No questions like this on midterm exam
... Complementary angles of fired projectiles travel the same horizontal distance. 29. A bullet is fired horizontally across a field, from a gun, while another identical bullet is dropped to the ground from the same height as the gun, at the instant the bullet is fired. Do both bullets hit the ground at ...
... Complementary angles of fired projectiles travel the same horizontal distance. 29. A bullet is fired horizontally across a field, from a gun, while another identical bullet is dropped to the ground from the same height as the gun, at the instant the bullet is fired. Do both bullets hit the ground at ...
C10, S3 – Newton`s First and Second Laws of Motion
... Weight varies with the ________________ of the gravitational force but ________________does not. ...
... Weight varies with the ________________ of the gravitational force but ________________does not. ...
Kines 171 Size, Mass, and Movement PowerPoint
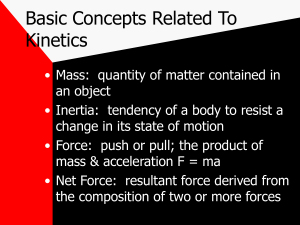
... Basic Concepts Related To Kinetics • Center of Gravity: point around which a body’s weight & mass are equally balanced in all directions • Weight: attractive force that the earth exerts on the body wt= mag • Pressure: force per unit of area over which the force acts p= F divided by A N/cm2 , Pascal ...
... Basic Concepts Related To Kinetics • Center of Gravity: point around which a body’s weight & mass are equally balanced in all directions • Weight: attractive force that the earth exerts on the body wt= mag • Pressure: force per unit of area over which the force acts p= F divided by A N/cm2 , Pascal ...
chapter 4 - forces and newton`s laws of motion
... The Normal Force is found by adding vectorially the normal components of all the other forces acting on the object. (1) If an object is resting on a horizontal surface, Fn = Mg (2) If an object on a horizontal surface is being partly lifted by another force, Fa, then Fn = Mg - Fa. (3) If an object o ...
... The Normal Force is found by adding vectorially the normal components of all the other forces acting on the object. (1) If an object is resting on a horizontal surface, Fn = Mg (2) If an object on a horizontal surface is being partly lifted by another force, Fa, then Fn = Mg - Fa. (3) If an object o ...
Newton`s Second Law
... Net Force, Mass and Acceleration Isaac Newton discovered one of the most important laws of nature; the relationship between net force, mass (inertia) and acceleration. Newton’s second law states that the net force acting on a mass causes the mass to accelerate in the direction of the net force. ...
... Net Force, Mass and Acceleration Isaac Newton discovered one of the most important laws of nature; the relationship between net force, mass (inertia) and acceleration. Newton’s second law states that the net force acting on a mass causes the mass to accelerate in the direction of the net force. ...
File - TuHS Physical Science
... 30. The acceleration of an object is equal to the net ____________________ acting on the object divided by the object’s ____________________. 31. If the forces acting on an object produce a net force of zero, the forces are called ____________________. 32. If a golf ball and bowling ball are rolling ...
... 30. The acceleration of an object is equal to the net ____________________ acting on the object divided by the object’s ____________________. 31. If the forces acting on an object produce a net force of zero, the forces are called ____________________. 32. If a golf ball and bowling ball are rolling ...
Unit 5 Notes: Forces
... ________________________ believed that heavier objects fall faster than lighter objects. ________________________ was able to prove that, neglecting air friction, all objects have the same acceleration due to gravity. _________________ is the amount of matter in an object. It does NOT change with lo ...
... ________________________ believed that heavier objects fall faster than lighter objects. ________________________ was able to prove that, neglecting air friction, all objects have the same acceleration due to gravity. _________________ is the amount of matter in an object. It does NOT change with lo ...
mechanical energy
... • A 4,000 kg satellite is traveling in a circular orbit 200 km above the surface of the earth. A 3.0 gram marble is dropped inside the satellite. What is the force of gravity on the marble as viewed by the observers on the earth? (Me = 5.98 x 1024 kg, Re = 6.37 x 106 m, G = 6.67 x 10-11 Nm2 /kg2) ...
... • A 4,000 kg satellite is traveling in a circular orbit 200 km above the surface of the earth. A 3.0 gram marble is dropped inside the satellite. What is the force of gravity on the marble as viewed by the observers on the earth? (Me = 5.98 x 1024 kg, Re = 6.37 x 106 m, G = 6.67 x 10-11 Nm2 /kg2) ...
m1 - dynamics - WordPress.com
... In other words, if an object A exerts a force on a second object B (by direct contact or at a distance by magnetic attraction, gravitation etc.) then B will exert a force on A. The two forces will be of equal magnitude and in opposite directions. If A and B are parts of the same system, the force of ...
... In other words, if an object A exerts a force on a second object B (by direct contact or at a distance by magnetic attraction, gravitation etc.) then B will exert a force on A. The two forces will be of equal magnitude and in opposite directions. If A and B are parts of the same system, the force of ...
Forces
... • The direction of the net force, ΣF, always indicates the direction of the acceleration, but not necessarily the direction of motion. • A force that acts in two dimensions is typically separated into it’s components. • Newton’s second law is most often applied in each dimension separately. ...
... • The direction of the net force, ΣF, always indicates the direction of the acceleration, but not necessarily the direction of motion. • A force that acts in two dimensions is typically separated into it’s components. • Newton’s second law is most often applied in each dimension separately. ...
Monday, June 21, 2004 - UTA High Energy Physics page.
... People have been very curious about the stars in the sky, making observations for a long time. But the data people collected have not been explained until Newton has discovered the law of gravitation. Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proporti ...
... People have been very curious about the stars in the sky, making observations for a long time. But the data people collected have not been explained until Newton has discovered the law of gravitation. Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proporti ...
normal force
... Force of Gravity (Weight) is the force of attraction between all objects acting downwards toward the centre of the Earth ...
... Force of Gravity (Weight) is the force of attraction between all objects acting downwards toward the centre of the Earth ...
Weight
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is usually taken to be the force on the object due to gravity. Weight is a vector whose magnitude (a scalar quantity), often denoted by an italic letter W, is the product of the mass m of the object and the magnitude of the local gravitational acceleration g; thus: W = mg. The unit of measurement for weight is that of force, which in the International System of Units (SI) is the newton. For example, an object with a mass of one kilogram has a weight of about 9.8 newtons on the surface of the Earth, and about one-sixth as much on the Moon. In this sense of weight, a body can be weightless only if it is far away (in principle infinitely far away) from any other mass. Although weight and mass are scientifically distinct quantities, the terms are often confused with each other in everyday use.There is also a rival tradition within Newtonian physics and engineering which sees weight as that which is measured when one uses scales. There the weight is a measure of the magnitude of the reaction force exerted on a body. Typically, in measuring an object's weight, the object is placed on scales at rest with respect to the earth, but the definition can be extended to other states of motion. Thus, in a state of free fall, the weight would be zero. In this second sense of weight, terrestrial objects can be weightless. Ignoring air resistance, the famous apple falling from the tree, on its way to meet the ground near Isaac Newton, is weightless.Further complications in elucidating the various concepts of weight have to do with the theory of relativity according to which gravity is modelled as a consequence of the curvature of spacetime. In the teaching community, a considerable debate has existed for over half a century on how to define weight for their students. The current situation is that a multiple set of concepts co-exist and find use in their various contexts.