PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and
... Like begets like, more or less! • Asexual reproduction! – Chromosomes are duplicated and cell divides ! – Each daughter cell is genetically identical to the parent and the other daughter! • Sexual reproduction! – Each offspring inherits a unique combination of genes from both parents! – Offspring ca ...
... Like begets like, more or less! • Asexual reproduction! – Chromosomes are duplicated and cell divides ! – Each daughter cell is genetically identical to the parent and the other daughter! • Sexual reproduction! – Each offspring inherits a unique combination of genes from both parents! – Offspring ca ...
Asymmetric Cell Division in Plant Development
... commonly exploited solution to the fundamental problem of creating cell diversity in multicellular organisms. This cellular specialization generates the structural and functional cell types that make up tissues and organs during development. Central to the process of asymmetric cell division is the ...
... commonly exploited solution to the fundamental problem of creating cell diversity in multicellular organisms. This cellular specialization generates the structural and functional cell types that make up tissues and organs during development. Central to the process of asymmetric cell division is the ...
Asymmetric Cell Division in Plant Development
... commonly exploited solution to the fundamental problem of creating cell diversity in multicellular organisms. This cellular specialization generates the structural and functional cell types that make up tissues and organs during development. Central to the process of asymmetric cell division is the ...
... commonly exploited solution to the fundamental problem of creating cell diversity in multicellular organisms. This cellular specialization generates the structural and functional cell types that make up tissues and organs during development. Central to the process of asymmetric cell division is the ...
Cell Structure
... Many one-celled organisms perform all their life functions by themselves. Cells in a many-celled organism, however, do not work alone. Each cell carries on its own life functions while depending in some way on other cells in the organism. ...
... Many one-celled organisms perform all their life functions by themselves. Cells in a many-celled organism, however, do not work alone. Each cell carries on its own life functions while depending in some way on other cells in the organism. ...
Introduction to Cytology Terminology
... their area. They will use this knowledge as needed in their role. HLC1O.01 Technical Skills Health Care Workers will apply technical skills required for all career specialties. They will demonstrate skills and knowledge as appropriate. TEKS 130.206 (c)(1)(A) demonstrate safe practices during labora ...
... their area. They will use this knowledge as needed in their role. HLC1O.01 Technical Skills Health Care Workers will apply technical skills required for all career specialties. They will demonstrate skills and knowledge as appropriate. TEKS 130.206 (c)(1)(A) demonstrate safe practices during labora ...
Presentation
... stomach, and intestines? The digestive system is an organ system. The stomach and intestines are organs that are parts of the digestive system. 2. What is the main difference between a unicellular organism and a multicellular organism in the way life processes are carried out? Sample answer: A u ...
... stomach, and intestines? The digestive system is an organ system. The stomach and intestines are organs that are parts of the digestive system. 2. What is the main difference between a unicellular organism and a multicellular organism in the way life processes are carried out? Sample answer: A u ...
Human ontogeny – notes for Human biology course Auxology
... - after these layers form, subpopulations of cells give rise to the organs – every body part develops from these 3 layers Foetal period – 2 to 9 months - growth and development continue dramatically - 3 months after conception the foetus has become very active, moving its arms and legs, opening and ...
... - after these layers form, subpopulations of cells give rise to the organs – every body part develops from these 3 layers Foetal period – 2 to 9 months - growth and development continue dramatically - 3 months after conception the foetus has become very active, moving its arms and legs, opening and ...
Cell Membrane
... • Two major types of genes cause cancer: • Oncogenes – activate other genes that increase cell division ...
... • Two major types of genes cause cancer: • Oncogenes – activate other genes that increase cell division ...
Chapter 2: Cells Unit 2.1 1 An eyepiece or ocular lens and objective
... 20 Consisting of a few large cells, we would be more vulnerable to damage. We would be less flexible. Our few cells would have to carry out all the functions rather than having cells specialised for different functions. It would be more difficult to maintain the shape of the human body, with arms, l ...
... 20 Consisting of a few large cells, we would be more vulnerable to damage. We would be less flexible. Our few cells would have to carry out all the functions rather than having cells specialised for different functions. It would be more difficult to maintain the shape of the human body, with arms, l ...
013368718X_CH10_143
... 2. Look at the triangles in each circle. Suppose they have to move to the dot in the center. (Assume the triangles are traveling at the same speed.) Which triangles would get to the center faster—those in Circle A or those in Circle B? ...
... 2. Look at the triangles in each circle. Suppose they have to move to the dot in the center. (Assume the triangles are traveling at the same speed.) Which triangles would get to the center faster—those in Circle A or those in Circle B? ...
Cell Level Systems
... OCR’s resources are provided to support the teaching of OCR specifications, but in no way constitute an endorsed teaching method that is required by the Board, and the decision to use them lies with the individual teacher. Whilst every effort is made to ensure the accuracy of the content, OCR cannot ...
... OCR’s resources are provided to support the teaching of OCR specifications, but in no way constitute an endorsed teaching method that is required by the Board, and the decision to use them lies with the individual teacher. Whilst every effort is made to ensure the accuracy of the content, OCR cannot ...
District Mid-Term Examination
... Patients with a specific medical condition have been provided with a new device that helps them manage their condition. The patients will be required to participate in a survey regarding the usefulness of the device. How can the manufacturer be certain that no bias enters into the surveys? A. by pay ...
... Patients with a specific medical condition have been provided with a new device that helps them manage their condition. The patients will be required to participate in a survey regarding the usefulness of the device. How can the manufacturer be certain that no bias enters into the surveys? A. by pay ...
Poultry Biology - Central Web Server 2
... myoglobin, the oxygen holding molecules in muscles, and because white muscles have a very definite fibrillar appearance whereas red fibers have a more granular appearance and more myoglobin. Muscles that are used more tend to accumulate more myoglobin, such as leg muscles and flight muscles in wild ...
... myoglobin, the oxygen holding molecules in muscles, and because white muscles have a very definite fibrillar appearance whereas red fibers have a more granular appearance and more myoglobin. Muscles that are used more tend to accumulate more myoglobin, such as leg muscles and flight muscles in wild ...
Cell Parts and Functions
... Cilia and flagella are present in most microorganisms and animals, but not in higher order plants. The function of these parts is to allow for movement either of the cell itself or of something past the cell. ...
... Cilia and flagella are present in most microorganisms and animals, but not in higher order plants. The function of these parts is to allow for movement either of the cell itself or of something past the cell. ...
8 - Hatboro
... 4. About how many different types of cells are there in our body?________________________________ 5. What is another word for adult stem cells? ________________________________________________ 6. What are somatic cells? Please give an example of somatic cells. _______________________________ _______ ...
... 4. About how many different types of cells are there in our body?________________________________ 5. What is another word for adult stem cells? ________________________________________________ 6. What are somatic cells? Please give an example of somatic cells. _______________________________ _______ ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
... (4) controls & coordinates body 2. The main function of the digestive system is to (1) breakdown foods for absorption into the blood. (2) Exchange oxygen & carbon dioxide in the lungs. (3) Release energy from sugars within the cells. Which two diseases in the table affect the digestive system? (4) C ...
... (4) controls & coordinates body 2. The main function of the digestive system is to (1) breakdown foods for absorption into the blood. (2) Exchange oxygen & carbon dioxide in the lungs. (3) Release energy from sugars within the cells. Which two diseases in the table affect the digestive system? (4) C ...
The Role of Differential Gene Expression in Cell Differentiation
... • In the body, stem cells have a limited ability to differentiate, but by manipulating the environment, stem cells can be made to differentiate. • An example of a stem cell differentiation in response to altered environmental signals in mice: Brain stem cells were transplanted to bone marrow, wher ...
... • In the body, stem cells have a limited ability to differentiate, but by manipulating the environment, stem cells can be made to differentiate. • An example of a stem cell differentiation in response to altered environmental signals in mice: Brain stem cells were transplanted to bone marrow, wher ...
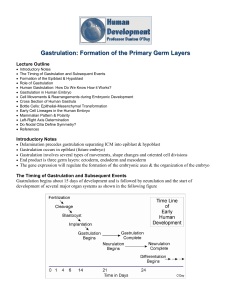
Gastrulation: Formation of the Primary Germ Layers
... Gastrulation: Formation of the Primary Germ Layers It is very likely that the anterior-posterior axis is established initially by implantation via mechanisms that remain to be elucidated. The establishment of the A-P Axis would in turn define the orientation of the primitive streak. In the mouse, t ...
... Gastrulation: Formation of the Primary Germ Layers It is very likely that the anterior-posterior axis is established initially by implantation via mechanisms that remain to be elucidated. The establishment of the A-P Axis would in turn define the orientation of the primitive streak. In the mouse, t ...
AS BIOLOGY UNITS
... A type of cell division that produces four haploid cells from a diploid parent cell (germ cell). Used by organisms to produce gametes or spores (plants), therefore linked to sexual reproduction. During meiosis, the alleles on the homologous pairs of chromosomes are recombined, producing chromosomes ...
... A type of cell division that produces four haploid cells from a diploid parent cell (germ cell). Used by organisms to produce gametes or spores (plants), therefore linked to sexual reproduction. During meiosis, the alleles on the homologous pairs of chromosomes are recombined, producing chromosomes ...
PART 1. Principles of development in biology
... development of a multicellular organism begins with a single cell the fertilized egg, or zygote, which divides mitotically to produce all the cells of the body. The study of animal development has traditionally been called embryology, from that stage of an organism that exists between fertilization ...
... development of a multicellular organism begins with a single cell the fertilized egg, or zygote, which divides mitotically to produce all the cells of the body. The study of animal development has traditionally been called embryology, from that stage of an organism that exists between fertilization ...
Standard 3 review notes The parts of the cell I want you to know are
... membrane. This requires energy that is made by the mitochondria from sugar that already got moved across the cell membrane. The mitochondria break down the sugar into smaller parts and that releases energy. The wastes produced by this process are moved OUT of the cell through the cell membrane. On r ...
... membrane. This requires energy that is made by the mitochondria from sugar that already got moved across the cell membrane. The mitochondria break down the sugar into smaller parts and that releases energy. The wastes produced by this process are moved OUT of the cell through the cell membrane. On r ...
33835_CellsBldgBlcks TG
... • All basic chemical and physiological functions—repair, growth, movement, immunity, communication, and digestion—are carried out inside of cells. • The activities of cells depends on the activities of sub-cellular structures within the cell (organelles, the plasma membrane, and the nucleus). Topic ...
... • All basic chemical and physiological functions—repair, growth, movement, immunity, communication, and digestion—are carried out inside of cells. • The activities of cells depends on the activities of sub-cellular structures within the cell (organelles, the plasma membrane, and the nucleus). Topic ...
Development
... (I) Embryonic Development In the early stages of development, the organism is called an embryo The process of embryonic ...
... (I) Embryonic Development In the early stages of development, the organism is called an embryo The process of embryonic ...
Name_____________________________________
... Occurs in the upper portion of the ________________________ (fallopian tube) If the egg is not ________________________________ within 24-48 hours after ovulation, it will die and be shed from the body during ______________________________________________. ________________________________ begins in ...
... Occurs in the upper portion of the ________________________ (fallopian tube) If the egg is not ________________________________ within 24-48 hours after ovulation, it will die and be shed from the body during ______________________________________________. ________________________________ begins in ...
2nd week of Development
... Outer cell mass :also differentiate into two layers 1. Layer of mononucleated cells called cytotrophblast. These cells are active mitotically 2. Layer of multinucleated zone without distinct cell bounderies called syncytotrophblast or syncitium Extraembryonic structures • The embryonic disc gives ri ...
... Outer cell mass :also differentiate into two layers 1. Layer of mononucleated cells called cytotrophblast. These cells are active mitotically 2. Layer of multinucleated zone without distinct cell bounderies called syncytotrophblast or syncitium Extraembryonic structures • The embryonic disc gives ri ...
Somatic cell nuclear transfer
In genetics and developmental biology, somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) is a laboratory strategy for creating a viable embryo from a body cell and an egg cell. The technique consists of taking an enucleated oocyte (egg cell) and implanting a donor nucleus from a somatic (body) cell. It is used in both therapeutic and reproductive cloning. Dolly the Sheep became famous for being the first successful case of the reproductive cloning of a mammal. ""Therapeutic cloning"" refers to the potential use of SCNT in regenerative medicine; this approach has been championed as an answer to the many issues concerning embryonic stem cells (ESC) and the destruction of viable embryos for medical use, though questions remain on how homologous the two cell types truly are.