Rr.destination
... Networks in Distributed Systems Distributed System is simply a collection of components that communicate to solve a problem Why should programmers of distributed systems know about networks? ...
... Networks in Distributed Systems Distributed System is simply a collection of components that communicate to solve a problem Why should programmers of distributed systems know about networks? ...
Slides
... Networks in Distributed Systems Distributed System is simply a collection of components that communicate to solve a problem Why should programmers of distributed systems know about networks? ...
... Networks in Distributed Systems Distributed System is simply a collection of components that communicate to solve a problem Why should programmers of distributed systems know about networks? ...
Chapter 4: Network Layer
... • each packet carries VC identifier (not destination host ID) • every router on source-dest path maintains “state” for each passing connection – (in contrast, transport-layer connection only involved two end systems) ...
... • each packet carries VC identifier (not destination host ID) • every router on source-dest path maintains “state” for each passing connection – (in contrast, transport-layer connection only involved two end systems) ...
SEMESTER 1 MODULE 1
... o Each TCP segment is given a label, called a header, containing information about which processes (or services) running on the destination computer should receive the message. * What is the purpose of the layer 3 (or internet layer, or network layer) packet headers? The Internet layer: Here the ...
... o Each TCP segment is given a label, called a header, containing information about which processes (or services) running on the destination computer should receive the message. * What is the purpose of the layer 3 (or internet layer, or network layer) packet headers? The Internet layer: Here the ...
Protocols and Interaction Models for Web Services
... Performs routing of datagrams from source to destination IP implementation at router maintains an inmemory routing table; used to search for next router or host to which to forward the datagram. ...
... Performs routing of datagrams from source to destination IP implementation at router maintains an inmemory routing table; used to search for next router or host to which to forward the datagram. ...
What are Networks? - Distributed Systems Group
... • The idea of introducing layers of software reduces the design complexity. It divides the large problem into smaller ones. • The number, name, contents and function of each layer vary from network to network. • However for each network the idea is that one layer offers something to a second layer w ...
... • The idea of introducing layers of software reduces the design complexity. It divides the large problem into smaller ones. • The number, name, contents and function of each layer vary from network to network. • However for each network the idea is that one layer offers something to a second layer w ...
Comparison and Contrast between the OSI and TCP/IP Model
... Since these two layers deal with functions that are so inherently specific to each individual networking technology, the layering principle of grouping them together related functions is largely ...
... Since these two layers deal with functions that are so inherently specific to each individual networking technology, the layering principle of grouping them together related functions is largely ...
Network
... (a) A router with five packets queued for line O. (b) Finishing times for the five packets. Packets send in the order of their finishing – ”fair queueing” byte-by-byte – equal priority ...
... (a) A router with five packets queued for line O. (b) Finishing times for the five packets. Packets send in the order of their finishing – ”fair queueing” byte-by-byte – equal priority ...
Slide 1
... Domain name resolvers (DNRs) are the bottom layer of servers which the ISPs hit with a domain name to resolve. If the DNR server has a match for the domain name in its IP address table cache, then the DNR server can resolve the domain name into an IP address. If not, then the DNR server hits the reg ...
... Domain name resolvers (DNRs) are the bottom layer of servers which the ISPs hit with a domain name to resolve. If the DNR server has a match for the domain name in its IP address table cache, then the DNR server can resolve the domain name into an IP address. If not, then the DNR server hits the reg ...
Blue Gene/L system architecture
... – Three high-band width, low-latency networks for data transmission and synchronization. • 3-D torus network for point-to-point communication • Collective network for global operations • Barrier network ...
... – Three high-band width, low-latency networks for data transmission and synchronization. • 3-D torus network for point-to-point communication • Collective network for global operations • Barrier network ...
Undergraduate Curriculum SIGCOMM 2002 Education Workshop Russell J Clark College of Computing
... Key Themes - Students’ View • Applications - HTTP, SMTP, POP, DNS Contrast of design, signaling. Demo using Telnet. • Transport - TCP, UDP Connection management, ARQ, Flow and Congestion Control • Network - IP, IPv6 Routing protocols, addressing, NAT, firewalls, IP vs MAC addressing, IPv6 transitio ...
... Key Themes - Students’ View • Applications - HTTP, SMTP, POP, DNS Contrast of design, signaling. Demo using Telnet. • Transport - TCP, UDP Connection management, ARQ, Flow and Congestion Control • Network - IP, IPv6 Routing protocols, addressing, NAT, firewalls, IP vs MAC addressing, IPv6 transitio ...
Chapter 2
... – A dedicated connection (circuit) is formed between two points – Guaranteed capacity at what cost? ...
... – A dedicated connection (circuit) is formed between two points – Guaranteed capacity at what cost? ...
TCP/IP Concepts (Part 1)
... If the SYN flag is set, that the TCP peer is ECN capable. If the SYN flag is clear, that a packet with Congestion Experienced flag in IP header set is received during normal transmission (added to header by RFC 3168). URG (1 bit) – indicates that the Urgent pointer field is significant ACK (1 bi ...
... If the SYN flag is set, that the TCP peer is ECN capable. If the SYN flag is clear, that a packet with Congestion Experienced flag in IP header set is received during normal transmission (added to header by RFC 3168). URG (1 bit) – indicates that the Urgent pointer field is significant ACK (1 bi ...
Internetworking
... cf) IEEE 802.11 (wireless LAN): geographically constrained • location independence over an area that is physically too large for any single medium such as Ethernet or RF ...
... cf) IEEE 802.11 (wireless LAN): geographically constrained • location independence over an area that is physically too large for any single medium such as Ethernet or RF ...
CSCI6268L19
... ports – Establish a connection with listen() and connect() • IP and UDP were “stateless” protocols ...
... ports – Establish a connection with listen() and connect() • IP and UDP were “stateless” protocols ...
The Internet and the World Wide Web
... electronic information exchange Open system protocols Any computer can communicate with other computers using the same protocols ...
... electronic information exchange Open system protocols Any computer can communicate with other computers using the same protocols ...
CSCI-1680 :: Computer Networks
... • Exploit hierarchical structure of addresses: need to know how to reach networks, not hosts Network ...
... • Exploit hierarchical structure of addresses: need to know how to reach networks, not hosts Network ...
TCP/IP
... timeout condition is reached or until successful delivery has been achieved. TCP can also recognize duplicate messages and will discard them appropriately. If the sending computer is transmitting too fast for the receiving computer, TCP can employ flow control mechanisms to slow data transfer. ...
... timeout condition is reached or until successful delivery has been achieved. TCP can also recognize duplicate messages and will discard them appropriately. If the sending computer is transmitting too fast for the receiving computer, TCP can employ flow control mechanisms to slow data transfer. ...
Project Title: Wireless Multimedia Mesh Networks
... QoS optimization: Since various digital media applications are co-existence in the network and each of them requires different types of QoS requirement such as delay, data rate, error rate and cost. An efficient QoS algorithm is needed to satisfy their QoS requirement and at the same time it can max ...
... QoS optimization: Since various digital media applications are co-existence in the network and each of them requires different types of QoS requirement such as delay, data rate, error rate and cost. An efficient QoS algorithm is needed to satisfy their QoS requirement and at the same time it can max ...
Document
... • Message is generated by the application of the source machine. • Message will be sent from the source to the destination. • Message “M” is transferred from layer 5 to layer 4, with a header containing control information, such as sequence numbers, which helps layer 4 maintain the message order. • ...
... • Message is generated by the application of the source machine. • Message will be sent from the source to the destination. • Message “M” is transferred from layer 5 to layer 4, with a header containing control information, such as sequence numbers, which helps layer 4 maintain the message order. • ...
ELECTRONIC COMMERCE
... Using HTTP you can transfer full motion video sequence, stereo sound tracks and high resolution images. MIME is extremely useful not only to HTTP but also to other protocols. MIME was originally developed to allow email messages to have multiple parts with different types of data in each part. ...
... Using HTTP you can transfer full motion video sequence, stereo sound tracks and high resolution images. MIME is extremely useful not only to HTTP but also to other protocols. MIME was originally developed to allow email messages to have multiple parts with different types of data in each part. ...
Module 2
... The network ID of the destination used to check whether the destination is in the same network with the computer or not Yes, use the ARP to determine the MAC address and forward the frame to it No, send it to the router (using the ip of the router) and the router looks into the Routing table for ...
... The network ID of the destination used to check whether the destination is in the same network with the computer or not Yes, use the ARP to determine the MAC address and forward the frame to it No, send it to the router (using the ip of the router) and the router looks into the Routing table for ...
TCP: Software for Reliable Communication
... Both X and Y send 5000 packets/s Network d may transmit 5000 packets/s; There is an excess of 5000 packets each ...
... Both X and Y send 5000 packets/s Network d may transmit 5000 packets/s; There is an excess of 5000 packets each ...
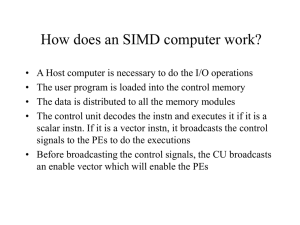
How does an SIMD computer work?
... • LDB: Local Data Buffer 64, 64-bit each • PEM: 2K X 64 bits memory ...
... • LDB: Local Data Buffer 64, 64-bit each • PEM: 2K X 64 bits memory ...
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA)

The Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) is a computer network architecture that unifies distributed computing and telecommunications. RINA's fundamental principle is that computer networking is just Inter-Process Communication or IPC. RINA reconstructs the overall structure of the Internet, forming a model that comprises a single repeating layer, the DIF (Distributed IPC Facility), which is the minimal set of components required to allow distributed IPC between application processes. RINA inherently supports mobility, multi-homing and Quality of Service without the need for extra mechanisms, provides a secure and programmable environment, motivates for a more competitive marketplace, and allows for a seamless adoption.