ppt
... endpoints should be able to communicate Failures (excepting network partition) should not interfere with endpoint semantics (why?) Maintain state only at end-points ...
... endpoints should be able to communicate Failures (excepting network partition) should not interfere with endpoint semantics (why?) Maintain state only at end-points ...
William Stallings Data and Computer Communications
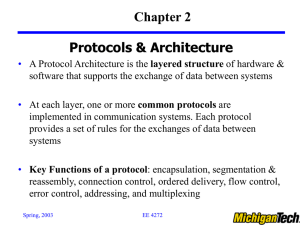
... • A Protocol Architecture is the layered structure of hardware & software that supports the exchange of data between systems • At each layer, one or more common protocols are implemented in communication systems. Each protocol provides a set of rules for the exchanges of data between systems ...
... • A Protocol Architecture is the layered structure of hardware & software that supports the exchange of data between systems • At each layer, one or more common protocols are implemented in communication systems. Each protocol provides a set of rules for the exchanges of data between systems ...
Darwin: Customizable Resource Management for Value
... Internetworking (72-80). » Multiple networks with inter-networking: networks are independent, but need some rules for interoperability » Key concepts: best effort service, “stateless” routers, decentralized control (very different from telephones!) » Basis for Internet: TCP, IP, congestion control, ...
... Internetworking (72-80). » Multiple networks with inter-networking: networks are independent, but need some rules for interoperability » Key concepts: best effort service, “stateless” routers, decentralized control (very different from telephones!) » Basis for Internet: TCP, IP, congestion control, ...
OSI Reference Model - Eastern Oregon University
... terminating network connections. Ex. File transfer – session layer establishes connection, reestablishes if lost, terminates when finished Examples include RPC’s (remote procedure calls) and NFS (Network File System) ...
... terminating network connections. Ex. File transfer – session layer establishes connection, reestablishes if lost, terminates when finished Examples include RPC’s (remote procedure calls) and NFS (Network File System) ...
Layer cake and an hourglass
... Data framing: boundaries between packets Media access control (MAC) Per-hop reliability and flow-control ...
... Data framing: boundaries between packets Media access control (MAC) Per-hop reliability and flow-control ...
Powerpoint format - Department of Computer and Information
... relationship of complex system’s pieces layered reference model for discussion modularization eases maintenance, updating of system change of implementation of layer’s service transparent to rest of system e.g., change in gate procedure doesn’t affect rest of system ...
... relationship of complex system’s pieces layered reference model for discussion modularization eases maintenance, updating of system change of implementation of layer’s service transparent to rest of system e.g., change in gate procedure doesn’t affect rest of system ...
Ans.Tutorial#2
... wrong station. In this case, however, the error detection mechanism, available in most data link protocols, will find the error and discard the frame. In both cases, the source will somehow be informed using one of the data link control mechanisms discussed in Chapter 11. 22- In Figure 2.22, assume ...
... wrong station. In this case, however, the error detection mechanism, available in most data link protocols, will find the error and discard the frame. In both cases, the source will somehow be informed using one of the data link control mechanisms discussed in Chapter 11. 22- In Figure 2.22, assume ...
NetworkingReview
... LAN, WAN, bridge, repeater, switch, router, gateway, backbone. 6. Explain the hidden terminal problem for wireless networks. What is a solution? 7. At what layer in the TCP/IP protocol hierarchy would a firewall be placed to filter messages based on a. Message content b. Source address c. Type of ap ...
... LAN, WAN, bridge, repeater, switch, router, gateway, backbone. 6. Explain the hidden terminal problem for wireless networks. What is a solution? 7. At what layer in the TCP/IP protocol hierarchy would a firewall be placed to filter messages based on a. Message content b. Source address c. Type of ap ...
The Internet
... Leased-lines from local telephone companies provide part of the network Transmit data at 1.54 megabits (Mbps) Backbone Provider – organization that supplies access to high-speed transmission lines used to connect to the Internet; some providers include: MCI, Sprint, UUNET, AGIS, BBN ...
... Leased-lines from local telephone companies provide part of the network Transmit data at 1.54 megabits (Mbps) Backbone Provider – organization that supplies access to high-speed transmission lines used to connect to the Internet; some providers include: MCI, Sprint, UUNET, AGIS, BBN ...
5 G ppt - WordPress.com
... Nano Technology :Nanotechnology is the application of nano science to control process on manometer scale. i.e. between 0.1 and100nm.The field is also known as molecular nanotechnology(MNT). It deals with control of the structure of matter based on atom-by-atom and molecule by molecule engineering. ...
... Nano Technology :Nanotechnology is the application of nano science to control process on manometer scale. i.e. between 0.1 and100nm.The field is also known as molecular nanotechnology(MNT). It deals with control of the structure of matter based on atom-by-atom and molecule by molecule engineering. ...
PDF
... at the end points of the communication system. Therefore, providing that questioned function as a feature of the communication system itself is not possible. (Sometimes an incomplete version of the function provided by the communication system may be useful as a performance enhancement.)" ...
... at the end points of the communication system. Therefore, providing that questioned function as a feature of the communication system itself is not possible. (Sometimes an incomplete version of the function provided by the communication system may be useful as a performance enhancement.)" ...
sumit_basu5QA - CIS @ Temple University
... into any network and have them travel independently to the destination. They may arrive in different order than they were sent, in which case it is the job of higher layers to rearrange them, if in-order delivery is desired. This layer defines an official packet format and protocol called IP (Intern ...
... into any network and have them travel independently to the destination. They may arrive in different order than they were sent, in which case it is the job of higher layers to rearrange them, if in-order delivery is desired. This layer defines an official packet format and protocol called IP (Intern ...
TCP, UDP, ICMP - Dr. Stephen C. Hayne
... packets may be permuted dropped packets are not retransmitted ...
... packets may be permuted dropped packets are not retransmitted ...
NETWORKING LAB -
... 4. Stick to one page, be brief! ------------------------------------------------------------------------BACKGROUND Switches are a fundamental part of most networks. They make it possible for several users to send information over a network at the same time without slowing each other down. Just like ...
... 4. Stick to one page, be brief! ------------------------------------------------------------------------BACKGROUND Switches are a fundamental part of most networks. They make it possible for several users to send information over a network at the same time without slowing each other down. Just like ...
Chapter 3: Network Protocols and Communications
... the address will be the same; only the host or device portion of the address will be different. When the sender and receiver of the IP packet are on the same network, the data link frame is sent directly to the receiving device. On an Ethernet network, the data link addresses are known as Ethernet M ...
... the address will be the same; only the host or device portion of the address will be different. When the sender and receiver of the IP packet are on the same network, the data link frame is sent directly to the receiving device. On an Ethernet network, the data link addresses are known as Ethernet M ...
Computer network
... – A phone modem converts computer data into an analog audio signal for transfer over a telephone line, and then a modem at the destination converts it back again into data – A digital subscriber line (DSL) uses regular copper phone lines to transfer digital data to and from the phone company’s ...
... – A phone modem converts computer data into an analog audio signal for transfer over a telephone line, and then a modem at the destination converts it back again into data – A digital subscriber line (DSL) uses regular copper phone lines to transfer digital data to and from the phone company’s ...
Network_Hist
... Other competing commercial providers created their own backbones and interconnections. Regional NAPs (network access points) became the primary interconnections between the many networks. The NSFNet was dropped as the main backbone, and commercial restrictions were gone. Deepanjal Shrestha (April 05 ...
... Other competing commercial providers created their own backbones and interconnections. Regional NAPs (network access points) became the primary interconnections between the many networks. The NSFNet was dropped as the main backbone, and commercial restrictions were gone. Deepanjal Shrestha (April 05 ...
Network Architectures - Computing Sciences
... • Supports packet data communication across an internetwork. • Source and Destination logical addressing, routing – IP addresses (not layer 2 MAC addressing) ...
... • Supports packet data communication across an internetwork. • Source and Destination logical addressing, routing – IP addresses (not layer 2 MAC addressing) ...
Network interface cards (NIC)
... Packet Switched Networks (Frame Relay, ATM) • Packets (messages or fragments of messages) are individually routed between nodes over data links which might be shared by many other nodes. • Packets between the same two nodes may take different routes. • Link fails or becomes unavailable, other links ...
... Packet Switched Networks (Frame Relay, ATM) • Packets (messages or fragments of messages) are individually routed between nodes over data links which might be shared by many other nodes. • Packets between the same two nodes may take different routes. • Link fails or becomes unavailable, other links ...
Internet Architecture
... Each application is effectively setting up its own network. But until now there is little work on simultaneous routing on many overlapping graphs Discovery How do applications discover and bind to a set of resources? ...
... Each application is effectively setting up its own network. But until now there is little work on simultaneous routing on many overlapping graphs Discovery How do applications discover and bind to a set of resources? ...
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA)

The Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) is a computer network architecture that unifies distributed computing and telecommunications. RINA's fundamental principle is that computer networking is just Inter-Process Communication or IPC. RINA reconstructs the overall structure of the Internet, forming a model that comprises a single repeating layer, the DIF (Distributed IPC Facility), which is the minimal set of components required to allow distributed IPC between application processes. RINA inherently supports mobility, multi-homing and Quality of Service without the need for extra mechanisms, provides a secure and programmable environment, motivates for a more competitive marketplace, and allows for a seamless adoption.