Study Notes for Chapter 19: The Ocean Basins Directions: Use the
... Study Notes for Chapter 19: The Ocean Basins Directions: Use the following notes to complete your study notes and then to prepare for the test. Please do not take this copy from the classroom. Thank you. Chapter 19 Section 1: The Water Planet 1. Earth’s oceans cover about ¾ th’s of Earth’s surface. ...
... Study Notes for Chapter 19: The Ocean Basins Directions: Use the following notes to complete your study notes and then to prepare for the test. Please do not take this copy from the classroom. Thank you. Chapter 19 Section 1: The Water Planet 1. Earth’s oceans cover about ¾ th’s of Earth’s surface. ...
Chapter 20 Study Notes Ocean Water
... • Ocean water ________ depends on the solar energy an area receives and the water’s ________________. – temperature – movement. ...
... • Ocean water ________ depends on the solar energy an area receives and the water’s ________________. – temperature – movement. ...
Chapter 20 Study Notes Ocean Water
... ocean because they form the base of the ocean ______ _____. – Plankton – food chain. ...
... ocean because they form the base of the ocean ______ _____. – Plankton – food chain. ...
Ocean Circulation - Physics Resources
... be found on the tops of mountains. What does that show about the Earth’s surface? Why is the seafloor lower than the surface of the continents? No oceanic crust older than about 160M years is known from the present oceans. Why are they so young? Would you expect lavas that erupt under water to cool ...
... be found on the tops of mountains. What does that show about the Earth’s surface? Why is the seafloor lower than the surface of the continents? No oceanic crust older than about 160M years is known from the present oceans. Why are they so young? Would you expect lavas that erupt under water to cool ...
06_Oceanic records
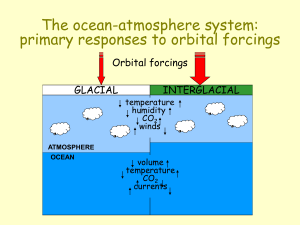
... The ocean-atmosphere system: primary responses to orbital forcings Orbital forcings GLACIAL ...
... The ocean-atmosphere system: primary responses to orbital forcings Orbital forcings GLACIAL ...
Ocean Fertilization
... research to answer questions about ocean fertilization with a view to exploring its potential as an effective avenue for mitigating climate change. One way to fund such research is by selling carbon offsets. To do so, it will be necessary to demonstrate that ocean fertilization effectively and quant ...
... research to answer questions about ocean fertilization with a view to exploring its potential as an effective avenue for mitigating climate change. One way to fund such research is by selling carbon offsets. To do so, it will be necessary to demonstrate that ocean fertilization effectively and quant ...
Slide 1
... Doney (2010) The Growing Human Footprint on Coastal and Open-Ocean Biogeochemistry Science 328, 1512 ...
... Doney (2010) The Growing Human Footprint on Coastal and Open-Ocean Biogeochemistry Science 328, 1512 ...
Seafloor Spreading
... form new ocean crust – Through time the new ocean crust moves away from the center of the mid-ocean ridge becoming cooler (and thus more dense) and sinks ...
... form new ocean crust – Through time the new ocean crust moves away from the center of the mid-ocean ridge becoming cooler (and thus more dense) and sinks ...
Geology of the Ocean Floor and Hydrothermal Vent / Deep Sea
... 10. What was the source of the water that gave rise to the oceans? 11. Why was Earth’s early atmosphere devoid of oxygen? 12. Describe the processes that account for the drifting of continents away from one another or toward one another. 13. Describe nine lines of evidence that support the theory of ...
... 10. What was the source of the water that gave rise to the oceans? 11. Why was Earth’s early atmosphere devoid of oxygen? 12. Describe the processes that account for the drifting of continents away from one another or toward one another. 13. Describe nine lines of evidence that support the theory of ...
World Meteorological Organization (WMO)
... restoration in order to achieve healthy and productive oceans [addressing also changes in the Arctic] The Arctic is the site of dramatic and unprecedented warming. This regional warming contributes to sea level rise, affects weather patterns around the world and threatens to trigger further changes ...
... restoration in order to achieve healthy and productive oceans [addressing also changes in the Arctic] The Arctic is the site of dramatic and unprecedented warming. This regional warming contributes to sea level rise, affects weather patterns around the world and threatens to trigger further changes ...
Deep seabed mining - Pacific Ecologist
... about mining methane ice, i.e. the methane clathrates or methane hydrates on the ocean floor. Methane, of course, is a highly potent greenhouse gas. To think to mine methane is begging for trouble in the oceans already beset by so many problems from our industrial over-activity. The trench-lines of ...
... about mining methane ice, i.e. the methane clathrates or methane hydrates on the ocean floor. Methane, of course, is a highly potent greenhouse gas. To think to mine methane is begging for trouble in the oceans already beset by so many problems from our industrial over-activity. The trench-lines of ...
1.7 MB - arcus
... Traditional methods of plankton collection are used to measure the distribution and abundance of adult and juvenile copepods and euphausiids over the shelves. New molecular techniques are being developed to identify juveniles of the dominant zooplankton taxa to determine which species utilize the sh ...
... Traditional methods of plankton collection are used to measure the distribution and abundance of adult and juvenile copepods and euphausiids over the shelves. New molecular techniques are being developed to identify juveniles of the dominant zooplankton taxa to determine which species utilize the sh ...
PDF: Printable Press Release
... zooplankton and other marine organisms.” Carbon that is exported to the deep sea via this “biological pump” contributes nothing to current global warming. Steinberg’s research has major implications for the computer models that are used to forecast the effects of climate change, revealing that it is ...
... zooplankton and other marine organisms.” Carbon that is exported to the deep sea via this “biological pump” contributes nothing to current global warming. Steinberg’s research has major implications for the computer models that are used to forecast the effects of climate change, revealing that it is ...
First day of Spring Semester
... ocean are salt, magnesium, bromine and oil from the sea bottom. ...
... ocean are salt, magnesium, bromine and oil from the sea bottom. ...
Ocean Food Chains - Santa Barbara Museum of Natural History
... Phytoplankton (plant plankton) and kelp are the main producers at the beginning of ocean food chains. These producers get their energy from the sun. Ocean animals, from sea stars to fish to marine mammals, depend on plankton for survival. Ocean animals are consumers. They can be catego ...
... Phytoplankton (plant plankton) and kelp are the main producers at the beginning of ocean food chains. These producers get their energy from the sun. Ocean animals, from sea stars to fish to marine mammals, depend on plankton for survival. Ocean animals are consumers. They can be catego ...
Continents and Oceans
... Africa, one of the largest (9) , is south of Europe and part of Asia. China, Japan, and India are located in (10) . South America, just like its name, is found below North America. Australia and Antarctica are the last two continents. Australia is the only continent that is an (11) . It is completel ...
... Africa, one of the largest (9) , is south of Europe and part of Asia. China, Japan, and India are located in (10) . South America, just like its name, is found below North America. Australia and Antarctica are the last two continents. Australia is the only continent that is an (11) . It is completel ...
Chapter 23
... waves can not penetrate to the sea floor, but they still can create a high resolution sea floor map based on the height of the sea level. ...
... waves can not penetrate to the sea floor, but they still can create a high resolution sea floor map based on the height of the sea level. ...
mitrie_sediment_marine
... Hazards of Heating the Oceans Seawater retains heat much better than air, leading to the supposition that most heat related to global warming would be expected to be incorporated into the oceans. Interactions between the atmosphere and the oceans, and thus global climate patterns, are likely to chan ...
... Hazards of Heating the Oceans Seawater retains heat much better than air, leading to the supposition that most heat related to global warming would be expected to be incorporated into the oceans. Interactions between the atmosphere and the oceans, and thus global climate patterns, are likely to chan ...
Key - University of California San Diego
... a) taste it and you can determine the salinity b) measure the conductivity of the seawater c) dry the sample and weigh the left over salt d) compare the sea water to freshwater by weighing both 18. Which does NOT describe turbidity currents: a) Sedimentation all jumbled up, so there are no graded be ...
... a) taste it and you can determine the salinity b) measure the conductivity of the seawater c) dry the sample and weigh the left over salt d) compare the sea water to freshwater by weighing both 18. Which does NOT describe turbidity currents: a) Sedimentation all jumbled up, so there are no graded be ...
Chapter 23 The Ocean Floor
... • SONAR • Sound signal is sent to the ocean floor and the time it takes to reach the ocean floor and return determines the depth ...
... • SONAR • Sound signal is sent to the ocean floor and the time it takes to reach the ocean floor and return determines the depth ...
Marine Parks: No-Take Marine Protected Area`s In
... where its bioregions are and a minimum amount of 3 no-take zones should be represented in each region to capture as many distinct ecosystems as possible. To minimize edge effects the aim should be to have the areas be a least 20 km’s long. 1.Government of Canada, 2011. Canada’s Oceans. Retrieved fro ...
... where its bioregions are and a minimum amount of 3 no-take zones should be represented in each region to capture as many distinct ecosystems as possible. To minimize edge effects the aim should be to have the areas be a least 20 km’s long. 1.Government of Canada, 2011. Canada’s Oceans. Retrieved fro ...
File
... Waves transport water particles in a circular pattern. As depth increases, the circular motion decreases. At the wave base, wave motion stops. Wave base is equal to ½ the wavelength of the wave ...
... Waves transport water particles in a circular pattern. As depth increases, the circular motion decreases. At the wave base, wave motion stops. Wave base is equal to ½ the wavelength of the wave ...
here - Great British Oceans
... the UKOTs, which support a large number of rare and threatened species and habitats found nowhere else on Earth. It makes good economic and environmental sense for the UK to work with its Territories to establish effective networks of marine protected areas throughout all waters under UK jurisdic ...
... the UKOTs, which support a large number of rare and threatened species and habitats found nowhere else on Earth. It makes good economic and environmental sense for the UK to work with its Territories to establish effective networks of marine protected areas throughout all waters under UK jurisdic ...
Name
... 2. Know what sonar stands for and how sonar works. Sonar stands for sound navigation and ranging. Scientists send sound pulses from a ship down into the ocean. The sound moves through the water, bounces off the ocean floor and returns to the ship. 3. Be able to explain why you think that geological ...
... 2. Know what sonar stands for and how sonar works. Sonar stands for sound navigation and ranging. Scientists send sound pulses from a ship down into the ocean. The sound moves through the water, bounces off the ocean floor and returns to the ship. 3. Be able to explain why you think that geological ...
Marine debris

Marine debris, also known as marine litter, is human-created waste that has deliberately or accidentally been released in a lake, sea, ocean or waterway. Floating oceanic debris tends to accumulate at the centre of gyres and on coastlines, frequently washing aground, when it is known as beach litter or tidewrack. Deliberate disposal of wastes at sea is called ocean dumping. Naturally occurring debris, such as driftwood, are also present.With the increasing use of plastic, human influence has become an issue as many types of plastics do not biodegrade. Waterborne plastic poses a serious threat to fish, seabirds, marine reptiles, and marine mammals, as well as to boats and coasts. Dumping, container spillages, litter washed into storm drains and waterways and wind-blown landfill waste all contribute to this problem.