06 _chapter 2
... The advantages which the soft ferrites have over other electromagnetic materials include their inherent high resistivity which results in low eddy current losses over wide frequency ranges, high magnetic permeability and stability over wide temperature ranges. For inductor cores, transformer cores a ...
... The advantages which the soft ferrites have over other electromagnetic materials include their inherent high resistivity which results in low eddy current losses over wide frequency ranges, high magnetic permeability and stability over wide temperature ranges. For inductor cores, transformer cores a ...
Fundamentals of NMR
... This two-state description is appropriate for most nuclei of biologic interest including 1H, 13C, 15N, 19F, and 31P; i.e., all those which have nuclear spin quantum number I = l/2. It is a quantum mechanical requirement that any individual nuclear spins of a nucleus with I = l/2 be in one of the tw ...
... This two-state description is appropriate for most nuclei of biologic interest including 1H, 13C, 15N, 19F, and 31P; i.e., all those which have nuclear spin quantum number I = l/2. It is a quantum mechanical requirement that any individual nuclear spins of a nucleus with I = l/2 be in one of the tw ...
Magnetic effects (PPT)
... acts on a charged particle only when the acts on a charged particle independent of the particle’s velocity. particle is in motion (F=0 if v=0), and only does the work when moving charge: if v and B do not point in the same or opposite The work, is converted into kinetic direction (sin 00 = sin ...
... acts on a charged particle only when the acts on a charged particle independent of the particle’s velocity. particle is in motion (F=0 if v=0), and only does the work when moving charge: if v and B do not point in the same or opposite The work, is converted into kinetic direction (sin 00 = sin ...
Electric dipoles and phase stability in nematic liquid crystals
... phases is a result of such interactions. Although it is now well established that the essential condition for liquid crystallinity is the anisotropy in the shape of the molecules [2] and not the presence of dipole moments, the latter are known to give rise to various phenomena in mesophases of compo ...
... phases is a result of such interactions. Although it is now well established that the essential condition for liquid crystallinity is the anisotropy in the shape of the molecules [2] and not the presence of dipole moments, the latter are known to give rise to various phenomena in mesophases of compo ...
Chapter 1 Fundamentals of NMR
... This two-state description is appropriate for most nuclei of biologic interest including 1H, 13C, 15N, 19F, and 31P; i.e., all those which have nuclear spin quantum number I = l/2. It is a quantum mechanical requirement that any individual nuclear spins of a nucleus with I = l/2 be in one of the tw ...
... This two-state description is appropriate for most nuclei of biologic interest including 1H, 13C, 15N, 19F, and 31P; i.e., all those which have nuclear spin quantum number I = l/2. It is a quantum mechanical requirement that any individual nuclear spins of a nucleus with I = l/2 be in one of the tw ...
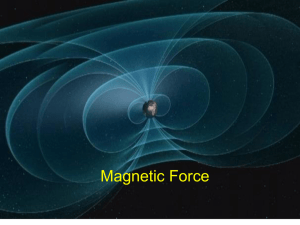
E6 MAGNETISM: FIELDS AND FORCES
... and much of the information used with computers is stored magnetically. Electric motors are driven by the magnetic force on an electric current, as are loudspeakers. The alignment of atomic nuclei in a magnetic field is the basis of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, an analytical technique of ...
... and much of the information used with computers is stored magnetically. Electric motors are driven by the magnetic force on an electric current, as are loudspeakers. The alignment of atomic nuclei in a magnetic field is the basis of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, an analytical technique of ...
AB Electronic Tubes and Quasi-Superconductivity at Room
... shown the charged tube filled by electron gas is electrically neutral, that can has a high internal pressure of the electron gas. The main property of AB electronic tube is a very low electric resistance because electrons have small friction on tube wall. (In conventional solid (metal) conductors, t ...
... shown the charged tube filled by electron gas is electrically neutral, that can has a high internal pressure of the electron gas. The main property of AB electronic tube is a very low electric resistance because electrons have small friction on tube wall. (In conventional solid (metal) conductors, t ...
Magnetism
... • Changing magnetic field can even create electric fields. • These phenomena signify an underlying unity of electricity and magnetism, which James Clerk Maxwell first described in the 19th century. • The ultimate source of any magnetic field is electric current. ...
... • Changing magnetic field can even create electric fields. • These phenomena signify an underlying unity of electricity and magnetism, which James Clerk Maxwell first described in the 19th century. • The ultimate source of any magnetic field is electric current. ...
Paper
... Much attention is paid to the sorbents possessing also magnetic properties. Magnetic sorbents in many cases are distinguished by increased absorbing capacity toward both organic and inorganic substances [8]. They are efficiently used as powder but not granules, which allows one to separate the worke ...
... Much attention is paid to the sorbents possessing also magnetic properties. Magnetic sorbents in many cases are distinguished by increased absorbing capacity toward both organic and inorganic substances [8]. They are efficiently used as powder but not granules, which allows one to separate the worke ...
final report - Cordis
... Abstract: We describe two quantum channels that individually cannot send any information, even classical, without some chance of decoding error. But together a single use of each channel can send quantum information perfectly reliably. This proves that the zero-error classical capacity exhibits supe ...
... Abstract: We describe two quantum channels that individually cannot send any information, even classical, without some chance of decoding error. But together a single use of each channel can send quantum information perfectly reliably. This proves that the zero-error classical capacity exhibits supe ...
Introduction to Materials
... properties. Semiconductors are mainly used for applications in electronics due to their electronic structure. Ceramics, because of their very high fusion points, low density, the nature of covalent and/or ionic chemical bonds, and mechanical properties, will have a widely varying range of applicatio ...
... properties. Semiconductors are mainly used for applications in electronics due to their electronic structure. Ceramics, because of their very high fusion points, low density, the nature of covalent and/or ionic chemical bonds, and mechanical properties, will have a widely varying range of applicatio ...
Introductory Physics
... The use of bilingual word-to-word dictionaries was allowed for current and former English language learner students only, during both Introductory Physics test sessions. No other reference tools or materials were allowed. ...
... The use of bilingual word-to-word dictionaries was allowed for current and former English language learner students only, during both Introductory Physics test sessions. No other reference tools or materials were allowed. ...
Quantum Mechanics in Three Dimensions
... EXAMPLE 8.2 The Second Excited State Determine the wavefunctions and energy for the second excited level of a particle in a cubic box of edge L. What is the degeneracy of this level? Solution The second excited level corresponds to the three combinations of quantum numbers n 1 ⫽ 2, ...
... EXAMPLE 8.2 The Second Excited State Determine the wavefunctions and energy for the second excited level of a particle in a cubic box of edge L. What is the degeneracy of this level? Solution The second excited level corresponds to the three combinations of quantum numbers n 1 ⫽ 2, ...
MAGNETIC MATERIALS
... is caused by electron orbiting and electron spin. The alignment can be destroyed by thermal agitation, and the ferromagnetism indeed disappears when the temperature exceeds a critical value known as the Curie point. In contrast to dielectric properties which are in most cases linear in the sense tha ...
... is caused by electron orbiting and electron spin. The alignment can be destroyed by thermal agitation, and the ferromagnetism indeed disappears when the temperature exceeds a critical value known as the Curie point. In contrast to dielectric properties which are in most cases linear in the sense tha ...
HSC 2007 - Board of Studies
... How has our understanding of time been influenced by the discovery of the constancy of the speed of light? ...
... How has our understanding of time been influenced by the discovery of the constancy of the speed of light? ...
Electron acoustic solitons in the presence of an electron beam and
... amplitude electron-acoustic solitary potentials in a plasma having stationary ions, cold inertial electrons and hot superthermal electrons. They found that as spectral index κ decreases, soliton amplitude increases while its width narrows down. Sahu (2010) studied the existence of small amplitude el ...
... amplitude electron-acoustic solitary potentials in a plasma having stationary ions, cold inertial electrons and hot superthermal electrons. They found that as spectral index κ decreases, soliton amplitude increases while its width narrows down. Sahu (2010) studied the existence of small amplitude el ...
Condensed matter physics

Condensed matter physics is a branch of physics that deals with the physical properties of condensed phases of matter. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by using physical laws. In particular, these include the laws of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism and statistical mechanics.The most familiar condensed phases are solids and liquids, while more exotic condensed phases include the superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at low temperature, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic phases of spins on atomic lattices, and the Bose–Einstein condensate found in cold atomic systems. The study of condensed matter physics involves measuring various material properties via experimental probes along with using techniques of theoretical physics to develop mathematical models that help in understanding physical behavior.The diversity of systems and phenomena available for study makes condensed matter physics the most active field of contemporary physics: one third of all American physicists identify themselves as condensed matter physicists, and the Division of Condensed Matter Physics is the largest division at the American Physical Society. The field overlaps with chemistry, materials science, and nanotechnology, and relates closely to atomic physics and biophysics. Theoretical condensed matter physics shares important concepts and techniques with theoretical particle and nuclear physics.A variety of topics in physics such as crystallography, metallurgy, elasticity, magnetism, etc., were treated as distinct areas, until the 1940s when they were grouped together as solid state physics. Around the 1960s, the study of physical properties of liquids was added to this list, forming the basis for the new, related specialty of condensed matter physics. According to physicist Phil Anderson, the term was coined by him and Volker Heine when they changed the name of their group at the Cavendish Laboratories, Cambridge from ""Solid state theory"" to ""Theory of Condensed Matter"" in 1967, as they felt it did not exclude their interests in the study of liquids, nuclear matter and so on. Although Anderson and Heine helped popularize the name ""condensed matter"", it had been present in Europe for some years, most prominently in the form of a journal published in English, French, and German by Springer-Verlag titled Physics of Condensed Matter, which was launched in 1963. The funding environment and Cold War politics of the 1960s and 1970s were also factors that lead some physicists to prefer the name ""condensed matter physics"", which emphasized the commonality of scientific problems encountered by physicists working on solids, liquids, plasmas, and other complex matter, over ""solid state physics"", which was often associated with the industrial applications of metals and semiconductors. The Bell Telephone Laboratories was one of the first institutes to conduct a research program in condensed matter physics.References to ""condensed"" state can be traced to earlier sources. For example, in the introduction to his 1947 ""Kinetic theory of liquids"" book, Yakov Frenkel proposed that ""The kinetic theory of liquids must accordingly be developed as a generalization and extension of the kinetic theory of solid bodies"". As a matter of fact, it would be more correct to unify them under the title of ""condensed bodies"".