Human populations are divided in three groups by their intestinal
... MetaHIT consortium has published in March 2010 the first comprehensive catalog of human intestinal bacterial genes, dubbed our second genome1. It was found that the gut bacteria encode 150 times as many genes as our own genome and that each individual harbors some 170 bacterial species out of a t ...
... MetaHIT consortium has published in March 2010 the first comprehensive catalog of human intestinal bacterial genes, dubbed our second genome1. It was found that the gut bacteria encode 150 times as many genes as our own genome and that each individual harbors some 170 bacterial species out of a t ...
Molecular identification of the bacterial microbiome resident in the hindgut... North American Beaver (Castor canadensis)
... method. DNA was PCR amplified from each animal using the primer set 27F and 519R to amplify only the bacterial V1-V3 region of the 16S rRNA gene. Samples were then sent to Molecular Research DNA (Stilwater, TX) for sequencing. A total of 61,614 sequences were obtained and ranged from 3,762 to 33,114 ...
... method. DNA was PCR amplified from each animal using the primer set 27F and 519R to amplify only the bacterial V1-V3 region of the 16S rRNA gene. Samples were then sent to Molecular Research DNA (Stilwater, TX) for sequencing. A total of 61,614 sequences were obtained and ranged from 3,762 to 33,114 ...
Chapter 11 – PROKARYOTES
... Dental caries (tooth decay) is caused by the normal microbiota of the mouth that form a biofilm (containing S.mutans) we call plaque on the tooth enamel surface: • due mainly to metabolism of the disaccharide sucrose ...
... Dental caries (tooth decay) is caused by the normal microbiota of the mouth that form a biofilm (containing S.mutans) we call plaque on the tooth enamel surface: • due mainly to metabolism of the disaccharide sucrose ...
1. the scabby horse - CK Mobile Equine Services
... dermatophilosis with moderate to sever dermatitis and exudation. Neglect of these areas can cause lameness but also can more commonly cause scabs, thickening and cracking of the area. This will release serum in the area to perpetuate the syndrome – and secondary pathogens such as Staphylococcus spp ...
... dermatophilosis with moderate to sever dermatitis and exudation. Neglect of these areas can cause lameness but also can more commonly cause scabs, thickening and cracking of the area. This will release serum in the area to perpetuate the syndrome – and secondary pathogens such as Staphylococcus spp ...
Spore Forming and Non-Spore Forming Gram
... intestinal cells by means of D-galactose residues on the bacterial surface which adhere to D-galactose receptors on susceptible intestinal cells The bacterium is taken up by induced phagocytosis, which is thought to be mediated by a membrane associated protein called internalin. Once ingested the ba ...
... intestinal cells by means of D-galactose residues on the bacterial surface which adhere to D-galactose receptors on susceptible intestinal cells The bacterium is taken up by induced phagocytosis, which is thought to be mediated by a membrane associated protein called internalin. Once ingested the ba ...
Bacteria
... they useful to us? [They play a role in making yogurt, cheese, and other foods. Bacteria also aid in digestion.] ...
... they useful to us? [They play a role in making yogurt, cheese, and other foods. Bacteria also aid in digestion.] ...
... Cell phones have become a necessity, imposing significant changes in modern society. Cell phones have favorable conditions for the growth of microorganisms due to heat emission or harboring dirt and sweat. In this study 166 equipment with traditional keyboard (n = 83) and touch screen (n = 83) were ...
Bacteria
... IV and DV worksheet Biome Measuring Bacteria Video Part I Bacteria Video Part II Bacteria Word Search ...
... IV and DV worksheet Biome Measuring Bacteria Video Part I Bacteria Video Part II Bacteria Word Search ...
Bacterial colony growth
... bacterial growth and of the various interactions between two touching/colliding bacteria. The bacterial growth is well characterized, and can be modeled to follow actual experimental observations, which we obtain from the Tans lab (TU Delft / AMOLF). The most basic interaction between two bacteria i ...
... bacterial growth and of the various interactions between two touching/colliding bacteria. The bacterial growth is well characterized, and can be modeled to follow actual experimental observations, which we obtain from the Tans lab (TU Delft / AMOLF). The most basic interaction between two bacteria i ...
Immobility, Skin Integrity, and Wound care
... injecting a sterile medication (usually a corticosteroid) into or just below a lesion. Skin lesions treated with intralesional therapy include psoriasis, keloids, and acne vulgaris. • Systemic Medications. These include corticosteroids for shortterm therapy for contact dermatitis or for long-term tr ...
... injecting a sterile medication (usually a corticosteroid) into or just below a lesion. Skin lesions treated with intralesional therapy include psoriasis, keloids, and acne vulgaris. • Systemic Medications. These include corticosteroids for shortterm therapy for contact dermatitis or for long-term tr ...
Antibiotic resistant bacteria
... to treat people with bacterial infections (does not treat viral infections) ...
... to treat people with bacterial infections (does not treat viral infections) ...
Importance of Bacteria
... hormones, insulin and other molecules. The DNA codes for insulin can be introduced into the bacteria, then the bacteria replicates them ( insulin genes ) during cell division. Since bacteria replicate relatively quickly, these substances can be produced in large quantities for a relatively low cost. ...
... hormones, insulin and other molecules. The DNA codes for insulin can be introduced into the bacteria, then the bacteria replicates them ( insulin genes ) during cell division. Since bacteria replicate relatively quickly, these substances can be produced in large quantities for a relatively low cost. ...
Phylum Chordata Subphylum Vertebrata Class Amphibia
... • eat earthworms and other invertebrates found in the soil. • have internal fertilization. ...
... • eat earthworms and other invertebrates found in the soil. • have internal fertilization. ...
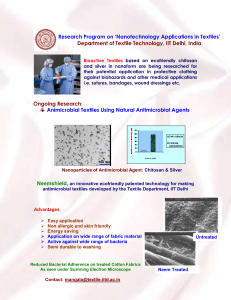
bioactive and functional textiles - Department of Textile Technology
... Research Program on ‘Nanotechnology Applications in Textiles’ Department of Textile Technology, IIT Delhi, India Bioactive Textiles based on ecofriendly chitosan and silver in nanoform are being researched for their potential application in protective clothing against biohazards and other medical ap ...
... Research Program on ‘Nanotechnology Applications in Textiles’ Department of Textile Technology, IIT Delhi, India Bioactive Textiles based on ecofriendly chitosan and silver in nanoform are being researched for their potential application in protective clothing against biohazards and other medical ap ...
Prokaryotes
... 4. Bacterial cell wall is composed of ______________. Gram positive bacteria have _______ peptidoglycan while Gram negative bacteria have ____________ peptidoglycan. 5. Gram-___________ bacteria have lipopolysaccharides on their cell wall, meaning they are ___________ resistant to antibiotics, which ...
... 4. Bacterial cell wall is composed of ______________. Gram positive bacteria have _______ peptidoglycan while Gram negative bacteria have ____________ peptidoglycan. 5. Gram-___________ bacteria have lipopolysaccharides on their cell wall, meaning they are ___________ resistant to antibiotics, which ...
Bacterial Classification (The second lecture)
... identifies the species within the genus. For example, humans belong to the genus Homo and within this genus to the species Homo sapiens. The binomial names of species are usually typeset in italics; for example, Staphylococcus aureus . Generally, the binomial should be printed in a font style differ ...
... identifies the species within the genus. For example, humans belong to the genus Homo and within this genus to the species Homo sapiens. The binomial names of species are usually typeset in italics; for example, Staphylococcus aureus . Generally, the binomial should be printed in a font style differ ...
Bacteria Notes
... division of bacteria into two identical cells Conjugation – sexual; two prokaryotes attach to each other and exchange genetic material; creates diversity among bacteria ...
... division of bacteria into two identical cells Conjugation – sexual; two prokaryotes attach to each other and exchange genetic material; creates diversity among bacteria ...
Phylum Chordata: Subphylum Vertebrata: Class Amphibia
... • Means of respiration: skin, external gills (when young & then disappear), lungs (except plethodontids) • Narrow head: small eyes • no ears but some species can pick up sound vibrations with body • Skin differences (Newts: dry warty skin) vs (Salamanders: smooth, slick skin) • Brightly colored skin ...
... • Means of respiration: skin, external gills (when young & then disappear), lungs (except plethodontids) • Narrow head: small eyes • no ears but some species can pick up sound vibrations with body • Skin differences (Newts: dry warty skin) vs (Salamanders: smooth, slick skin) • Brightly colored skin ...
Prokaryotes
... B. live in unusual habitats or generate unusual metabolic byproducts. C. have the same cell wall composition as other prokaryotes. D. are classified in one phylum. ...
... B. live in unusual habitats or generate unusual metabolic byproducts. C. have the same cell wall composition as other prokaryotes. D. are classified in one phylum. ...
Skin flora

The skin flora, more properly referred to as the skin microbiota, are the microorganisms which reside on the skin. Most research has been upon those that reside upon the 2 square metres of human skin, cf. the human microbiome. The skin microbiome refer to their genomes.Many of them are bacteria of which there are around 1000 species upon human skin from 19 phyla. The total number of bacteria on an average human has been estimated at 1012 (1 trillion). Most are found in the superficial layers of the epidermis and the upper parts of hair follicles.Skin flora is usually non-pathogenic, and either commensal (are not harmful to their host) or mutualistic (offer a benefit). The benefits bacteria can offer include preventing transient pathogenic organisms from colonizing the skin surface, either by competing for nutrients, secreting chemicals against them, or stimulating the skin's immune system. However, resident microbes can cause skin diseases and enter the blood system creating life-threatening diseases particularly in immunosuppressed people.A major nonhuman skin flora is Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, a chytrid and non-hyphal zoosporic fungus that causes chytridiomycosis, an infectious disease thought to be responsible for the decline in amphibian populations.