases of hepatitis B virus transmission in the Community
... to a comparison group. The prevalence of antibodies against HBV was higher in the group of 176 barbers (39.8%) than in the control group (28.3%). Most of the seropositive subjects had been exposed to needle pricks or scissor cuts. link: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11872792 ...
... to a comparison group. The prevalence of antibodies against HBV was higher in the group of 176 barbers (39.8%) than in the control group (28.3%). Most of the seropositive subjects had been exposed to needle pricks or scissor cuts. link: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11872792 ...
Bloodborne Pathogens Annual Training Module
... *85% progress to chronic infection *Risk of HCV infection after single positive needle stick is 3-10% ( CDC, 1996 ) *HCV accounts for more liver transplants in the U.S. than any other condition. The incubation period ranges from 2-6 months, most commonly 2-3 months. The period of communicability ra ...
... *85% progress to chronic infection *Risk of HCV infection after single positive needle stick is 3-10% ( CDC, 1996 ) *HCV accounts for more liver transplants in the U.S. than any other condition. The incubation period ranges from 2-6 months, most commonly 2-3 months. The period of communicability ra ...
at Infection - SPICEducation
... Factors related to increased severity Chronic liver disease, large inoculum, pregnancy ...
... Factors related to increased severity Chronic liver disease, large inoculum, pregnancy ...
Hepatomagaly in children - Prof. Dr. Cengiz Canpolat
... distention, hepatomegaly, and pitting edema suggest pulmonary emphysema and cor pulmonale • Fever, tender hepatomegaly, and jaundice suggest viral hepatitis or cholangitis • Hepatomagaly and ascites suggest cirrhosis ...
... distention, hepatomegaly, and pitting edema suggest pulmonary emphysema and cor pulmonale • Fever, tender hepatomegaly, and jaundice suggest viral hepatitis or cholangitis • Hepatomagaly and ascites suggest cirrhosis ...
TWINRIX® ADULT and TWINRIX® JUNIOR
... sharing razors or toothbrushes, or working with human blood or body fluids) an infected mother passing the virus onto her baby during or shortly after birth. ...
... sharing razors or toothbrushes, or working with human blood or body fluids) an infected mother passing the virus onto her baby during or shortly after birth. ...
Bloodborne Pathogen Training
... A safe and effective vaccine against Hepatitis B is available to all “potentially at risk” University individuals. Contact Risk Management and Safety at 631-5037, if you think you may be at risk and need the vaccination. ...
... A safe and effective vaccine against Hepatitis B is available to all “potentially at risk” University individuals. Contact Risk Management and Safety at 631-5037, if you think you may be at risk and need the vaccination. ...
Immunizations for Kenya - Maseno Health Alliance
... before scheduling your appointment. The CDC website also has lists of clinics providing the yellow fever vaccine. Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B: Recommended for all unvaccinated people traveling to or working in countries with an intermediate or high level of hepatitis A virus infection where exposure ...
... before scheduling your appointment. The CDC website also has lists of clinics providing the yellow fever vaccine. Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B: Recommended for all unvaccinated people traveling to or working in countries with an intermediate or high level of hepatitis A virus infection where exposure ...
The prevention of hepatitis B transmission in dental
... carrier, certain precautions would be recommended. Ideally, direct providers should be immune to hepatitis B: they should already have had hepatitis B and have naturally formed anti-HB~ or have been vaccinated. To have a population of anti-HB~ positive personnel, it is reasonable for all health care ...
... carrier, certain precautions would be recommended. Ideally, direct providers should be immune to hepatitis B: they should already have had hepatitis B and have naturally formed anti-HB~ or have been vaccinated. To have a population of anti-HB~ positive personnel, it is reasonable for all health care ...
Bloodborne Pathogens Training Presentation
... that can lead to AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) HIV damages a person’s immune system which helps the body fight disease. First info published in medical journal about this virus was May 20, 1983 ...
... that can lead to AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) HIV damages a person’s immune system which helps the body fight disease. First info published in medical journal about this virus was May 20, 1983 ...
Hepatitis

Hepatitis (plural: hepatitides) is a medical condition defined by the inflammation of the liver and characterized by the presence of inflammatory cells in the tissue of the organ. Hepatitis may occur with limited or no symptoms, but often leads to jaundice (a yellow discoloration of the skin, mucous membrane, and conjunctiva), poor appetite, and malaise. Hepatitis is acute when it lasts less than six months and chronic when it persists longer.Acute hepatitis can be self-limiting (healing on its own), can progress to chronic hepatitis, or, rarely, can cause acute liver failure. Chronic hepatitis may have no symptoms, or may progress over time to fibrosis (scarring of the liver) and cirrhosis (chronic liver failure). Cirrhosis of the liver increases the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (a form of liver cancer).Worldwide, viral hepatitis is the most common cause of liver inflammation. Other causes include autoimmune diseases and ingestion of toxic substances (notably alcohol), certain medications (such as paracetamol), some industrial organic solvents, and plants.The term is derived from the Greek hêpar (ἧπαρ), meaning ""liver"", and the suffix -itis (-ῖτις), meaning ""inflammation"" (c. 1727).