A Study of Electric Breakdown Theory to Model Dielectric Surface
... SEEA involves the high electric field stresses felt at the cathode causing field emission of electrons from the “triple junction” between the insulator, cathode, and air (gas) surroundings. Some electrons travel outwards into the gas, but some travel along the surface colliding with it. By an elasti ...
... SEEA involves the high electric field stresses felt at the cathode causing field emission of electrons from the “triple junction” between the insulator, cathode, and air (gas) surroundings. Some electrons travel outwards into the gas, but some travel along the surface colliding with it. By an elasti ...
Heros in EM wave history
... death, named Terrella. In his book named [ About a magnet] the element of the terrestrial magnetism were defined coition , direction , variation , declination , revolution . People are calling the element of the terrestrial magnetism to such name in today. Electricity of the ancient constructed als ...
... death, named Terrella. In his book named [ About a magnet] the element of the terrestrial magnetism were defined coition , direction , variation , declination , revolution . People are calling the element of the terrestrial magnetism to such name in today. Electricity of the ancient constructed als ...
PHY481 - Lecture 17: Magnets field lines, North and South. Lorentz
... magnetic North pole is actually about 11.3 degrees from the geographic South pole. The magnitude of the earths field at the earths surface is around 30 − 60µT . In the past couple of years there have been exciting research developments in magnetostatics with the discovery of solid state magnetic mat ...
... magnetic North pole is actually about 11.3 degrees from the geographic South pole. The magnitude of the earths field at the earths surface is around 30 − 60µT . In the past couple of years there have been exciting research developments in magnetostatics with the discovery of solid state magnetic mat ...
Document
... Review Example 2: Wire in Earth’s B Field A wire carries a current of 22 A from east to west. Assume that at this location the magnetic field of the earth is horizontal and directed from south to north, and has a magnitude of 0.50 x 10-4 T. Find the magnetic force on a 36-m length of wire. What hap ...
... Review Example 2: Wire in Earth’s B Field A wire carries a current of 22 A from east to west. Assume that at this location the magnetic field of the earth is horizontal and directed from south to north, and has a magnitude of 0.50 x 10-4 T. Find the magnetic force on a 36-m length of wire. What hap ...
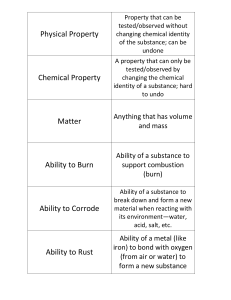
Physical Property
... A property that can only be tested/observed by changing the chemical identity of a substance; hard to undo ...
... A property that can only be tested/observed by changing the chemical identity of a substance; hard to undo ...
Document
... An electron in a television picture tube moves toward the front of the tube with a speed of 8.0 x 106 m/s along the x axis. Surrounding the neck of the tube are coils of wire that create a magnetic field of magnitude 0.025 T, directed at an angle of 60 to the x axis and lying in the xy plane. Calcu ...
... An electron in a television picture tube moves toward the front of the tube with a speed of 8.0 x 106 m/s along the x axis. Surrounding the neck of the tube are coils of wire that create a magnetic field of magnitude 0.025 T, directed at an angle of 60 to the x axis and lying in the xy plane. Calcu ...
Magnetic field dependence of sputtering magnetron
... principal result) is probably predicted with enough accuracy, provided that B,,,)104 6. We summarize with two criteria for magnetron design. First, for designs of different sizes but the same proportions, a larger magnetron should have magnets with a weaker magnetization. This will provide a weaker ...
... principal result) is probably predicted with enough accuracy, provided that B,,,)104 6. We summarize with two criteria for magnetron design. First, for designs of different sizes but the same proportions, a larger magnetron should have magnets with a weaker magnetization. This will provide a weaker ...
Chemistry Note PowerPoint
... • An atom’s valance electrons are those that have the highest energy levels and are held most loosely. • The number of valance electrons determine many properties of that element, including the ways in which the atom combines with other atoms ...
... • An atom’s valance electrons are those that have the highest energy levels and are held most loosely. • The number of valance electrons determine many properties of that element, including the ways in which the atom combines with other atoms ...
the bohr-sommerfeld model of the atom
... 4a. Overview. The Bohr model can be applied to two-particle atomic systems other than atomic hydrogen. For example, it can be applied to any hydrogen-like ion that consists of a single electron orbiting a nucleus containing more than one proton. Such a system is obtained by ionizing (removing) all b ...
... 4a. Overview. The Bohr model can be applied to two-particle atomic systems other than atomic hydrogen. For example, it can be applied to any hydrogen-like ion that consists of a single electron orbiting a nucleus containing more than one proton. Such a system is obtained by ionizing (removing) all b ...
Magnetic Field Lines
... Guided notes on magnetic fields. A magnetic field is the area around a magnetic object with which the force of magnetism acts. Also define a magnetic force. A magnetic force is the force between magnetic poles. Magnetism Lab – It is your choice if you do this as a demonstration or put stu ...
... Guided notes on magnetic fields. A magnetic field is the area around a magnetic object with which the force of magnetism acts. Also define a magnetic force. A magnetic force is the force between magnetic poles. Magnetism Lab – It is your choice if you do this as a demonstration or put stu ...
Communication: Evidence of hydrated electrons injected by a
... n . Recent photophysics studies suggest that in water the electrons can be added in localized electronic states (one electron in a type s state or one electron in nearly three-fold degenerate type p state) or injected into the conduction band of the water, delocalized on hundreds of molecules in the ...
... n . Recent photophysics studies suggest that in water the electrons can be added in localized electronic states (one electron in a type s state or one electron in nearly three-fold degenerate type p state) or injected into the conduction band of the water, delocalized on hundreds of molecules in the ...
challenges in detecting crystalline phase in an amorphous
... specificity of new drug candidates are improving, the solubility is often becoming extremely poor. This can result in poor bioavailability of the active pharmaceutical ingridient (API), unless basic characteristics of the APl are altered. One way to achieve the alteration is to stabilize the API in ...
... specificity of new drug candidates are improving, the solubility is often becoming extremely poor. This can result in poor bioavailability of the active pharmaceutical ingridient (API), unless basic characteristics of the APl are altered. One way to achieve the alteration is to stabilize the API in ...
vacuum particle creation in strong fields as the field induced phase
... We have obtained on nonperturbative basis the kinetic equation for describing the electron-hole excitations in graphene under the action of a spatially homogeneous electric field with an arbitrary time dependence and polarization. This is done by analogy with the well developed case o D = 3 + 1 QED ...
... We have obtained on nonperturbative basis the kinetic equation for describing the electron-hole excitations in graphene under the action of a spatially homogeneous electric field with an arbitrary time dependence and polarization. This is done by analogy with the well developed case o D = 3 + 1 QED ...
the magnetic field the electric field
... It is perpendicular to the magnetic field and the wire. Instead the verse is given by the right hand rule. • When B is perpendicular the magnetic force is maximum. • When B is inclined, B is lower. • When B is parallel to the wire,the magnetic force is zero. ...
... It is perpendicular to the magnetic field and the wire. Instead the verse is given by the right hand rule. • When B is perpendicular the magnetic force is maximum. • When B is inclined, B is lower. • When B is parallel to the wire,the magnetic force is zero. ...
Notes - Organization of Matter
... • Compounds are pure substances that are composed of two or more atoms that are chemically combined • Compounds can only be changed into simpler substances called elements by chemical changes ...
... • Compounds are pure substances that are composed of two or more atoms that are chemically combined • Compounds can only be changed into simpler substances called elements by chemical changes ...
Lecture 9 NMR 2
... Hext : external magnetic field Hlocal: local field induced by the external field Hlocal: Electrons in a chemical bond are considered to be in motion and are charged. This induces a local magnetic field which can shield (oppose) or deshield (enhance) the magnetic field experienced by the nucleus. Sin ...
... Hext : external magnetic field Hlocal: local field induced by the external field Hlocal: Electrons in a chemical bond are considered to be in motion and are charged. This induces a local magnetic field which can shield (oppose) or deshield (enhance) the magnetic field experienced by the nucleus. Sin ...
Chapter Summary
... Answer to Essential Question 19.8: This situation involves much of what we learned in this chapter. First, what is the connection between all this information? We can connect everything via the magnetic field. With the information about the electron, we can use equation 19.4 to solve for the magneti ...
... Answer to Essential Question 19.8: This situation involves much of what we learned in this chapter. First, what is the connection between all this information? We can connect everything via the magnetic field. With the information about the electron, we can use equation 19.4 to solve for the magneti ...
Condensed matter physics

Condensed matter physics is a branch of physics that deals with the physical properties of condensed phases of matter. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by using physical laws. In particular, these include the laws of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism and statistical mechanics.The most familiar condensed phases are solids and liquids, while more exotic condensed phases include the superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at low temperature, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic phases of spins on atomic lattices, and the Bose–Einstein condensate found in cold atomic systems. The study of condensed matter physics involves measuring various material properties via experimental probes along with using techniques of theoretical physics to develop mathematical models that help in understanding physical behavior.The diversity of systems and phenomena available for study makes condensed matter physics the most active field of contemporary physics: one third of all American physicists identify themselves as condensed matter physicists, and the Division of Condensed Matter Physics is the largest division at the American Physical Society. The field overlaps with chemistry, materials science, and nanotechnology, and relates closely to atomic physics and biophysics. Theoretical condensed matter physics shares important concepts and techniques with theoretical particle and nuclear physics.A variety of topics in physics such as crystallography, metallurgy, elasticity, magnetism, etc., were treated as distinct areas, until the 1940s when they were grouped together as solid state physics. Around the 1960s, the study of physical properties of liquids was added to this list, forming the basis for the new, related specialty of condensed matter physics. According to physicist Phil Anderson, the term was coined by him and Volker Heine when they changed the name of their group at the Cavendish Laboratories, Cambridge from ""Solid state theory"" to ""Theory of Condensed Matter"" in 1967, as they felt it did not exclude their interests in the study of liquids, nuclear matter and so on. Although Anderson and Heine helped popularize the name ""condensed matter"", it had been present in Europe for some years, most prominently in the form of a journal published in English, French, and German by Springer-Verlag titled Physics of Condensed Matter, which was launched in 1963. The funding environment and Cold War politics of the 1960s and 1970s were also factors that lead some physicists to prefer the name ""condensed matter physics"", which emphasized the commonality of scientific problems encountered by physicists working on solids, liquids, plasmas, and other complex matter, over ""solid state physics"", which was often associated with the industrial applications of metals and semiconductors. The Bell Telephone Laboratories was one of the first institutes to conduct a research program in condensed matter physics.References to ""condensed"" state can be traced to earlier sources. For example, in the introduction to his 1947 ""Kinetic theory of liquids"" book, Yakov Frenkel proposed that ""The kinetic theory of liquids must accordingly be developed as a generalization and extension of the kinetic theory of solid bodies"". As a matter of fact, it would be more correct to unify them under the title of ""condensed bodies"".