Myers AP - Unit 03B PowerPoint
... = areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking. ...
... = areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking. ...
Introduction: The Human Brain
... the cell bodies of the neurons, while the white matter is the branching network of thread-like tendrils called dendrites and axons - that spread out from the cell bodies to connect to other neurons. But the brain also has another, even more numerous type of cell, called glial cells. These outnumber ...
... the cell bodies of the neurons, while the white matter is the branching network of thread-like tendrils called dendrites and axons - that spread out from the cell bodies to connect to other neurons. But the brain also has another, even more numerous type of cell, called glial cells. These outnumber ...
Brain Development Infancy and Early Childhood Phyllis L
... n Has a greater density of synaptic connections than the adult brain n The smarter we are the more synaptic connections we have. 2 years of age n Fully wired brains n Greater maturity in motor areas n Physical ability exceeds common sense ...
... n Has a greater density of synaptic connections than the adult brain n The smarter we are the more synaptic connections we have. 2 years of age n Fully wired brains n Greater maturity in motor areas n Physical ability exceeds common sense ...
Older Brain Structures
... Located on top of the brainstem Functions: Directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex Transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla ...
... Located on top of the brainstem Functions: Directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex Transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla ...
The Human Nervous System
... such as the knee jerk reflex, follows. 1. A tap on the knee stimulates sensory receptors (tendon), generating a nerve signal. 2. The signal travels along a nerve to the spinal cord. 3. In the spinal cord, the signal is transmitted from the sensory nerve to a motor nerve. 4. The motor nerve sends the ...
... such as the knee jerk reflex, follows. 1. A tap on the knee stimulates sensory receptors (tendon), generating a nerve signal. 2. The signal travels along a nerve to the spinal cord. 3. In the spinal cord, the signal is transmitted from the sensory nerve to a motor nerve. 4. The motor nerve sends the ...
Introduction to Psychology
... Hypothalamus structure lying below (hypo) the thalamus; directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature) helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland linked to emotion as well sexual arousal, satiation, pleasure (or rewards) centers ...
... Hypothalamus structure lying below (hypo) the thalamus; directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature) helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland linked to emotion as well sexual arousal, satiation, pleasure (or rewards) centers ...
Chapter 3 - Victoria College
... INTRODUCTION • Brain = center for registering sensations, correlating them with one another and with stored information, making decisions, and taking action • Center for intellect, emotions, behavior, and memory ...
... INTRODUCTION • Brain = center for registering sensations, correlating them with one another and with stored information, making decisions, and taking action • Center for intellect, emotions, behavior, and memory ...
Introduction to the brain and behaviour
... It consists of 100 billion neurons. Time until unconsciousness after loss of blood supply to brain is 8 – 10 secs. Approximately 75% of it is water. If you could harness the power used by your brain you could power as a 10 watt light bulb! ...
... It consists of 100 billion neurons. Time until unconsciousness after loss of blood supply to brain is 8 – 10 secs. Approximately 75% of it is water. If you could harness the power used by your brain you could power as a 10 watt light bulb! ...
Pharmacology - The reward pathway
... crosses the emotional centre of the brain and connects to the decision-making part of the brain-will reinforce a behaviour. It does so because it produces a pleasurable feeling. Dopamine is a monoamine. Our mood is affected by the monoamines. There's an association between the altered function of mo ...
... crosses the emotional centre of the brain and connects to the decision-making part of the brain-will reinforce a behaviour. It does so because it produces a pleasurable feeling. Dopamine is a monoamine. Our mood is affected by the monoamines. There's an association between the altered function of mo ...
The Brain - Gordon State College
... processes, and movement patterns. Consists of: – Thalamus: the brain’s sensory relay station – Limbic system: influences fear, aggression, and new memories – Cerebral cortex: located on top of these structures; the most complex part of the brain ...
... processes, and movement patterns. Consists of: – Thalamus: the brain’s sensory relay station – Limbic system: influences fear, aggression, and new memories – Cerebral cortex: located on top of these structures; the most complex part of the brain ...
Neuroanatomy 6-12
... o Using observations, allow the students to describe the visual differences between a rat, mouse, sheep, and human brain. § How are the brains alike and different? o Use a sheet of paper to describe why we have sulci and gyri on our brain. The sheet of paper represents all the surface of our brain, ...
... o Using observations, allow the students to describe the visual differences between a rat, mouse, sheep, and human brain. § How are the brains alike and different? o Use a sheet of paper to describe why we have sulci and gyri on our brain. The sheet of paper represents all the surface of our brain, ...
Chapter 1 - Center for Advanced Brain Imaging
... of the brain responsible for processing or receiving input Example: visual cortex ...
... of the brain responsible for processing or receiving input Example: visual cortex ...
Brain Day - No Regrets
... The ear is divided into three parts: outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. The outer ear (pinna) collects sound waves and sends them through the ear canal to the eardrum (tympanic membrane). The middle ear is air-filled space containing ossicles, the three smallest bones in the human body (malleus, ...
... The ear is divided into three parts: outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. The outer ear (pinna) collects sound waves and sends them through the ear canal to the eardrum (tympanic membrane). The middle ear is air-filled space containing ossicles, the three smallest bones in the human body (malleus, ...
Wallin_Back_to_School_with_the_Thinking_Maps
... Your Objective: Shout out the answer to this question: “What do these symbols make you THINK?” ...
... Your Objective: Shout out the answer to this question: “What do these symbols make you THINK?” ...
1. Semester Introduction to functional neurobiology
... Which fungus is eatable and which one is toxic? ...
... Which fungus is eatable and which one is toxic? ...
questions from - AP Psychology: 6(A)
... can now speak as he did before his accident. This is an example of the brain’s __________, which allowed the structure and function of his brain cells to change to adjust to the trauma. 29. The division of the nervous system that allows the brain and the spinal cord to communicate with the sensory s ...
... can now speak as he did before his accident. This is an example of the brain’s __________, which allowed the structure and function of his brain cells to change to adjust to the trauma. 29. The division of the nervous system that allows the brain and the spinal cord to communicate with the sensory s ...
Psychology-Parts-of-the-Brain-and-Their
... The limbic system contains glands which help relay emotions. Many hormonal responses that the body generates are initiated in this area. The limbic system includes the amygdala, hippocampus, hypothalamus and thalamus. Amygdala:The amygdala helps the body responds to emotions, memories and fear. It i ...
... The limbic system contains glands which help relay emotions. Many hormonal responses that the body generates are initiated in this area. The limbic system includes the amygdala, hippocampus, hypothalamus and thalamus. Amygdala:The amygdala helps the body responds to emotions, memories and fear. It i ...
Nervous System
... Memory formation—case studies that shed light on location in the brain where new meories are formed • The case of H.M.—After surgery to treat seizures, in which the amygdala, uncus, hippocampal gyrus and anterior two-thirds of the hippocampus were removed, H.M. could not form long-term memories • T ...
... Memory formation—case studies that shed light on location in the brain where new meories are formed • The case of H.M.—After surgery to treat seizures, in which the amygdala, uncus, hippocampal gyrus and anterior two-thirds of the hippocampus were removed, H.M. could not form long-term memories • T ...
Presentation - Ch 2 Sections Demo-6-7
... Close-up: The Tools of Discovery How do neurobiologists investigate the inner workings of the brain? ...
... Close-up: The Tools of Discovery How do neurobiologists investigate the inner workings of the brain? ...
Slide 1
... Wernicke’s area (usually in left temporal lobe), causing the affected person to be unable to understand or produce meaningful language. Spatial neglect - condition produced by damage to the association areas of the right hemisphere resulting in an inability to recognize objects or body parts in the ...
... Wernicke’s area (usually in left temporal lobe), causing the affected person to be unable to understand or produce meaningful language. Spatial neglect - condition produced by damage to the association areas of the right hemisphere resulting in an inability to recognize objects or body parts in the ...
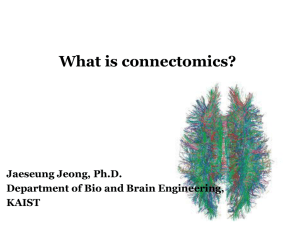
What is connectomics? - Brain Dynamics Laboratory
... • The connectome naturally places strong constraints on which neurons or neural populations can interact, or how strong or direct their interactions are (Scholarpedia). ...
... • The connectome naturally places strong constraints on which neurons or neural populations can interact, or how strong or direct their interactions are (Scholarpedia). ...
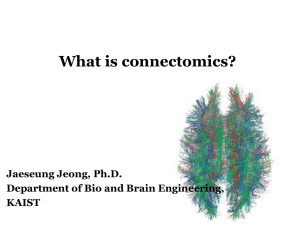
What is connectomics? - Brain Dynamics Laboratory
... • The connectome naturally places strong constraints on which neurons or neural populations can interact, or how strong or direct their interactions are (Scholarpedia). ...
... • The connectome naturally places strong constraints on which neurons or neural populations can interact, or how strong or direct their interactions are (Scholarpedia). ...
File Now
... Glutamate – excitatory most widely available neurotransmitter, paradoxically both main neurotransmitter for memory and main one responsible for cell death ...
... Glutamate – excitatory most widely available neurotransmitter, paradoxically both main neurotransmitter for memory and main one responsible for cell death ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint Notes
... linked to the emotions of fear and anger. The Hypothalamus lies below (hypo) the thalamus. It directs several maintenance activities like eating, drinking, body temperature, and control of emotions. It helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. o Reward Center - Rats cross an electri ...
... linked to the emotions of fear and anger. The Hypothalamus lies below (hypo) the thalamus. It directs several maintenance activities like eating, drinking, body temperature, and control of emotions. It helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. o Reward Center - Rats cross an electri ...