Sterilization & Disinfection
... disinfection, and sanitization 2. Differentiate between bactericidal and bacteriostatic agents 3. Explain the process of pasteurization and lyophilization 4. List several methods used to inhibit the growth of microorganisms 5. Identify several factors that can influence the effectiveness of disinfec ...
... disinfection, and sanitization 2. Differentiate between bactericidal and bacteriostatic agents 3. Explain the process of pasteurization and lyophilization 4. List several methods used to inhibit the growth of microorganisms 5. Identify several factors that can influence the effectiveness of disinfec ...
MEMBRANES
... 1. Eccrine (Merocrine) glands – excrete body waste, assist in temp regulation, deter bacterial growth a. located everywhere --- skin may contain 2-5 million per square inch b. sweat composition: 99% water, salt, metabolic waste (urea, uric acid & ammonia) c. pH of sweat 4-6….sweat is an acidic solut ...
... 1. Eccrine (Merocrine) glands – excrete body waste, assist in temp regulation, deter bacterial growth a. located everywhere --- skin may contain 2-5 million per square inch b. sweat composition: 99% water, salt, metabolic waste (urea, uric acid & ammonia) c. pH of sweat 4-6….sweat is an acidic solut ...
Bacterial tumor therapy 최현일 Mailing address: Department of
... Mailing address: Department of Microbiology, Chonnam National University Medical School, 5, Hak 1 dong, Dong-gu, Gwangju 501-746, Republic of Korea E mail : hyonchoy@jnu.ac.kr Certain strains of bacteria, such as E. coli, Salmonella, and Clostridium, selectively colonize and grow in tumors. We have ...
... Mailing address: Department of Microbiology, Chonnam National University Medical School, 5, Hak 1 dong, Dong-gu, Gwangju 501-746, Republic of Korea E mail : hyonchoy@jnu.ac.kr Certain strains of bacteria, such as E. coli, Salmonella, and Clostridium, selectively colonize and grow in tumors. We have ...
Classification of Microorganisms:
... staining reaction into the following groups: 1- Filamentous bacteria: Streptomyces: antibiotic producers. 2- True bacteria: Cocci: Gram positive: Gram negative: Bacilli: Gram positive: Gram negative: ...
... staining reaction into the following groups: 1- Filamentous bacteria: Streptomyces: antibiotic producers. 2- True bacteria: Cocci: Gram positive: Gram negative: Bacilli: Gram positive: Gram negative: ...
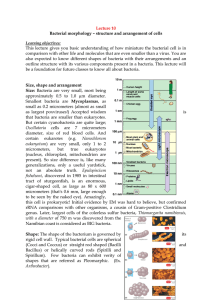
Lecture 10 Bacterial morphology – structure and arrangement of
... to be seen by the naked eye). Amazingly, this cell is prokaryotic! Initial evidence by EM was hard to believe, but confirmed rRNA comparisons with other organisms, a cousin of Gram-positive Clostridium genus. Later, largest cells of the colorless sulfur bacteria, Thiomargarita namibiensis, with a di ...
... to be seen by the naked eye). Amazingly, this cell is prokaryotic! Initial evidence by EM was hard to believe, but confirmed rRNA comparisons with other organisms, a cousin of Gram-positive Clostridium genus. Later, largest cells of the colorless sulfur bacteria, Thiomargarita namibiensis, with a di ...
bacteria
... (Beneficial Bacteria) • Saprophytes (decomposers) – Breaks down dead organisms and decaying matter – Returns nutrients to soil ...
... (Beneficial Bacteria) • Saprophytes (decomposers) – Breaks down dead organisms and decaying matter – Returns nutrients to soil ...
Chapter 1: The Microbial World and You
... stabilizing agent in many products including water-based paints and cosmetics. ...
... stabilizing agent in many products including water-based paints and cosmetics. ...
Characteristics of Amphibians
... significant advantage over the “singleloop” circulation of a fish—faster blood flow to the body. In a fish, the blood loses some of its force as it passes through the narrow capillaries of the gills, and blood flow slows as a result. ...
... significant advantage over the “singleloop” circulation of a fish—faster blood flow to the body. In a fish, the blood loses some of its force as it passes through the narrow capillaries of the gills, and blood flow slows as a result. ...
Introductory slides - first couple of lectures
... Place the cell into a cubic swimming pool 1 cm on each side, then expand the entire system so that the cell is now 2 m long (equivalent to a tall [6’6”] human): Swimming pool is just over 6 miles on a side!! ...
... Place the cell into a cubic swimming pool 1 cm on each side, then expand the entire system so that the cell is now 2 m long (equivalent to a tall [6’6”] human): Swimming pool is just over 6 miles on a side!! ...
Chapter 10 Microbiology
... Pathogens that cause body to produce antibodies. Allergen An antigen that causes an over-reaction Can cause anaphylactic shock. ...
... Pathogens that cause body to produce antibodies. Allergen An antigen that causes an over-reaction Can cause anaphylactic shock. ...
GCSE Revision Booklet Biology Unit B1 Influences of life
... The number of people who suffer from type 2 diabetes is rising due to increasing obesity. A person in considered obese if they have a body mass index (BMI) of over 30, if they have a BMI of 20 or under they are considered to be underweight. weight in kilorams (kg) The formula for BMI is: height in m ...
... The number of people who suffer from type 2 diabetes is rising due to increasing obesity. A person in considered obese if they have a body mass index (BMI) of over 30, if they have a BMI of 20 or under they are considered to be underweight. weight in kilorams (kg) The formula for BMI is: height in m ...
Your Skin - Super Teacher Worksheets
... What is the largest organ in your body? Your heart? It is the largest muscle in your body, but you do have larger organs. Your brain? The brain inside your skull is pretty big, but it's not the biggest. How about the liver? It is the heaviest organ. How about your skin? Yes, your skin is an organ, j ...
... What is the largest organ in your body? Your heart? It is the largest muscle in your body, but you do have larger organs. Your brain? The brain inside your skull is pretty big, but it's not the biggest. How about the liver? It is the heaviest organ. How about your skin? Yes, your skin is an organ, j ...
Your Skin - Super Teacher Worksheets
... What is the largest organ in your body? Your heart? It is the largest muscle in your body, but you do have larger organs. Your brain? The brain inside your skull is pretty big, but it's not the biggest. How about the liver? It is the heaviest organ. How about your skin? Yes, your skin is an organ, j ...
... What is the largest organ in your body? Your heart? It is the largest muscle in your body, but you do have larger organs. Your brain? The brain inside your skull is pretty big, but it's not the biggest. How about the liver? It is the heaviest organ. How about your skin? Yes, your skin is an organ, j ...
Structure and Movement The Skin Functions of the Skin
... You have read that the skin can make vitamin D and that it protects the body from outside substances. Both of these functions help regulate the body’s internal environment. The skin also works with other body systems to maintain homeostasis. The skin and circulatory system help cool the body when it ...
... You have read that the skin can make vitamin D and that it protects the body from outside substances. Both of these functions help regulate the body’s internal environment. The skin also works with other body systems to maintain homeostasis. The skin and circulatory system help cool the body when it ...
lecture 03a
... – UV used to sterilize air, surfaces in hospitals, etc. – Ionizing radiation: x-rays (electron beam) and gamma rays; important treatment of plastics, various foods. – Irradiation of meat important tool in food safety. ...
... – UV used to sterilize air, surfaces in hospitals, etc. – Ionizing radiation: x-rays (electron beam) and gamma rays; important treatment of plastics, various foods. – Irradiation of meat important tool in food safety. ...
Bacteria Prokaryotes Eubacteria Archaebacteria
... · themoacidophiles - love hot (above 80 C) and acidic (pH 1-2) environments ...
... · themoacidophiles - love hot (above 80 C) and acidic (pH 1-2) environments ...
Chapter 23 Bacteria Guided Reading
... 2. What are the 2 domains of prokaryotes? Why are bacteria classified in one group or the other? ...
... 2. What are the 2 domains of prokaryotes? Why are bacteria classified in one group or the other? ...
Functions of Skin - Mounds Park Academy Blogs
... liquid that produces a noticeable odor. The apocrine glands become very active with the onset of puberty. They are found in the armpit and the genital area. The milk glands in the breasts are modified apocrine sweat glands. Body odor is produced by micro-organisms that grow where the apocrine glands ...
... liquid that produces a noticeable odor. The apocrine glands become very active with the onset of puberty. They are found in the armpit and the genital area. The milk glands in the breasts are modified apocrine sweat glands. Body odor is produced by micro-organisms that grow where the apocrine glands ...
Chapter 12 Infectious Diseases
... 34. Answers may vary. The internal and external body surfaces are always in contact with microorganisms that could include pathogens. The body’s outermost skin is composed of many layers of scaly, overlapping cells that form a nearly impenetrable physical barrier to pathogens. The skin is also dry ...
... 34. Answers may vary. The internal and external body surfaces are always in contact with microorganisms that could include pathogens. The body’s outermost skin is composed of many layers of scaly, overlapping cells that form a nearly impenetrable physical barrier to pathogens. The skin is also dry ...
Chapter 20 Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea
... • Characteristics of Bacterial Cells – Bacteria are the more common type of prokaryote. – Bacterial cell walls are protected by peptidoglycan, a complex of polysaccharides linked by amino acids. – The Gram stain procedure (developed in the late 1880s by Hans Christian Gram) differentiates bacteria. ...
... • Characteristics of Bacterial Cells – Bacteria are the more common type of prokaryote. – Bacterial cell walls are protected by peptidoglycan, a complex of polysaccharides linked by amino acids. – The Gram stain procedure (developed in the late 1880s by Hans Christian Gram) differentiates bacteria. ...
Title - Iowa State University
... o Parasitism: a parasite eats the tissues or fluids of its host, which harms the host Archaea 1. Name the three types of extremophiles, and describe their living conditions/preferences: Halophiles Either tolerate or prefer highly saline environments. ...
... o Parasitism: a parasite eats the tissues or fluids of its host, which harms the host Archaea 1. Name the three types of extremophiles, and describe their living conditions/preferences: Halophiles Either tolerate or prefer highly saline environments. ...
Math 161 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Worksheet Find (f
... 9. loga 4/ a6b5 √ a2b3 Express as a single logarithm: 10. 5ln a + (2ln b – ln (x + y)) Solve: 11. 5x+2 = 31-x 12. log4(x + 3) + log4(x – 2) = 4 13. In 1623, Peter Minuit of the Dutch West India Company purchased Manhattan Island from the Native Americans for $24. Assuming an exponential rate of infl ...
... 9. loga 4/ a6b5 √ a2b3 Express as a single logarithm: 10. 5ln a + (2ln b – ln (x + y)) Solve: 11. 5x+2 = 31-x 12. log4(x + 3) + log4(x – 2) = 4 13. In 1623, Peter Minuit of the Dutch West India Company purchased Manhattan Island from the Native Americans for $24. Assuming an exponential rate of infl ...
Bacteria
... the cell membranes of some Gram-negative bacteria, that are poisonous. They are released when the bacteria die. ...
... the cell membranes of some Gram-negative bacteria, that are poisonous. They are released when the bacteria die. ...
Skin flora

The skin flora, more properly referred to as the skin microbiota, are the microorganisms which reside on the skin. Most research has been upon those that reside upon the 2 square metres of human skin, cf. the human microbiome. The skin microbiome refer to their genomes.Many of them are bacteria of which there are around 1000 species upon human skin from 19 phyla. The total number of bacteria on an average human has been estimated at 1012 (1 trillion). Most are found in the superficial layers of the epidermis and the upper parts of hair follicles.Skin flora is usually non-pathogenic, and either commensal (are not harmful to their host) or mutualistic (offer a benefit). The benefits bacteria can offer include preventing transient pathogenic organisms from colonizing the skin surface, either by competing for nutrients, secreting chemicals against them, or stimulating the skin's immune system. However, resident microbes can cause skin diseases and enter the blood system creating life-threatening diseases particularly in immunosuppressed people.A major nonhuman skin flora is Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, a chytrid and non-hyphal zoosporic fungus that causes chytridiomycosis, an infectious disease thought to be responsible for the decline in amphibian populations.