POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE INTEGERS
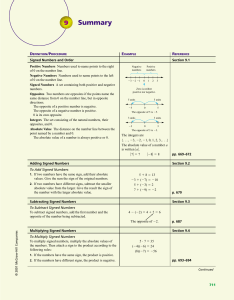
... When a number of mathematical operations are to be performed in a problem, you must follow a specific order for solving the problem Step 1 – Do anything that is inside parentheses Step 2 - Solve anything that contains an exponent (a power – 52 – the 2 is the exponent and it means the base number is ...
... When a number of mathematical operations are to be performed in a problem, you must follow a specific order for solving the problem Step 1 – Do anything that is inside parentheses Step 2 - Solve anything that contains an exponent (a power – 52 – the 2 is the exponent and it means the base number is ...
Year 4 maths-support-booklet PDF File
... Add & subtract using a number line or expanded method thousands ...
... Add & subtract using a number line or expanded method thousands ...
KU Mult 4 Decimals by single digit numbers Session plan
... number as a factor (e.g. choosing three numbers from one times table). The other player guesses the factor. Are there any other numbers which are also a factor? Repeat so that pupils have three goes each. Teacher input with whole class Write 54 on the board and remind pupils how to find all the ...
... number as a factor (e.g. choosing three numbers from one times table). The other player guesses the factor. Are there any other numbers which are also a factor? Repeat so that pupils have three goes each. Teacher input with whole class Write 54 on the board and remind pupils how to find all the ...
Document
... one digit two digits (two significant figures = 2 sig. figs.) three digits,etc. (300 how many digits?) ...
... one digit two digits (two significant figures = 2 sig. figs.) three digits,etc. (300 how many digits?) ...