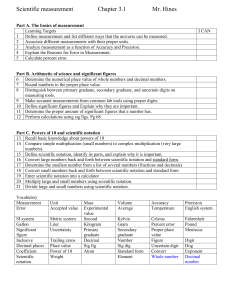
Math 1 – Basic Operations Part 1 NUMBER DEFINITIONS
... The remainder is the number left over after division. If you divided 48 by 5, you'd first find the nearest multiple of 5 to 48, which is 45 (9 x 5). This means 5 goes into 48 nine times, but then there is still 3 left over, which makes the remainder 3. Sample Questions: 40. How many times does 2 go ...
... The remainder is the number left over after division. If you divided 48 by 5, you'd first find the nearest multiple of 5 to 48, which is 45 (9 x 5). This means 5 goes into 48 nine times, but then there is still 3 left over, which makes the remainder 3. Sample Questions: 40. How many times does 2 go ...
This is just a test to see if notes will appear here…
... 1. Happy days! The question has told us that we are dealing with inverse proportion, and unless it says otherwise, we can also assume that there are no nasty squares or cubes around. 2. The expression to say that z is inversely proportional to t is: 3. Rule: Replace the ...
... 1. Happy days! The question has told us that we are dealing with inverse proportion, and unless it says otherwise, we can also assume that there are no nasty squares or cubes around. 2. The expression to say that z is inversely proportional to t is: 3. Rule: Replace the ...
Full text
... When we normalize D to make the where d = x Thus we have M leading entry 1,, the second diagonal entry is less than one and so the sequence of its powers converges to ...
... When we normalize D to make the where d = x Thus we have M leading entry 1,, the second diagonal entry is less than one and so the sequence of its powers converges to ...
COS 423 Lecture 1 Counting in Binary Amortized and Worst-Case Efficiency
... one, unless cost is k + 1 or more. (We call the add expensive.) In this case n mod 2k = 2k – 1, so Φ decreases by 2k – 1. This can happen at most n/2k times out of n: Φ = n - e2k ≥ 0, where e = #expensive adds. ...
... one, unless cost is k + 1 or more. (We call the add expensive.) In this case n mod 2k = 2k – 1, so Φ decreases by 2k – 1. This can happen at most n/2k times out of n: Φ = n - e2k ≥ 0, where e = #expensive adds. ...