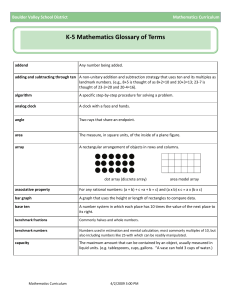
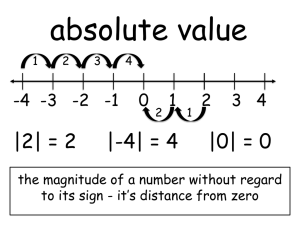
Final Exam Study Guide Name: Date:______ Convert numbers from
... Translation – a slide can go left or right and also up or down. Reflection – a flip – if over x-axis the x coordinate does not change - if over y-axis the y coordinate does not change Rotation – a turn – if 90° you switch the x and y coordinate and adjust for which quadrant you end on. - if 180° you ...
... Translation – a slide can go left or right and also up or down. Reflection – a flip – if over x-axis the x coordinate does not change - if over y-axis the y coordinate does not change Rotation – a turn – if 90° you switch the x and y coordinate and adjust for which quadrant you end on. - if 180° you ...
Real Numbers and Their Graphs
... smaller (see Figure 1-4(b)). The point with coordinate –6 lies to the left of the point with coordinate –3 so it follows that –6 –3. ...
... smaller (see Figure 1-4(b)). The point with coordinate –6 lies to the left of the point with coordinate –3 so it follows that –6 –3. ...
NANC 147
... Currently there is no strategy defined for rollover if the maximum value for any of the id fields (sv id, lrn id, or npa-nxx id) is reached. One should be defined so that the vendor implementations are in sync. Currently the max value used by Lockheed is a 4 byte-signed integer and for Perot it is a ...
... Currently there is no strategy defined for rollover if the maximum value for any of the id fields (sv id, lrn id, or npa-nxx id) is reached. One should be defined so that the vendor implementations are in sync. Currently the max value used by Lockheed is a 4 byte-signed integer and for Perot it is a ...
4.6: Formalizing Relations and Functions
... ordered pairs (x, y). In this case, the domain is the set of x-values and the range is the set of y-values. ...
... ordered pairs (x, y). In this case, the domain is the set of x-values and the range is the set of y-values. ...
Power Point Notes
... What if…? The tallest known iceberg in the North Atlantic rose 550 feet above the oceans surface. How many feet would it be from the top of the tallest iceberg to the wreckage of the Titanic, which is at an elevation of –12,468 feet? ...
... What if…? The tallest known iceberg in the North Atlantic rose 550 feet above the oceans surface. How many feet would it be from the top of the tallest iceberg to the wreckage of the Titanic, which is at an elevation of –12,468 feet? ...
what is chemistry - Maria Regina High School
... 3. Zeros at the beginning of a number are NOT significant = placeholders ex. .0025 = 2 sig figs 4. Zeros at the end of a number are only significant if they follow a decimal ex. 7500 = 2 sig figs ex. 75.00 = 4 sig figs 5. Counted numbers = unlimited sig figs ...
... 3. Zeros at the beginning of a number are NOT significant = placeholders ex. .0025 = 2 sig figs 4. Zeros at the end of a number are only significant if they follow a decimal ex. 7500 = 2 sig figs ex. 75.00 = 4 sig figs 5. Counted numbers = unlimited sig figs ...