The-Cosmic-Perspective-Media-Update-with
... 37) All of the following statements are true. Which one explains the reason why there is not a solar eclipse at every new Moon? A) The nodes of the Moon's orbit precess with an 18-year period. B) The orbital plane of the Moon is tilted by about 5° to the ecliptic plane. C) The Moon rotates synchron ...
... 37) All of the following statements are true. Which one explains the reason why there is not a solar eclipse at every new Moon? A) The nodes of the Moon's orbit precess with an 18-year period. B) The orbital plane of the Moon is tilted by about 5° to the ecliptic plane. C) The Moon rotates synchron ...
Finding habitable earths around white dwarfs with a robotic
... life during which its luminosity is nearly constant: that of a white dwarf. Figure 1a shows the luminosity of a star slightly more massive than our Sun versus time: a comparable amount of time is spent in the main sequence phase as the white dwarf phase, and the rate of change of luminosity is gradu ...
... life during which its luminosity is nearly constant: that of a white dwarf. Figure 1a shows the luminosity of a star slightly more massive than our Sun versus time: a comparable amount of time is spent in the main sequence phase as the white dwarf phase, and the rate of change of luminosity is gradu ...
SUN, MOON, AND PLANETS Overview
... (Mercury and Venus), and five are in orbits outside Earth’s orbit (Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune). These eight planets and the Sun are the major players in the solar system. The Sun is a star. In a dark location on a clear night, scores of other stars can be seen shining in the sky. The ...
... (Mercury and Venus), and five are in orbits outside Earth’s orbit (Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune). These eight planets and the Sun are the major players in the solar system. The Sun is a star. In a dark location on a clear night, scores of other stars can be seen shining in the sky. The ...
1 We finished our last lecture by examining the “Jovian planets” of
... Kuiper Belt – and so different from the terrestrial and Jovian planets – only a few astronomers (mostly those associated with their discovery!) really suggested thinking of them as “planets”.. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Kuiper Belt – and so different from the terrestrial and Jovian planets – only a few astronomers (mostly those associated with their discovery!) really suggested thinking of them as “planets”.. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
The Time of Perihelion Passage and the Longitude of Perihelion of
... perturbations have been detected. This can be explained if Nemesis is comprised of two stars with complementary orbits such that their perturbing accelerations tend to cancel at the Sun. If these orbits are also inclined by 90° to the ecliptic plane, the planet orbit perturbations could have been mi ...
... perturbations have been detected. This can be explained if Nemesis is comprised of two stars with complementary orbits such that their perturbing accelerations tend to cancel at the Sun. If these orbits are also inclined by 90° to the ecliptic plane, the planet orbit perturbations could have been mi ...
Preview Sample 3
... 7) If Earth's axis had no tilt, would we still have seasons? Why or why not? Answer: We would no longer have seasons, because the Sun's light would hit at the same angle all throughout the year, depending only on where you lived. The slight change in distance between Earth and the Sun during the yea ...
... 7) If Earth's axis had no tilt, would we still have seasons? Why or why not? Answer: We would no longer have seasons, because the Sun's light would hit at the same angle all throughout the year, depending only on where you lived. The slight change in distance between Earth and the Sun during the yea ...
Sample
... 7) If Earth's axis had no tilt, would we still have seasons? Why or why not? Answer: We would no longer have seasons, because the Sun's light would hit at the same angle all throughout the year, depending only on where you lived. The slight change in distance between Earth and the Sun during the yea ...
... 7) If Earth's axis had no tilt, would we still have seasons? Why or why not? Answer: We would no longer have seasons, because the Sun's light would hit at the same angle all throughout the year, depending only on where you lived. The slight change in distance between Earth and the Sun during the yea ...
Signatures of Planets in Protoplanetary and Debris
... We now discuss observable quantities under the assumption that the disk is seen face-on since this orientation allows a direct view on the planetary region. The thermal dust reemission of circumstellar disks can be mapped with (sub) millimeter observations and it has been performed successfully for ...
... We now discuss observable quantities under the assumption that the disk is seen face-on since this orientation allows a direct view on the planetary region. The thermal dust reemission of circumstellar disks can be mapped with (sub) millimeter observations and it has been performed successfully for ...
The Night Sky - University of Saskatchewan
... of this unit because the Dëne translation of “the night sky” is seldom used in La Loche and the word happens to sound similar to the Dëne word for “lice.” The English word “astronomy” relates singularly to the context of Western science. The English title of this unit, “The Night Sky,” seems to be a ...
... of this unit because the Dëne translation of “the night sky” is seldom used in La Loche and the word happens to sound similar to the Dëne word for “lice.” The English word “astronomy” relates singularly to the context of Western science. The English title of this unit, “The Night Sky,” seems to be a ...
Word Document - Montana State University
... Students plot and analyze NASA data to determine the period of an invisible planet orbiting a wobbling star. In this three-part guided inquiry activity, students first explore the motion of a two-body system around a center of mass to better understand how extra-solar planets are discovered. Student ...
... Students plot and analyze NASA data to determine the period of an invisible planet orbiting a wobbling star. In this three-part guided inquiry activity, students first explore the motion of a two-body system around a center of mass to better understand how extra-solar planets are discovered. Student ...
The Little Star That Could - Challenger Learning Center
... The Earth is the third planet from the Sun in a system that includes the Moon, the Sun, eight other planets and their moons, and smaller objects, such as asteroids and comets. The Sun, an average star, is the central and largest body in the Solar System. (5 – 8 Standard) ...
... The Earth is the third planet from the Sun in a system that includes the Moon, the Sun, eight other planets and their moons, and smaller objects, such as asteroids and comets. The Sun, an average star, is the central and largest body in the Solar System. (5 – 8 Standard) ...
Geometry of orbits - Harpursville Middle School
... Chunks of rock and metal that circle the sun Range in size from hundreds of km to mm Most are in a belt between Mars and Jupiter Rarely cross Earth’s orbit May have caused the extinction of dinosaurs ...
... Chunks of rock and metal that circle the sun Range in size from hundreds of km to mm Most are in a belt between Mars and Jupiter Rarely cross Earth’s orbit May have caused the extinction of dinosaurs ...
Pattern Recognition in Physics The complex planetary
... (1) the orbit of every planet is an ellipse (instead of Copernicus’ perfect cycles) with the Sun at one of the two foci (instead of being in the center of the cycle), (2) a line joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas during equal intervals of time, and (3) the square of the orbital peri ...
... (1) the orbit of every planet is an ellipse (instead of Copernicus’ perfect cycles) with the Sun at one of the two foci (instead of being in the center of the cycle), (2) a line joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas during equal intervals of time, and (3) the square of the orbital peri ...
The Moon
... brightness is the result of the planet blocking some of the starlight when it is between Ogle-Tr-3 and Earth. This observation allowed scientists to find not only the planet, but also to determine the planet’s mass and density The mass has been calculated to be approximately 159 times the mass of Ea ...
... brightness is the result of the planet blocking some of the starlight when it is between Ogle-Tr-3 and Earth. This observation allowed scientists to find not only the planet, but also to determine the planet’s mass and density The mass has been calculated to be approximately 159 times the mass of Ea ...
THe SCieNCe OF ASTrONOMY
... lunar calendar has 12 months, with some months lasting 29 days and others lasting 30 days; the lengths are chosen to make the average agree with the approximately 2912 -day lunar cycle. A 12-month lunar calendar therefore has only 354 or 355 days, or about 11 days fewer than a calendar based on the ...
... lunar calendar has 12 months, with some months lasting 29 days and others lasting 30 days; the lengths are chosen to make the average agree with the approximately 2912 -day lunar cycle. A 12-month lunar calendar therefore has only 354 or 355 days, or about 11 days fewer than a calendar based on the ...
The Moon
... brightness is the result of the planet blocking some of the starlight when it is between Ogle-Tr-3 and Earth. This observation allowed scientists to find not only the planet, but also to determine the planet’s mass and density The mass has been calculated to be approximately 159 times the mass of Ea ...
... brightness is the result of the planet blocking some of the starlight when it is between Ogle-Tr-3 and Earth. This observation allowed scientists to find not only the planet, but also to determine the planet’s mass and density The mass has been calculated to be approximately 159 times the mass of Ea ...
Astonomy-Space The Final Frontier
... Explain how Kepler’s laws allow us to construct a scale model of the solar system, and explain the technique used to determine the actual size of the planetary orbits. Be able to state Newton’s laws of gravitation and explain how they account for Kepler’s laws. Explain how the law of gravitati ...
... Explain how Kepler’s laws allow us to construct a scale model of the solar system, and explain the technique used to determine the actual size of the planetary orbits. Be able to state Newton’s laws of gravitation and explain how they account for Kepler’s laws. Explain how the law of gravitati ...
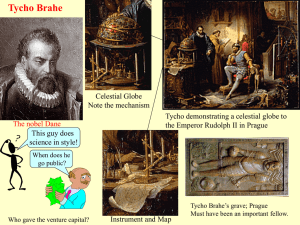
Brahe, Kepler
... ``Consecrated to the all-good, great God and Posterity. Tycho Brahe, Son of Otto, who realized that Astronomy, the oldest and most distinguished of all sciences, had indeed been studied for a long time and to a great extent, but still had not obtained sufficient firmness or had been purified of erro ...
... ``Consecrated to the all-good, great God and Posterity. Tycho Brahe, Son of Otto, who realized that Astronomy, the oldest and most distinguished of all sciences, had indeed been studied for a long time and to a great extent, but still had not obtained sufficient firmness or had been purified of erro ...
Teachers Edition Sample Chapter (1.2MB PDF)
... flashlight, which is held at the same level as the ball. Observe the Moon in each of the positions shown in Figure 2. Face the ball at each position. For each position, indicate how much of the ball is dark and how much is illuminated. Use a pencil to show the shaded region. Leave the illuminated pa ...
... flashlight, which is held at the same level as the ball. Observe the Moon in each of the positions shown in Figure 2. Face the ball at each position. For each position, indicate how much of the ball is dark and how much is illuminated. Use a pencil to show the shaded region. Leave the illuminated pa ...
Pluto Challenge - Cedar Amateur Astronomers
... the telescope’s field of view (FOV). Stars are very, very distance objects and as a result do not move within the FOV over time. However, objects within the solar system are relatively close and always in motion around the Sun. If photographs taken at different times include solar system objects suc ...
... the telescope’s field of view (FOV). Stars are very, very distance objects and as a result do not move within the FOV over time. However, objects within the solar system are relatively close and always in motion around the Sun. If photographs taken at different times include solar system objects suc ...
the gravitational force
... immeasurably small when both interacting particles are common objects such as baseballs or cars (which have masses roughly between 1 kg and 1000 kg). Furthermore, the gravitational force is utterly negligible when both particles are atoms or molecules since these have exceedingly small masses. On th ...
... immeasurably small when both interacting particles are common objects such as baseballs or cars (which have masses roughly between 1 kg and 1000 kg). Furthermore, the gravitational force is utterly negligible when both particles are atoms or molecules since these have exceedingly small masses. On th ...
Package `moonsun`
... Julian Day Number, default today name of a planet (appended to dates in result) TRUE if it is inner, FALSE if outer planet period of a planet (tropical years) longitude at epoch 1990 January 0.00 (degrees) longitude of the perihelion (degrees) eccentricity of the orbit semi-major axis of the orbit ( ...
... Julian Day Number, default today name of a planet (appended to dates in result) TRUE if it is inner, FALSE if outer planet period of a planet (tropical years) longitude at epoch 1990 January 0.00 (degrees) longitude of the perihelion (degrees) eccentricity of the orbit semi-major axis of the orbit ( ...
Astronomy and the Quran
... Aristotelian/Ptolemaic model of the universe where the earth was at the center and was surrounded by 7 spherical domes. And celestial bodies were believed to move in these spheres, or spheres themselves were believed to move in a course. The fact that the Qur’an speaks of seven heavens strongly sugg ...
... Aristotelian/Ptolemaic model of the universe where the earth was at the center and was surrounded by 7 spherical domes. And celestial bodies were believed to move in these spheres, or spheres themselves were believed to move in a course. The fact that the Qur’an speaks of seven heavens strongly sugg ...
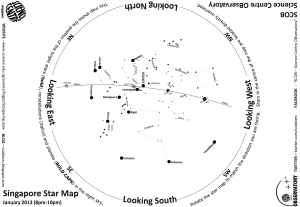
B LOG - Science Centre
... The Dipper is part of a much larger star pattern, the constellation Ursa Major (Greater Bear) although it had a variety of meanings in many cultures. Most common is that of a bear or a ladle/dipper used for scooping water. Other representations include a plough, an ox or horse pulling a plough and t ...
... The Dipper is part of a much larger star pattern, the constellation Ursa Major (Greater Bear) although it had a variety of meanings in many cultures. Most common is that of a bear or a ladle/dipper used for scooping water. Other representations include a plough, an ox or horse pulling a plough and t ...
Unit 5
... the moon more closely. In 1609, the Italian scientist Galileo Galilei heard about a telescope, a device built to observe distant objects by making them appear closer. Galileo soon made his own telescope by putting two lenses in a wooden tube. The lenses focused the light coming through the tube, mak ...
... the moon more closely. In 1609, the Italian scientist Galileo Galilei heard about a telescope, a device built to observe distant objects by making them appear closer. Galileo soon made his own telescope by putting two lenses in a wooden tube. The lenses focused the light coming through the tube, mak ...
Satellite system (astronomy)

A satellite system is a set of gravitationally bound objects in orbit around a planetary mass object or minor planet. Generally speaking, it is a set of natural satellites (moons), although such systems may also consist of bodies such as circumplanetary disks, ring systems, moonlets, minor-planet moons and artificial satellites any of which may themselves have satellite systems of their own. Some satellite systems have complex interactions with both their parent and other moons, including magnetic, tidal, atmospheric and orbital interactions such as orbital resonances and libration. Individually major satellite objects are designated in Roman numerals. Satellite systems are referred to either by the possessive adjectives of their primary (e.g. ""Jovian system""), or less commonly by the name of their primary (e.g. ""Jupiter system""). Where only one satellite is known, or it is a binary orbiting a common centre of gravity, it may be referred to using the hyphenated names of the primary and major satellite (e.g. the ""Earth-Moon system"").Many Solar System objects are known to possess satellite systems, though their origin is still unclear. Notable examples include the largest satellite system, the Jovian system, with 67 known moons (including the large Galilean moons) and the Saturnian System with 62 known moons (and the most visible ring system in the Solar System). Both satellite systems are large and diverse. In fact all of the giant planets of the Solar System possess large satellite systems as well as planetary rings, and it is inferred that this is a general pattern. Several objects farther from the Sun also have satellite systems consisting of multiple moons, including the complex Plutonian system where multiple objects orbit a common center of mass, as well as many asteroids and plutinos. Apart from the Earth-Moon system and Mars' system of two tiny natural satellites, the other terrestrial planets are generally not considered satellite systems, although some have been orbited by artificial satellites originating from Earth.Little is known of satellite systems beyond the Solar System, although it is inferred that natural satellites are common. J1407b is an example of an extrasolar satellite system. It is also theorised that Rogue planets ejected from their planetary system could retain a system of satellites.