Chapter 4
... We can show this on different line spectrum or lineemission spectrum. Each of the colored lines is produced by light of a different wavelength. ...
... We can show this on different line spectrum or lineemission spectrum. Each of the colored lines is produced by light of a different wavelength. ...
DO PHYSICS ONLINE JJ THOMPSON`S e/m EXPERIMENT
... Even though Thompson used several different gases in his tube and different metals for his electrodes, he found a consistent value for the e/me ratio. From this observation he argued that there was only one type of electron which must be contained in all atoms. The basic research into electrical di ...
... Even though Thompson used several different gases in his tube and different metals for his electrodes, he found a consistent value for the e/me ratio. From this observation he argued that there was only one type of electron which must be contained in all atoms. The basic research into electrical di ...
Study Guide Matter: Building Blocks of the Universe
... You should be prepared to answer questions on these topics. * Know the key people in the history of the atom and their contribution to our understanding of the atom. These should be in your lab book conclusion for shoe box atoms. * Know the atomic particles: electron, neutron, and proton. where are ...
... You should be prepared to answer questions on these topics. * Know the key people in the history of the atom and their contribution to our understanding of the atom. These should be in your lab book conclusion for shoe box atoms. * Know the atomic particles: electron, neutron, and proton. where are ...
CHAPTER 3: The Experimental Basis of Quantum
... Discovery of the X-Ray and the Electron Determination of Electron Charge ...
... Discovery of the X-Ray and the Electron Determination of Electron Charge ...
Introductory Physics for Biological Sciences B (3l, 3p) 2017
... The topics covered in this module, including waves, sound, temperature, gas laws, heat, electricity, magnetism, radioactivity, measurement and uncertainty, have been chosen to provide students with an understanding of basic physics principles, and skills in problem solving, scientific reasoning, mea ...
... The topics covered in this module, including waves, sound, temperature, gas laws, heat, electricity, magnetism, radioactivity, measurement and uncertainty, have been chosen to provide students with an understanding of basic physics principles, and skills in problem solving, scientific reasoning, mea ...
Primary electrons make random elastic and inelastic collision either
... emission of X-ray photon, and it would be all possible energy up to E0… Secondary electron, (<50 eV, normally around 2-6 eV, larger than sample’s work function) excitations result to loose bound valence electrons, which are promoted from the valence band to the conduction band in insulators and semi ...
... emission of X-ray photon, and it would be all possible energy up to E0… Secondary electron, (<50 eV, normally around 2-6 eV, larger than sample’s work function) excitations result to loose bound valence electrons, which are promoted from the valence band to the conduction band in insulators and semi ...
unit - i principles of dynamics (9)
... In many of today's most interesting materials strong interactions prevail upon the magnetic moments, the electrons and the underlying crystal structure, often forming strong links between these different aspects of the system. Such materials can exhibit exciting physical phenomena whose description ...
... In many of today's most interesting materials strong interactions prevail upon the magnetic moments, the electrons and the underlying crystal structure, often forming strong links between these different aspects of the system. Such materials can exhibit exciting physical phenomena whose description ...
CH 1-PHYSICAL WORLD
... Optics- deals with the phenomena of light and explains working of mirrors, lenses, microscopes and telescopes. Thermodynamics- Deals with heat and its relationship with other forms of energy and work. 2) Quantum physics deals with microscopic phenomena. In quantum physics, mass and energy are not co ...
... Optics- deals with the phenomena of light and explains working of mirrors, lenses, microscopes and telescopes. Thermodynamics- Deals with heat and its relationship with other forms of energy and work. 2) Quantum physics deals with microscopic phenomena. In quantum physics, mass and energy are not co ...
Lecture 6 – Bloch`s theorem
... happen - but does not need to happen - if Z is even. If Z is odd, there are always partially filled bands and a Fermi surface is formed. If the material has a Fermi surface, it also has metallic properties. • Density of states The density of states of the system with a periodic potential can be divi ...
... happen - but does not need to happen - if Z is even. If Z is odd, there are always partially filled bands and a Fermi surface is formed. If the material has a Fermi surface, it also has metallic properties. • Density of states The density of states of the system with a periodic potential can be divi ...
Properties of magnetic materials
... the electron and (ii) the electron orbiting the nucleus of the atom. ...
... the electron and (ii) the electron orbiting the nucleus of the atom. ...
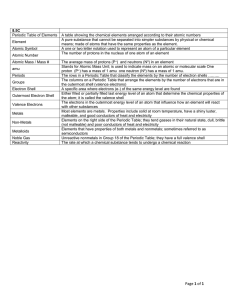
8.5C Vocabulary
... The columns on a Periodic Table that arrange the elements by the number of electrons that are in the outermost shell (valence electrons) A specific area where electrons (e-) of the same energy level are found Either filled or partially filled last energy level of an atom that determine the chemical ...
... The columns on a Periodic Table that arrange the elements by the number of electrons that are in the outermost shell (valence electrons) A specific area where electrons (e-) of the same energy level are found Either filled or partially filled last energy level of an atom that determine the chemical ...
The Electrical Conductivity of a Partially Ionized Argon
... plasma. The distribution function is expanded according to LAGUERRE polynomials up to the order of 3 . In this order the electrical conductivity of a LORENTZ gas, which is known exactly, is obtained to an accuracy of roughly 5%. The approximation tested in this way was then used to calculate the con ...
... plasma. The distribution function is expanded according to LAGUERRE polynomials up to the order of 3 . In this order the electrical conductivity of a LORENTZ gas, which is known exactly, is obtained to an accuracy of roughly 5%. The approximation tested in this way was then used to calculate the con ...
Notes-17
... electrons, higher order EM transitions can occur. They are called E2, E3,.. M1, M2.., so on, or electric multipole and magnetic multipole transitions. By going beyond the first-order perturbation theory, one can also have multi-photon transitions. For example, the 1s-2s transition in atomic hydrogen ...
... electrons, higher order EM transitions can occur. They are called E2, E3,.. M1, M2.., so on, or electric multipole and magnetic multipole transitions. By going beyond the first-order perturbation theory, one can also have multi-photon transitions. For example, the 1s-2s transition in atomic hydrogen ...
File - SCIS PHYSICS
... The magnetic deflection is given by φ = Bel/mv The magnetic field was varied until the magnetic and electric deflections were the same, when Θ = φ and Eel/mv2= Bel/mv. This can be simplified to give m/e = B2l/HΘ. The electric deflection was measured separately to give Θ and H, F and l were k ...
... The magnetic deflection is given by φ = Bel/mv The magnetic field was varied until the magnetic and electric deflections were the same, when Θ = φ and Eel/mv2= Bel/mv. This can be simplified to give m/e = B2l/HΘ. The electric deflection was measured separately to give Θ and H, F and l were k ...
here
... p = 1/3 n vm < c2 >; temperature defined by pVm = RT; p = n vkT. (see 9.3) The Avogadro constant [see 2(b)]. A simplified treatment (e.g. particles in a rectangular box with statistics treated by dividing the molecules into three groups) will suffice. The assumptions for ideal gas behaviour and thei ...
... p = 1/3 n vm < c2 >; temperature defined by pVm = RT; p = n vkT. (see 9.3) The Avogadro constant [see 2(b)]. A simplified treatment (e.g. particles in a rectangular box with statistics treated by dividing the molecules into three groups) will suffice. The assumptions for ideal gas behaviour and thei ...
Condensed matter physics

Condensed matter physics is a branch of physics that deals with the physical properties of condensed phases of matter. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by using physical laws. In particular, these include the laws of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism and statistical mechanics.The most familiar condensed phases are solids and liquids, while more exotic condensed phases include the superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at low temperature, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic phases of spins on atomic lattices, and the Bose–Einstein condensate found in cold atomic systems. The study of condensed matter physics involves measuring various material properties via experimental probes along with using techniques of theoretical physics to develop mathematical models that help in understanding physical behavior.The diversity of systems and phenomena available for study makes condensed matter physics the most active field of contemporary physics: one third of all American physicists identify themselves as condensed matter physicists, and the Division of Condensed Matter Physics is the largest division at the American Physical Society. The field overlaps with chemistry, materials science, and nanotechnology, and relates closely to atomic physics and biophysics. Theoretical condensed matter physics shares important concepts and techniques with theoretical particle and nuclear physics.A variety of topics in physics such as crystallography, metallurgy, elasticity, magnetism, etc., were treated as distinct areas, until the 1940s when they were grouped together as solid state physics. Around the 1960s, the study of physical properties of liquids was added to this list, forming the basis for the new, related specialty of condensed matter physics. According to physicist Phil Anderson, the term was coined by him and Volker Heine when they changed the name of their group at the Cavendish Laboratories, Cambridge from ""Solid state theory"" to ""Theory of Condensed Matter"" in 1967, as they felt it did not exclude their interests in the study of liquids, nuclear matter and so on. Although Anderson and Heine helped popularize the name ""condensed matter"", it had been present in Europe for some years, most prominently in the form of a journal published in English, French, and German by Springer-Verlag titled Physics of Condensed Matter, which was launched in 1963. The funding environment and Cold War politics of the 1960s and 1970s were also factors that lead some physicists to prefer the name ""condensed matter physics"", which emphasized the commonality of scientific problems encountered by physicists working on solids, liquids, plasmas, and other complex matter, over ""solid state physics"", which was often associated with the industrial applications of metals and semiconductors. The Bell Telephone Laboratories was one of the first institutes to conduct a research program in condensed matter physics.References to ""condensed"" state can be traced to earlier sources. For example, in the introduction to his 1947 ""Kinetic theory of liquids"" book, Yakov Frenkel proposed that ""The kinetic theory of liquids must accordingly be developed as a generalization and extension of the kinetic theory of solid bodies"". As a matter of fact, it would be more correct to unify them under the title of ""condensed bodies"".