Adding Fractions with Different Denominators Subtracting Fractions
... there are. The fraction 3/8 indicates that there are three pieces. The denominator of a fraction tells how many pieces an object was divided into. The fraction 3/8 indicates that the whole object was divided into 8 pieces. If the numerators of two fractions are the same, the fraction with the smalle ...
... there are. The fraction 3/8 indicates that there are three pieces. The denominator of a fraction tells how many pieces an object was divided into. The fraction 3/8 indicates that the whole object was divided into 8 pieces. If the numerators of two fractions are the same, the fraction with the smalle ...
Mathematical Investigation: Paper Size
... When you go to the next row, each of the four consecutive natural numbers will increase by 1. Therefore, the next number that can be written as the sum of four consecutive natural numbers will increase by 4. This explains why the (common) difference between successive terms is 4. [In fact, the patte ...
... When you go to the next row, each of the four consecutive natural numbers will increase by 1. Therefore, the next number that can be written as the sum of four consecutive natural numbers will increase by 4. This explains why the (common) difference between successive terms is 4. [In fact, the patte ...
After studying this chapter you will be able to get a - e
... ð When the digits of a number are added until a single digit number is obtained it is called the digital index of the number. ð If the digital index of a number is 3, 6 or 9 that number is divisible by 3. ð If the number formed by the last two digits of a number is divisible by 4 or the last two dig ...
... ð When the digits of a number are added until a single digit number is obtained it is called the digital index of the number. ð If the digital index of a number is 3, 6 or 9 that number is divisible by 3. ð If the number formed by the last two digits of a number is divisible by 4 or the last two dig ...
Numbers! Steven Charlton - Fachbereich | Mathematik
... The ‘natural numbers’ N are maybe the only numbers which did not need to be discovered, having been known since ancient times. Every other system of numbers builds on top of the natural numbers (directly, or indirectly) in order to generalise some desirable/interesting property, or fix some gap/inco ...
... The ‘natural numbers’ N are maybe the only numbers which did not need to be discovered, having been known since ancient times. Every other system of numbers builds on top of the natural numbers (directly, or indirectly) in order to generalise some desirable/interesting property, or fix some gap/inco ...
Sums of Continued Fractions to the Nearest Integer
... and 2b regular continued fractions, where b of them have real partial quotients an ≥ b while the others have partial quotients of the form ±ian with integral an ≥ b. Here the set of partial quotients Z is replaced by the set of Gaussian integers Z[i]. Using Theorem 1.1 we may deduce in the same way ...
... and 2b regular continued fractions, where b of them have real partial quotients an ≥ b while the others have partial quotients of the form ±ian with integral an ≥ b. Here the set of partial quotients Z is replaced by the set of Gaussian integers Z[i]. Using Theorem 1.1 we may deduce in the same way ...
The secret life of 1/n: A journey far beyond the decimal point
... if we were to pay attention to all of the digits past the decimal point? Is there anything more interesting that these decimal expansions have to offer besides their role as everyday computational workhorses? In this exposition, we’ll explore this question for the decimal expansions of the very simp ...
... if we were to pay attention to all of the digits past the decimal point? Is there anything more interesting that these decimal expansions have to offer besides their role as everyday computational workhorses? In this exposition, we’ll explore this question for the decimal expansions of the very simp ...
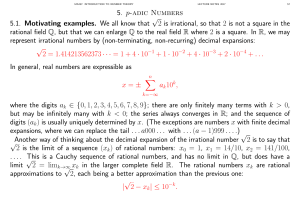
5. p-adic Numbers 5.1. Motivating examples. We all know that √2 is
... The field F , equipped with the metric from a norm on F , becomes a metric space, and hence also a topological space, so that we may consider such concepts as convergence of sequences and continuous functions on F . If F has more than one norm, this will lead to different metrics and (in general) di ...
... The field F , equipped with the metric from a norm on F , becomes a metric space, and hence also a topological space, so that we may consider such concepts as convergence of sequences and continuous functions on F . If F has more than one norm, this will lead to different metrics and (in general) di ...