PPT File
... ESC cultures may be sources of differentiated cells to repair damaged tissues, as in diabetes or Parkinson’s disease. ESCs can be harvested from human embryos conceived by in vitro fertilization, with consent of the donors. However: • Some people object to the destruction of human embryos for this p ...
... ESC cultures may be sources of differentiated cells to repair damaged tissues, as in diabetes or Parkinson’s disease. ESCs can be harvested from human embryos conceived by in vitro fertilization, with consent of the donors. However: • Some people object to the destruction of human embryos for this p ...
Unit 1 Cell Biology Topic 3: Producing new cells
... the new cells. Genes are the basic unit of inheritance, and are responsible for the characteristics of an organism (e.g. what it looks like, its behaviour and all its chemical reactions). Genes are located on chromosomes, which are threadlike structures found in the nucleus of most cells (remember r ...
... the new cells. Genes are the basic unit of inheritance, and are responsible for the characteristics of an organism (e.g. what it looks like, its behaviour and all its chemical reactions). Genes are located on chromosomes, which are threadlike structures found in the nucleus of most cells (remember r ...
Developmental Genomics
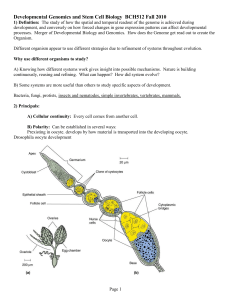
... Polarity: The finding of differences between different regions of a single cell or a group of cells. For example, polarity can be induced in an oocyte by fertililization. Polarity can be established in embryos by gradients of gene expression in specific groups of cells. Gradients: Distributions of m ...
... Polarity: The finding of differences between different regions of a single cell or a group of cells. For example, polarity can be induced in an oocyte by fertililization. Polarity can be established in embryos by gradients of gene expression in specific groups of cells. Gradients: Distributions of m ...
Lesson Plan - Colorado FFA
... Ask each team to have a representative from their group answer each question. Tell them they will have 15 seconds to give the correct answer. Keep track of the points and give out a small prize (candy, points) to the winning team. Start by presenting slide#23with directions to the class. Then show t ...
... Ask each team to have a representative from their group answer each question. Tell them they will have 15 seconds to give the correct answer. Keep track of the points and give out a small prize (candy, points) to the winning team. Start by presenting slide#23with directions to the class. Then show t ...
A. Why is cell division important?
... 2. However, bacteria do not have a nucleus so they can’t use mitosis. Instead, bacteria reproduce asexually by fission. 3. During fission, an organism whose cells do not contain a nucleus copies its genetic material and then divides into two identical organisms. ...
... 2. However, bacteria do not have a nucleus so they can’t use mitosis. Instead, bacteria reproduce asexually by fission. 3. During fission, an organism whose cells do not contain a nucleus copies its genetic material and then divides into two identical organisms. ...
Student Learning Objectives
... Ask each team to have a representative from their group answer each question. Tell them they will have 15 seconds to give the correct answer. Keep track of the points and give out a small prize (candy, points) to the winning team. Start by presenting slide#23with directions to the class. Then show t ...
... Ask each team to have a representative from their group answer each question. Tell them they will have 15 seconds to give the correct answer. Keep track of the points and give out a small prize (candy, points) to the winning team. Start by presenting slide#23with directions to the class. Then show t ...
Embryology (Josh`s Notes)
... tumor. Because these tumors are formed from a variety of cells, they contain various types of tissues. These are the most common type of tumors in newborns and occurs in about 1:35,000. Usually, they are surgically excised without a problem. Also during the third week, the notochord develops and ser ...
... tumor. Because these tumors are formed from a variety of cells, they contain various types of tissues. These are the most common type of tumors in newborns and occurs in about 1:35,000. Usually, they are surgically excised without a problem. Also during the third week, the notochord develops and ser ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR 6TH GRADE SCIENCE MIDTERM EXAM
... (Why do scientists use it?) 2 Name the steps of the scientific method in order ...
... (Why do scientists use it?) 2 Name the steps of the scientific method in order ...
Cellular Reproduction notes
... 2 new nuclei are formed Spindles break apart and disappear Nucleolus becomes visible in each daughter nucleus Mitosis is complete ...
... 2 new nuclei are formed Spindles break apart and disappear Nucleolus becomes visible in each daughter nucleus Mitosis is complete ...
Cell Division
... Consists of two processes: mitosis and cytokinesis During mitosis, the chromosomes divide and are distributed into two daughter nuclei During cytokinesis, the cytoplasm is divided into two These two processes result in the production of two genetically identical daughter cells ...
... Consists of two processes: mitosis and cytokinesis During mitosis, the chromosomes divide and are distributed into two daughter nuclei During cytokinesis, the cytoplasm is divided into two These two processes result in the production of two genetically identical daughter cells ...
Levels of Organization
... do you think this happened? 3. Looking through the EYEPIECE, move the slide to the upper right area of the stage. What direction does the image move through the eyepiece? 4. How does the ink appear under the microscope compared to normal view? 5. Why do you think a specimen placed under the microsco ...
... do you think this happened? 3. Looking through the EYEPIECE, move the slide to the upper right area of the stage. What direction does the image move through the eyepiece? 4. How does the ink appear under the microscope compared to normal view? 5. Why do you think a specimen placed under the microsco ...
Levels of Organization
... do you think this happened? 3. Looking through the EYEPIECE, move the slide to the upper right area of the stage. What direction does the image move through the eyepiece? 4. How does the ink appear under the microscope compared to normal view? 5. Why do you think a specimen placed under the microsco ...
... do you think this happened? 3. Looking through the EYEPIECE, move the slide to the upper right area of the stage. What direction does the image move through the eyepiece? 4. How does the ink appear under the microscope compared to normal view? 5. Why do you think a specimen placed under the microsco ...
Aim: How does the endocrine system control activities of the body?
... Use of sound and echo to create an image of the developing embryo ...
... Use of sound and echo to create an image of the developing embryo ...
Supplementary Information
... was performed to check the viability of the fura-2 dextran-injected, in vitro fertilised egg protoplasts. Figure S5a shows that following microinjection and electrofusion the microinjected cells to be subsequently ratio-imaged were viable as demonstrated by the positive membrane esterase activity. F ...
... was performed to check the viability of the fura-2 dextran-injected, in vitro fertilised egg protoplasts. Figure S5a shows that following microinjection and electrofusion the microinjected cells to be subsequently ratio-imaged were viable as demonstrated by the positive membrane esterase activity. F ...
Lecture Notes on Cells
... contract and relax and mix the food well with the digestive juices Connective tissue which helps to connect the other tissues. ...
... contract and relax and mix the food well with the digestive juices Connective tissue which helps to connect the other tissues. ...
Sub-topics include: 3.1 Cells, Tissues and Organs 3.2 Stem Cells
... brain cells that keep unneeded muscles from moving. Embryonic stem cells have recently been directed to differentiate into these types of cells, and so treatments are promising. Cell deficiency therapy Healthy heart cells developed in a laboratory may one day be transplanted into patients with heart ...
... brain cells that keep unneeded muscles from moving. Embryonic stem cells have recently been directed to differentiate into these types of cells, and so treatments are promising. Cell deficiency therapy Healthy heart cells developed in a laboratory may one day be transplanted into patients with heart ...
From skin to the treatment of diseases the possibilities of iPS cell
... The quest for finding sources of pluripotent cells raises the question as to whether adult somatic cells are restricted to one’s fate. Nuclear transfer studies proved that genes are not lost or permanently silenced during cell determination and differentiation. The pilot project was conducted by Bri ...
... The quest for finding sources of pluripotent cells raises the question as to whether adult somatic cells are restricted to one’s fate. Nuclear transfer studies proved that genes are not lost or permanently silenced during cell determination and differentiation. The pilot project was conducted by Bri ...
Baggie Cell Model - DNALC::Protocols
... As mentioned previously, the shape of the cell is intrinsically connected to its job. This is a concept in biology referred to as “form fits function”. That is, the shape of a cell determines its job. The red blood cell provides an excellent example. The small, round, flexible shape of the cell make ...
... As mentioned previously, the shape of the cell is intrinsically connected to its job. This is a concept in biology referred to as “form fits function”. That is, the shape of a cell determines its job. The red blood cell provides an excellent example. The small, round, flexible shape of the cell make ...
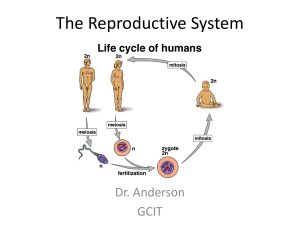
Cells and reproduction Jordanhill School S1 Science
... The sex cells are the cells that fuse together during sexual reproduction to form a new cell that will eventually form a new organism. The female sex cell is called the egg or ovum and is produced in the ovary. These round cells are the largest in the human body. They have a cell membrane, cytoplasm ...
... The sex cells are the cells that fuse together during sexual reproduction to form a new cell that will eventually form a new organism. The female sex cell is called the egg or ovum and is produced in the ovary. These round cells are the largest in the human body. They have a cell membrane, cytoplasm ...
the cell cycle
... Some treatments for cancer involve the use of drugs that specifically attack cells that are actively dividing. Why would this be effective for fighting cancerous cells? ...
... Some treatments for cancer involve the use of drugs that specifically attack cells that are actively dividing. Why would this be effective for fighting cancerous cells? ...
CH 11 Meiosis
... breaks down. The nuclear membranes and nucleoli reform. • Cytoplasm divides (cytokinesis) to form two cells. Cells are haploid at the end of meiosis I ...
... breaks down. The nuclear membranes and nucleoli reform. • Cytoplasm divides (cytokinesis) to form two cells. Cells are haploid at the end of meiosis I ...
the endocrine system
... sets of chromosomes are termed polyploid. Chromosomes that carry the same genes are termed homologous chromosomes. Humans receive one set of homologous chromosomes from each parent. Meiosis is a special type of nuclear division which segregates one copy of each homologous chromosome into each new "g ...
... sets of chromosomes are termed polyploid. Chromosomes that carry the same genes are termed homologous chromosomes. Humans receive one set of homologous chromosomes from each parent. Meiosis is a special type of nuclear division which segregates one copy of each homologous chromosome into each new "g ...
Somatic cell nuclear transfer
In genetics and developmental biology, somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) is a laboratory strategy for creating a viable embryo from a body cell and an egg cell. The technique consists of taking an enucleated oocyte (egg cell) and implanting a donor nucleus from a somatic (body) cell. It is used in both therapeutic and reproductive cloning. Dolly the Sheep became famous for being the first successful case of the reproductive cloning of a mammal. ""Therapeutic cloning"" refers to the potential use of SCNT in regenerative medicine; this approach has been championed as an answer to the many issues concerning embryonic stem cells (ESC) and the destruction of viable embryos for medical use, though questions remain on how homologous the two cell types truly are.