5th GRADE MATH STUDY GUIDE – unit 1
... I can explain how place value is related to addition and subtraction of decimals; e.g., 0.2 + 0.14; the two tenths is added to the one tenth because they are both tenths. Example – When adding and subtracting decimal numbers the decimal point and place values must be lined up vertically. ...
... I can explain how place value is related to addition and subtraction of decimals; e.g., 0.2 + 0.14; the two tenths is added to the one tenth because they are both tenths. Example – When adding and subtracting decimal numbers the decimal point and place values must be lined up vertically. ...
Honors Pre-Calculus
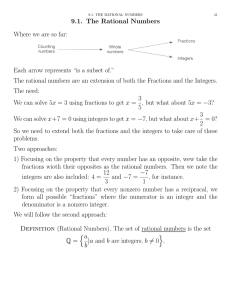
... • A numerical set is said to be closed under a given operation if when that operation is performed on any element in the set the result of that operation is in that set. • For example {x|x is even} is closed under addition because an even number plus an even number is even. • {x|x is odd} is not clo ...
... • A numerical set is said to be closed under a given operation if when that operation is performed on any element in the set the result of that operation is in that set. • For example {x|x is even} is closed under addition because an even number plus an even number is even. • {x|x is odd} is not clo ...
9. Factors and Multiples E
... 4 Find the HCF of these pairs of numbers. a 8 and 10 b 6 and 15 c 18 and 30 d 7 and 29 e What can you say about the numbers in part d? 5 True or false? Explain your answers. a The smallest factor of any number is 1. b All numbers except 1 have an even number of factors. c Any multiple of 8 is also a ...
... 4 Find the HCF of these pairs of numbers. a 8 and 10 b 6 and 15 c 18 and 30 d 7 and 29 e What can you say about the numbers in part d? 5 True or false? Explain your answers. a The smallest factor of any number is 1. b All numbers except 1 have an even number of factors. c Any multiple of 8 is also a ...
Types of Numbers, Skip Counting, and Factoring
... is the number being multiplied by itself. For example, 5 x 5 = 25. In this case, 25 is a perfect square and 5 is the square root of 25. ...
... is the number being multiplied by itself. For example, 5 x 5 = 25. In this case, 25 is a perfect square and 5 is the square root of 25. ...
computer applications - IndiaStudyChannel.com
... 7. Accept the names of 'n' animals in a one dimentional array. Sort these animals alphabetically using the Bubble Sort technique only. [Eg: If inputs= Cow, Cockroach, Crow, Cat, Camel, Calf, Centipede. outputs= Calf, Camel, Cat, Centipede, Cockroach, Cow, Crow.] [15] 8. Use a constructor to accept a ...
... 7. Accept the names of 'n' animals in a one dimentional array. Sort these animals alphabetically using the Bubble Sort technique only. [Eg: If inputs= Cow, Cockroach, Crow, Cat, Camel, Calf, Centipede. outputs= Calf, Camel, Cat, Centipede, Cockroach, Cow, Crow.] [15] 8. Use a constructor to accept a ...
Integer Explanation
... change. Which integer represents the amount of money Julie spent on clothes? Which integer represents the change Julie received? ...
... change. Which integer represents the amount of money Julie spent on clothes? Which integer represents the change Julie received? ...
Integrated Algebra B
... Practice: True or False -3 is a whole number. _______ 9 is an irrational number. _______ ...
... Practice: True or False -3 is a whole number. _______ 9 is an irrational number. _______ ...
Questions
... The sequence 9, 17, 24, 36 is one in which each term is the sum of the corresponding terms of two other sequences. The first of these is formed after the first two terms by each term being the sum of the previous two terms. The second is an arithmetic sequence (whose consecutive terms have a constan ...
... The sequence 9, 17, 24, 36 is one in which each term is the sum of the corresponding terms of two other sequences. The first of these is formed after the first two terms by each term being the sum of the previous two terms. The second is an arithmetic sequence (whose consecutive terms have a constan ...
On the number e, its irrationality, and factorials
... number of times. Therefore there can be no integers a and b for which 2 = a/b. All proofs that a number r is irrational follow this pattern of logic, called proof by contradiction: To prove that r is irrational we assume r = a/b for some integers a and b and then show (somehow) that this assumption ...
... number of times. Therefore there can be no integers a and b for which 2 = a/b. All proofs that a number r is irrational follow this pattern of logic, called proof by contradiction: To prove that r is irrational we assume r = a/b for some integers a and b and then show (somehow) that this assumption ...
A group is a non-empty set G equipped with a binary operation * that
... 4. For each a ∈ G , there is an element d ∈ G (called the inverse of a) such that a ∗ d = e = d ∗ a. A group is said to be abelian if it also satisfies 5. Commutativity: a ∗ b = b ∗ a for all a, b ∈ G . A group is said to be finite (or of finite order) if it has a finite number of elements. In this ...
... 4. For each a ∈ G , there is an element d ∈ G (called the inverse of a) such that a ∗ d = e = d ∗ a. A group is said to be abelian if it also satisfies 5. Commutativity: a ∗ b = b ∗ a for all a, b ∈ G . A group is said to be finite (or of finite order) if it has a finite number of elements. In this ...
PowerPoint Student
... left to right. Addition and Subtraction are also a pair….do in order from left to right. ...
... left to right. Addition and Subtraction are also a pair….do in order from left to right. ...
Extra Practice = Bonus Points
... *Remember, you can use any of the three methods shown in class… 1. GCF: Write down all factors of both numbers and circle the largest one they have in common. LCM: Write down multiples of the numbers, and search for the lowest they have in common. Examples: Factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12 Multip ...
... *Remember, you can use any of the three methods shown in class… 1. GCF: Write down all factors of both numbers and circle the largest one they have in common. LCM: Write down multiples of the numbers, and search for the lowest they have in common. Examples: Factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12 Multip ...
On Comprehending The Infinite in Meditation III
... infinity. The rough idea is this. An actually infinite collection has infinitely many things in it all at the same time. A potentially infinite collection is one that could be indefinitely increased. An image might help. Imagine you are walking down a road. A potentially infinite road is one that co ...
... infinity. The rough idea is this. An actually infinite collection has infinitely many things in it all at the same time. A potentially infinite collection is one that could be indefinitely increased. An image might help. Imagine you are walking down a road. A potentially infinite road is one that co ...