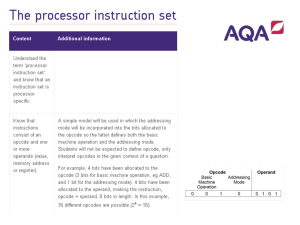
Physics_Scientific_Notation_Week 3 PPT
... • If the exponents are not the same then it is necessary to change one of the numbers so that both numbers have the same exponential value. ...
... • If the exponents are not the same then it is necessary to change one of the numbers so that both numbers have the same exponential value. ...
Modular Arithmetic
... The final digit of a 12-digit Universal Product Code (UPC) is a check digit. Suppose the digits of a UPS are represented by X1X2X3X4X5X6-X7X8X9X10X11Xc To calculate the check digit Xc, first compute 3(X1+X3+X5+X7+X9+X11) + (X2+X4+X6+X8+X10) (mod 10). If this number is zero, then Xc=0, If not, subtra ...
... The final digit of a 12-digit Universal Product Code (UPC) is a check digit. Suppose the digits of a UPS are represented by X1X2X3X4X5X6-X7X8X9X10X11Xc To calculate the check digit Xc, first compute 3(X1+X3+X5+X7+X9+X11) + (X2+X4+X6+X8+X10) (mod 10). If this number is zero, then Xc=0, If not, subtra ...
Add this to your Formula Chart
... • Determinants are square arrays of numbers. • Each number in the array is an element • A two by two array is called a second order determinant. (2 rows and 2 columns) ...
... • Determinants are square arrays of numbers. • Each number in the array is an element • A two by two array is called a second order determinant. (2 rows and 2 columns) ...
Extra Practice 1 Lesson 1.1: Square Numbers and Area Models 1
... a) 19 is between 18 and 20. b) 101 is greater than 10. c) 5 + 10 is less than 5 + 10 . d) 3 8 is less than 36 . e) 12 + 10 is less than 32 – 10 . ...
... a) 19 is between 18 and 20. b) 101 is greater than 10. c) 5 + 10 is less than 5 + 10 . d) 3 8 is less than 36 . e) 12 + 10 is less than 32 – 10 . ...
Scientific Notation and Error
... very small numbers in the form: M x 10n M is a number between 1 and 10 n is an integer ...
... very small numbers in the form: M x 10n M is a number between 1 and 10 n is an integer ...