Seawater Articles - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... How do marine mammals minimize salt and water balance problems? What can the sea lions eat and not need fresh water at all? What species do drink seawater? What is one thing seals do to get fresh water? How do whales and dolphins get fresh water? ...
... How do marine mammals minimize salt and water balance problems? What can the sea lions eat and not need fresh water at all? What species do drink seawater? What is one thing seals do to get fresh water? How do whales and dolphins get fresh water? ...
Coral Reefs - COSEE Florida
... All life on Earth depends on the ocean — and we’re not just talking about fish. The water in the ocean evaporates into the atmosphere, producing precipitation that allows us to farm and grow food. The ocean provides us with seafood and food additives that make up a large part of our diet. Our climat ...
... All life on Earth depends on the ocean — and we’re not just talking about fish. The water in the ocean evaporates into the atmosphere, producing precipitation that allows us to farm and grow food. The ocean provides us with seafood and food additives that make up a large part of our diet. Our climat ...
The Southern Ocean Observing System (SOOS)
... of the ice sheets to sea level rise 3. The role of the ocean in the stability of the Antarctic ice sheet Southern Ocean overturning shapes the global ocean and its contribution to sea-level rise; circulation and climate 4. The future and consequences of Southern Ocean carbon uptake; 5. The future of ...
... of the ice sheets to sea level rise 3. The role of the ocean in the stability of the Antarctic ice sheet Southern Ocean overturning shapes the global ocean and its contribution to sea-level rise; circulation and climate 4. The future and consequences of Southern Ocean carbon uptake; 5. The future of ...
The Ocean Floor
... home to a huge variety of animals. o It's the shallowest of the zones, but is more crowded with creatures than the other zones. ...
... home to a huge variety of animals. o It's the shallowest of the zones, but is more crowded with creatures than the other zones. ...
First Newsletter published by Mozambique National
... Welcome to the Mozambique National Oceanographic Data and Information Center Newsletter. It’s objective is to inform on the activities undertaken by the center, within the framework of ODINAFRICA1 and related programs. The present issue presents an article emphasizing the importance of the ARGO2 dat ...
... Welcome to the Mozambique National Oceanographic Data and Information Center Newsletter. It’s objective is to inform on the activities undertaken by the center, within the framework of ODINAFRICA1 and related programs. The present issue presents an article emphasizing the importance of the ARGO2 dat ...
Linking the world`s oceans: the Antarctic Circumpolar Current
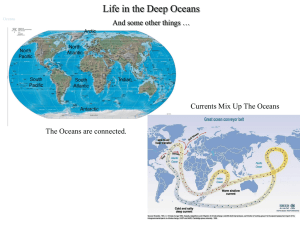
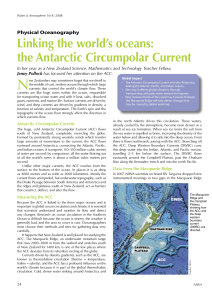
... for transporting ocean water and with it heat, salts, dissolved gases, nutrients, and marine life. Surface currents are driven by wind, and deep currents are driven by gradients in density, a function of salinity and temperature. The Earth’s spin and the topography of the ocean floor strongly affect ...
... for transporting ocean water and with it heat, salts, dissolved gases, nutrients, and marine life. Surface currents are driven by wind, and deep currents are driven by gradients in density, a function of salinity and temperature. The Earth’s spin and the topography of the ocean floor strongly affect ...
The Cape Verde Ocean Observatories
... The region is home to one of the major and most productive upwelling systems, which represents a biodiversity hotspot that is under growing human pressure. ...
... The region is home to one of the major and most productive upwelling systems, which represents a biodiversity hotspot that is under growing human pressure. ...
Unit 2 Vocabulary Review
... a layer in a body of water in which water temperature drops with increased depth faster than it does in other layers ...
... a layer in a body of water in which water temperature drops with increased depth faster than it does in other layers ...
Unit 2 Vocabulary Review
... a layer in a body of water in which water temperature drops with increased depth faster than it does in other layers ...
... a layer in a body of water in which water temperature drops with increased depth faster than it does in other layers ...
Ocean The World Ocean Ocean Floor Features
... 1 list the three types of ocean floor sediments. 2 describe the formation of terrigenous, biogenous and hydrogenous sediments. Resources from the Seafloor 1 identify ocean resources used for energy production. 2 explain how gas hydrates are formed. 3 list other types of ocean resources. Composition ...
... 1 list the three types of ocean floor sediments. 2 describe the formation of terrigenous, biogenous and hydrogenous sediments. Resources from the Seafloor 1 identify ocean resources used for energy production. 2 explain how gas hydrates are formed. 3 list other types of ocean resources. Composition ...
Lecture 4:the observed mean circulation
... •Using the geostrophic balance, gradients in the dynamics topography can be used to estimate the surface circulation. ...
... •Using the geostrophic balance, gradients in the dynamics topography can be used to estimate the surface circulation. ...
Talking points --- The High Seas: Common Heritage
... • For the Ocean to carry on functioning as a key life-support system, providing food, jobs and oxygen to name just a few of the things we term economic “services”, we cannot ignore the 2/3 of the Ocean that makes up the high seas (as this short film shows). ...
... • For the Ocean to carry on functioning as a key life-support system, providing food, jobs and oxygen to name just a few of the things we term economic “services”, we cannot ignore the 2/3 of the Ocean that makes up the high seas (as this short film shows). ...
16_3eIG
... amounts of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere, exacerbating global climate change. 3. We extract minerals from the seafloor. C. Marine pollution threatens resources. D. Nets and plastic debris endanger marine life. 1. Because most plastic is not biodegradable, it can drift for dec ...
... amounts of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere, exacerbating global climate change. 3. We extract minerals from the seafloor. C. Marine pollution threatens resources. D. Nets and plastic debris endanger marine life. 1. Because most plastic is not biodegradable, it can drift for dec ...
highest species diversity of all fresh water ecosystems.
... • Plants and animals in freshwater regions are adjusted to the low salt content and would not be able to survive in areas of high salt concentration (i.e, ocean) ...
... • Plants and animals in freshwater regions are adjusted to the low salt content and would not be able to survive in areas of high salt concentration (i.e, ocean) ...
History of Ocean Exploration
... • 1st marine biologist • “Father of natural history” • He identified a variety of marine species such as crustaceans, echinoderms, mollusks, fish and mammals • Identified differences between oviparous and viviparous ...
... • 1st marine biologist • “Father of natural history” • He identified a variety of marine species such as crustaceans, echinoderms, mollusks, fish and mammals • Identified differences between oviparous and viviparous ...
Oceanography
... aluminium, silicon and oxygen. There is a continental crust, and an oceanic crust. The latter is very thin (only between 3-10km thick), while continental crust is 35-50km thick. The mantle lies below the crust and is relatively thicker and is composed of higher density material, mostly magnesium, ir ...
... aluminium, silicon and oxygen. There is a continental crust, and an oceanic crust. The latter is very thin (only between 3-10km thick), while continental crust is 35-50km thick. The mantle lies below the crust and is relatively thicker and is composed of higher density material, mostly magnesium, ir ...
Changes in Ocean Geometry Over the Past Billion Years
... stable and lasted about 200 My. But in the meantime, Gondwanaland drifted over the South Pole. ...
... stable and lasted about 200 My. But in the meantime, Gondwanaland drifted over the South Pole. ...
Intro to Oceanography
... After millions of years, Earth cooled allowing rain to fall to the surface Rain collected in basins on Earth’s crust; 20 million years of rain led to erosion of rocks ...
... After millions of years, Earth cooled allowing rain to fall to the surface Rain collected in basins on Earth’s crust; 20 million years of rain led to erosion of rocks ...
Currents: Upwelling What is an upwelling current? Why are they
... What is an upwelling current? Why are they important? ...
... What is an upwelling current? Why are they important? ...
Ocean Floor
... • Continental Shelf – is the shallow part of the ocean that is close to the edge of the continent. Living Organisms are abundant (lots) here because this area gets the most sunlight. • Continental Slope – located at the edge of the shelf. Slopes down to the deep water of the ocean basin Ocean basin ...
... • Continental Shelf – is the shallow part of the ocean that is close to the edge of the continent. Living Organisms are abundant (lots) here because this area gets the most sunlight. • Continental Slope – located at the edge of the shelf. Slopes down to the deep water of the ocean basin Ocean basin ...
prologue
... United States from Hawaii on the north to New Zealand in the southwest and Easter Island in the east. Without the ability to determine latitude and longitude, and hence actual position on the globe, early explorers observed a variety of natural phenomena to help them in their travel when they were o ...
... United States from Hawaii on the north to New Zealand in the southwest and Easter Island in the east. Without the ability to determine latitude and longitude, and hence actual position on the globe, early explorers observed a variety of natural phenomena to help them in their travel when they were o ...
Ch 20 Ocean Water Notes
... • Ocean water becomes denser as it becomes colder and less dense as it becomes warmer. The densest ocean water is found at the polar regions causing it to sink. ...
... • Ocean water becomes denser as it becomes colder and less dense as it becomes warmer. The densest ocean water is found at the polar regions causing it to sink. ...
a print-ready set with all 3 pages
... scientific exploration. It is still considered one of the greatest scientific expeditions of all time. In 1912, the German scientist Alfred Wegener introduced the theory of “ continental drift” – which claimed that the earth’s continents had at one point been one supercontinent. This theory was deba ...
... scientific exploration. It is still considered one of the greatest scientific expeditions of all time. In 1912, the German scientist Alfred Wegener introduced the theory of “ continental drift” – which claimed that the earth’s continents had at one point been one supercontinent. This theory was deba ...
Marine Technology in Spain
... The CSIC decided in December 2000 to encourage marine science & technology taking advantage of the existence service UGBO, with the aim to reorganize and lead the marine technology within the CSIC with a vision of assuring a more competitive service and to establish new technological developments in ...
... The CSIC decided in December 2000 to encourage marine science & technology taking advantage of the existence service UGBO, with the aim to reorganize and lead the marine technology within the CSIC with a vision of assuring a more competitive service and to establish new technological developments in ...
Marine debris

Marine debris, also known as marine litter, is human-created waste that has deliberately or accidentally been released in a lake, sea, ocean or waterway. Floating oceanic debris tends to accumulate at the centre of gyres and on coastlines, frequently washing aground, when it is known as beach litter or tidewrack. Deliberate disposal of wastes at sea is called ocean dumping. Naturally occurring debris, such as driftwood, are also present.With the increasing use of plastic, human influence has become an issue as many types of plastics do not biodegrade. Waterborne plastic poses a serious threat to fish, seabirds, marine reptiles, and marine mammals, as well as to boats and coasts. Dumping, container spillages, litter washed into storm drains and waterways and wind-blown landfill waste all contribute to this problem.