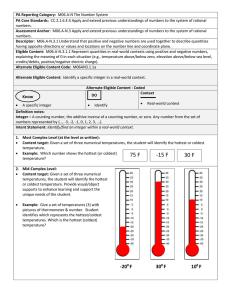
Responses: Euclid`s Algorithm
... benchmark for what a good algorithm should be because it a) always terminates at the correct answer b) is easy to perform (and automate) c) is lightning quick – as we shall see! Another vital asset of the method is that, unlike the most elementary way to find HCFs, we do not need to know the prime f ...
... benchmark for what a good algorithm should be because it a) always terminates at the correct answer b) is easy to perform (and automate) c) is lightning quick – as we shall see! Another vital asset of the method is that, unlike the most elementary way to find HCFs, we do not need to know the prime f ...
A ratio is a comparison of two numbers by division. An integer is a
... number) by the denominator (bottom number). The decimals that are formed are either terminating decimals or repeating decimals. Terminating decimals end. For example: 0.35 is a terminating decimal because it stops. Repeating decimals continue on forever with a repeating pattern. Sometimes it is one ...
... number) by the denominator (bottom number). The decimals that are formed are either terminating decimals or repeating decimals. Terminating decimals end. For example: 0.35 is a terminating decimal because it stops. Repeating decimals continue on forever with a repeating pattern. Sometimes it is one ...
Geometric Series
... We will be interested in discovering the sum of the Infinite series. In some cases the sum will actually converge to a finite number, in which case we say the series converges. Of course in other cases the series may diverge. At this point one needs to be clear of the difference between a sequence a ...
... We will be interested in discovering the sum of the Infinite series. In some cases the sum will actually converge to a finite number, in which case we say the series converges. Of course in other cases the series may diverge. At this point one needs to be clear of the difference between a sequence a ...
Calculus I - Chabot College
... 5. create mathematical models using algebraic or transcendental functions; 6. use sign graphs to solve non-linear inequalities; 7. construct a proof using mathematical induction; 8. graph using translations, reflections and distortions; 9. identify and use the trigonometric functions in problem solv ...
... 5. create mathematical models using algebraic or transcendental functions; 6. use sign graphs to solve non-linear inequalities; 7. construct a proof using mathematical induction; 8. graph using translations, reflections and distortions; 9. identify and use the trigonometric functions in problem solv ...
Roundoff Errors and Computer Arithmetic
... • The arithmetic performed by a calculator or computer is different from the arithmetic in algebra and calculus courses. • In our traditional mathematical world we permit numbers with an infinite number of digits. • The arithmetic we use in this world defines as that unique positive number that when ...
... • The arithmetic performed by a calculator or computer is different from the arithmetic in algebra and calculus courses. • In our traditional mathematical world we permit numbers with an infinite number of digits. • The arithmetic we use in this world defines as that unique positive number that when ...