Question Answer 1 This part of a plant protects the seeds Fruit 2
... Part of the pistil that is between the stigma and the ovary Part of the flower where the ovules are located Ovary develops into a Process that transfers pollen from anther to stigma Process in which sperm unites with ovule Part of a seed that is the “tiny plant” Part of the seed containing food for ...
... Part of the pistil that is between the stigma and the ovary Part of the flower where the ovules are located Ovary develops into a Process that transfers pollen from anther to stigma Process in which sperm unites with ovule Part of a seed that is the “tiny plant” Part of the seed containing food for ...
22.2 Reproduction in Flowering Plants
... 22.2 Reproduction in Flowering Plants • One female gametophyte can form in each ovule of a flower’s ovary. – four female spores produced in ovule by meiosis – one spore develops into female gametophyte – female gametophyte contains seven cells – one cell has two nuclei, or polar nuclei ...
... 22.2 Reproduction in Flowering Plants • One female gametophyte can form in each ovule of a flower’s ovary. – four female spores produced in ovule by meiosis – one spore develops into female gametophyte – female gametophyte contains seven cells – one cell has two nuclei, or polar nuclei ...
22.2 Reproduction in Flowering Plants
... 22.2 Reproduction in Flowering Plants • One female gametophyte can form in each ovule of a flower’s ovary. – four female spores produced in ovule by meiosis – one spore develops into female gametophyte – female gametophyte contains seven cells – one cell has two nuclei, or polar nuclei ...
... 22.2 Reproduction in Flowering Plants • One female gametophyte can form in each ovule of a flower’s ovary. – four female spores produced in ovule by meiosis – one spore develops into female gametophyte – female gametophyte contains seven cells – one cell has two nuclei, or polar nuclei ...
Lecture 1 Thursday Jan. 4, 2001
... ancestor with Anthophyta) 15. Vessels: large volume, thick walled (with spiral or transverse ridges) cells with connecting pits at their ends, for much more efficient water transport upwards. Enables height growth under drier conditions. (Note that the world’s tallest trees are all gymnosperms that ...
... ancestor with Anthophyta) 15. Vessels: large volume, thick walled (with spiral or transverse ridges) cells with connecting pits at their ends, for much more efficient water transport upwards. Enables height growth under drier conditions. (Note that the world’s tallest trees are all gymnosperms that ...
Chapter 30 Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants seed
... - microspores develop into pollen grains which mature to form male gametophytes - carried by wind or animals - sperm cells sometimes flagellated gymnosperms - vascular plant bearing naked seeds not enclosed in a special chamber - 4 groups: cycads ginkgo gnetophytes conifers - largest division - most ...
... - microspores develop into pollen grains which mature to form male gametophytes - carried by wind or animals - sperm cells sometimes flagellated gymnosperms - vascular plant bearing naked seeds not enclosed in a special chamber - 4 groups: cycads ginkgo gnetophytes conifers - largest division - most ...
Fantastic Flowers Pre-visit Package
... Honey bees are one of the most common types of bees that farmers use. Introduce the lifecycle of a honeybee to your students. Ask them to illustrate their own life cycle. The example image below is just one way in which they could do this. 1. The queen lays each egg in a different cell of the honeyc ...
... Honey bees are one of the most common types of bees that farmers use. Introduce the lifecycle of a honeybee to your students. Ask them to illustrate their own life cycle. The example image below is just one way in which they could do this. 1. The queen lays each egg in a different cell of the honeyc ...
CHAPTER 30 - Doral Academy Preparatory
... from the anther The pollen grows a tube down through the style Meiosis occurs in the ovary to produce haploid ovules ...
... from the anther The pollen grows a tube down through the style Meiosis occurs in the ovary to produce haploid ovules ...
Plant Reproduction
... 31. Grows from pollen grains that land on the female part of the plant and which sperm travel down 32. Type of asexual reproduction in plants using parts of stems or leaves 33. Embryonic leaf of a seed 34. Whorl inside of the sepals that may be brightly colored to attract insect pollinations 35. sta ...
... 31. Grows from pollen grains that land on the female part of the plant and which sperm travel down 32. Type of asexual reproduction in plants using parts of stems or leaves 33. Embryonic leaf of a seed 34. Whorl inside of the sepals that may be brightly colored to attract insect pollinations 35. sta ...
Test Five
... The WAXY waterproof layer that covers the top of many plant leaves to help them retain water is the a. stomata ...
... The WAXY waterproof layer that covers the top of many plant leaves to help them retain water is the a. stomata ...
Bio Revision
... • Almost no chance of an evolution taking place. • Identical to the parents, so diseases and bad qualities are also passed down • Struggle for light, space, nutrients and soil so most plants will remain less healthy. ...
... • Almost no chance of an evolution taking place. • Identical to the parents, so diseases and bad qualities are also passed down • Struggle for light, space, nutrients and soil so most plants will remain less healthy. ...
Gymnosperms
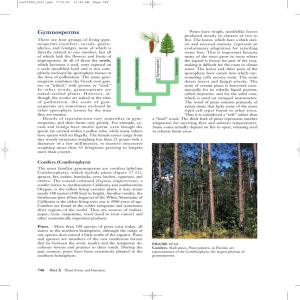
... megasporangium called the nucellus. The nucellus itself is completely sur- FIGURE 37.13 rounded by a thick layer of cells called Life cycle of a typical pine. The male and female gametophytes are dramatically reduced the integument that has a small open- in size in these plants. Wind generally dispe ...
... megasporangium called the nucellus. The nucellus itself is completely sur- FIGURE 37.13 rounded by a thick layer of cells called Life cycle of a typical pine. The male and female gametophytes are dramatically reduced the integument that has a small open- in size in these plants. Wind generally dispe ...
Dry Land Plantsmod
... What are some examples of conifers? What are some examples of flowering plants? ...
... What are some examples of conifers? What are some examples of flowering plants? ...
Flower Parts and Function
... • Ovule: The “egg cell” of the plant – becomes the seed when fertilized. • Pollen tube: Transfers pollen from stigma to ovule. • Pistil – Stigma (part of pistil): Collects pollen. – Style (part of pistil): Supports stigma. – Ovary (part of pistil): Contains one or more ovules. ...
... • Ovule: The “egg cell” of the plant – becomes the seed when fertilized. • Pollen tube: Transfers pollen from stigma to ovule. • Pistil – Stigma (part of pistil): Collects pollen. – Style (part of pistil): Supports stigma. – Ovary (part of pistil): Contains one or more ovules. ...
Angiosperm Life Cycle
... – Attract animals to help spread pollen – Forms fruit to protect and spread seeds ...
... – Attract animals to help spread pollen – Forms fruit to protect and spread seeds ...
Carpels
... Evolution of pollen made it possible for male gametes to reach female gametophyte without water This selective advantage allowed pollen- ...
... Evolution of pollen made it possible for male gametes to reach female gametophyte without water This selective advantage allowed pollen- ...
plants - Cloudfront.net
... and thus can selfpollinate or cross pollinate. • Others have only male or female parts and can cross pollinate with other plants ...
... and thus can selfpollinate or cross pollinate. • Others have only male or female parts and can cross pollinate with other plants ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... 1. Seeds and pollen enable plants to live and reproduce in dry climates because pollen does not require environmental water to reach female tissues that contain eggs. Seeds contain ...
... 1. Seeds and pollen enable plants to live and reproduce in dry climates because pollen does not require environmental water to reach female tissues that contain eggs. Seeds contain ...
Biology 12.4 Plant Reproduction Reproduction 1. Asexual a
... 1. natural VR when the plant reproduces itself a. a portion of the plant can form a complete new plant b. underground roots and stems can develop new plants (mint, weeds, bulbs, potato tubers) c. runners are surface stems can develop into new plants (strawberry plants and spider plants) d. Adventiti ...
... 1. natural VR when the plant reproduces itself a. a portion of the plant can form a complete new plant b. underground roots and stems can develop new plants (mint, weeds, bulbs, potato tubers) c. runners are surface stems can develop into new plants (strawberry plants and spider plants) d. Adventiti ...
Flower Structure and Function
... 6. What are the reproductive structures of angiosperms? 7. T or F- Some flowers have male and female parts 8. What are the 4 reproductive parts to flowers? Describe each one. 9. What is fertilization and describe how it occurs? 10. What is pollination? 11. What 2 things attract pollinators? 12. What ...
... 6. What are the reproductive structures of angiosperms? 7. T or F- Some flowers have male and female parts 8. What are the 4 reproductive parts to flowers? Describe each one. 9. What is fertilization and describe how it occurs? 10. What is pollination? 11. What 2 things attract pollinators? 12. What ...
Angiosperms
... have become pollen grains. The outer pollen grain wall layer often becomes beautifully sculptured, and it contains chemicals that may react with others in a stigma to signal whether or not development of the male gametophyte should proceed to completion. The pollen grain has areas called apertures, ...
... have become pollen grains. The outer pollen grain wall layer often becomes beautifully sculptured, and it contains chemicals that may react with others in a stigma to signal whether or not development of the male gametophyte should proceed to completion. The pollen grain has areas called apertures, ...
ppt
... and advertising the location with large colorful petals, pollinators learn to visit flowers for food – and they “trapline”, going from flower to flower. Pollen transport is much more efficient than wind dispersal; less pollen is needed (but there are additional costs of flower ad nectar production. ...
... and advertising the location with large colorful petals, pollinators learn to visit flowers for food – and they “trapline”, going from flower to flower. Pollen transport is much more efficient than wind dispersal; less pollen is needed (but there are additional costs of flower ad nectar production. ...
Plant fungi study guide
... The ancestors of land plants were _____, they lived _____ Know diagram of the Flower Differentiate between Bryophytes (Bryophytes) and Tracheophytes (ferns, gymnosperms & angiosperms). Know all their individual characteristics and examples of both. o Non-vascular tissue o Vascular tissue- xylem, phl ...
... The ancestors of land plants were _____, they lived _____ Know diagram of the Flower Differentiate between Bryophytes (Bryophytes) and Tracheophytes (ferns, gymnosperms & angiosperms). Know all their individual characteristics and examples of both. o Non-vascular tissue o Vascular tissue- xylem, phl ...
Name: Unit Two: Flowers and Plant Life Cycles Review Worksheet
... 21. Draw a basic picture of the gymnosperm life cycle showing the following: mature sporophyte, pollen cone, seed cone, female gametophyte, pollen tube, zygote, embryo, seed coat, seedling ...
... 21. Draw a basic picture of the gymnosperm life cycle showing the following: mature sporophyte, pollen cone, seed cone, female gametophyte, pollen tube, zygote, embryo, seed coat, seedling ...
Pollination

Pollination is a process by which pollen is transferred from the anther to the stigma of the plant, thereby enabling fertilization and reproduction. It is unique to the angiosperms, the flower-bearing plants.In spite of a common perception that pollen grains are gametes, like the sperm cells of animals, this is incorrect; pollination is an event in the alternation of generations. Each pollen grain is a male haploid gametophyte, adapted to being transported to the female gametophyte, where it can effect fertilization by producing the male gamete (or gametes), in the process of double fertilization). A successful angiosperm pollen grain (gametophyte) containing the male gametes is transported to the stigma, where it germinates and its pollen tube grows down the style to the ovary. Its two gametes travel down the tube to where the gametophyte(s) containing the female gametes are held within the carpel. One nucleus fuses with the polar bodies to produce the endosperm tissues, and the other with the ovule to produce the embryo Hence the term: ""double fertilization"".In gymnosperms, the ovule is not contained in a carpel, but exposed on the surface of a dedicated support organ, such as the scale of a cone, so that the penetration of carpel tissue is unnecessary. Details of the process vary according to the division of gymnosperms in question.The receptive part of the carpel is called a stigma in the flowers of angiosperms. The receptive part of the gymnosperm ovule is called the micropyle. Pollination is a necessary step in the reproduction of flowering plants, resulting in the production of offspring that are genetically diverse.The study of pollination brings together many disciplines, such as botany, horticulture, entomology, and ecology. The pollination process as an interaction between flower and pollen vector was first addressed in the 18th century by Christian Konrad Sprengel. It is important in horticulture and agriculture, because fruiting is dependent on fertilization: the result of pollination. The study of pollination by insects is known as anthecology.