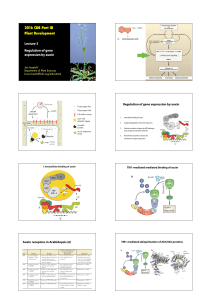
Structural differences in two biochemically-defined
... complexes situated in crista membranes are affected by membrane conformation. For example, Schàgger17 has described ‘supercomplexes,’ assemblies of the electron-transport chain complexes that require close association to operate at maximum efficiency. The possibility also exists that the biochemical ...
... complexes situated in crista membranes are affected by membrane conformation. For example, Schàgger17 has described ‘supercomplexes,’ assemblies of the electron-transport chain complexes that require close association to operate at maximum efficiency. The possibility also exists that the biochemical ...
Mitochondrial trafficking and anchoring in neurons
... KIF5 heavy chain (KHC) contains a motor domain with ATPase at the N terminus and a C-terminal tail for binding cargo directly or indirectly via a cargo adaptor. Three isoforms (KIF5A, KIF5B, and KIF5C) of the KIF5 family are found in mammals, of which KIF5B is expressed ubiquitously whereas KIF5A an ...
... KIF5 heavy chain (KHC) contains a motor domain with ATPase at the N terminus and a C-terminal tail for binding cargo directly or indirectly via a cargo adaptor. Three isoforms (KIF5A, KIF5B, and KIF5C) of the KIF5 family are found in mammals, of which KIF5B is expressed ubiquitously whereas KIF5A an ...
Oxidative stress stimulates multiple MAPK signalling pathways and
... causing oxidation of various cellular components, including proteins, DNA and membrane lipids (Shlafer et al., 1987; Kehrer, 1993; Halliwell, 1994; Kramer et al., 1994; Wang et al., 1998a). The electron carriers of the mitochondrial respiratory chain are reduced during ischaemia, whereas immediate r ...
... causing oxidation of various cellular components, including proteins, DNA and membrane lipids (Shlafer et al., 1987; Kehrer, 1993; Halliwell, 1994; Kramer et al., 1994; Wang et al., 1998a). The electron carriers of the mitochondrial respiratory chain are reduced during ischaemia, whereas immediate r ...
sLeX inhibits Ply hemolytic activity by blocking binding of the toxin to
... Hemolysis assays and flow cytometric analysis of RBC binding were performed with SLO in the presence of lacto-N-neotetraose (LNnT) (highest affinity binding in SPR KD=0.6nM) D-cellobiose (Glcβ(14)Glc) included as a negative control Free LNnT blocked SLO hemolytic activity. ...
... Hemolysis assays and flow cytometric analysis of RBC binding were performed with SLO in the presence of lacto-N-neotetraose (LNnT) (highest affinity binding in SPR KD=0.6nM) D-cellobiose (Glcβ(14)Glc) included as a negative control Free LNnT blocked SLO hemolytic activity. ...
REVIEWS - Haseloff Lab
... C-terminal Gly carboxyl group of ubiquitin is linked through an isopeptide bond to an accessible amino group (typically a Lys ε-amino) in the target. By attaching ubiquitin in various ways, distinct target fates can be achieved. For example, by reiterative rounds of ubiquitylation, polymeric ubiquit ...
... C-terminal Gly carboxyl group of ubiquitin is linked through an isopeptide bond to an accessible amino group (typically a Lys ε-amino) in the target. By attaching ubiquitin in various ways, distinct target fates can be achieved. For example, by reiterative rounds of ubiquitylation, polymeric ubiquit ...
Acute Knockdown of Uncoupling Protein-2 Increases Uncoupling via the Adenine
... but not scrambled siRNA, increased glutamate-stimulated O2 consumption in both controls and diabetics. GDP inhibited glutamate-stimulated O2 consumption in untreated diabetics and diabetic animals receiving scrambled siRNA. No effect of GDP was observed in any of the control groups (Fig. 3). ADP inh ...
... but not scrambled siRNA, increased glutamate-stimulated O2 consumption in both controls and diabetics. GDP inhibited glutamate-stimulated O2 consumption in untreated diabetics and diabetic animals receiving scrambled siRNA. No effect of GDP was observed in any of the control groups (Fig. 3). ADP inh ...
Mitochondrial translation factors of Trypanosoma brucei: elongation
... GTPase EF-G has two functions. It catalyses the translocation step after peptide bond formation and is involved in ribosome recycling. Interestingly, mitochondria have two orthologues of EF-G: EF-G1 and EF-G2, which are required for ribosomal translocation and recycling respectively. Finally, transl ...
... GTPase EF-G has two functions. It catalyses the translocation step after peptide bond formation and is involved in ribosome recycling. Interestingly, mitochondria have two orthologues of EF-G: EF-G1 and EF-G2, which are required for ribosomal translocation and recycling respectively. Finally, transl ...
Arabidopsis Kinetochore Fiber-Associated MAP65-4
... part, which includes the most evolutionarily conserved domain of the MAP65 family (referred to as to 3N), and the C-terminal part, which is divergent among the MAP65 members (referred as to 3C) (Figure 3A). High-speed centrifugation of MAP65-4 and of truncated proteins after incubation with MTs demo ...
... part, which includes the most evolutionarily conserved domain of the MAP65 family (referred to as to 3N), and the C-terminal part, which is divergent among the MAP65 members (referred as to 3C) (Figure 3A). High-speed centrifugation of MAP65-4 and of truncated proteins after incubation with MTs demo ...
Guanine Nucleotide Exchange-Independent Activation of Gs Protein
... Pharmacology, Istituto Superiore di Sanità, Rome, Italy (P.M., C.A.) Received December 14, 2004; accepted June 1, 2005 ...
... Pharmacology, Istituto Superiore di Sanità, Rome, Italy (P.M., C.A.) Received December 14, 2004; accepted June 1, 2005 ...
What recent ribosome structures have revealed
... IF2, a GTPase, promotes subunit joining to form the 70S initiation complex (70S-IC), which is accompanied by IF3 release13–15. After GTP hydrolysis and phosphate release from IF2 (refs 16, 17), fMettRNAfMet moves into the PTC, readying the ribosome for elongation. The mechanism of initiation is stil ...
... IF2, a GTPase, promotes subunit joining to form the 70S initiation complex (70S-IC), which is accompanied by IF3 release13–15. After GTP hydrolysis and phosphate release from IF2 (refs 16, 17), fMettRNAfMet moves into the PTC, readying the ribosome for elongation. The mechanism of initiation is stil ...
Classes of programmed cell death in plants
... Permeabilization of lysosomes can release cathepsins B and D into the cytoplasm. These cause proteolytic activation of the pro-apoptotic protein Bid, which then induces mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization and PCD through caspase activation. In other examples, such as lung cancer cells, the ...
... Permeabilization of lysosomes can release cathepsins B and D into the cytoplasm. These cause proteolytic activation of the pro-apoptotic protein Bid, which then induces mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization and PCD through caspase activation. In other examples, such as lung cancer cells, the ...
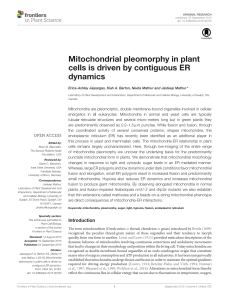
Mitochondrial pleomorphy in plant cells is driven
... so far in plants, at least two major factors have been wellcharacterized. These are Fission1, a tail-anchored membrane protein (hFis1 in mammals: Yoon et al., 2003; Stojanovski et al., 2004; Fis1p in yeast: Mozdy et al., 2000; Tieu and Nunnari, 2000; Fis1/BIGYIN in plants: Scott et al., 2006) and a ...
... so far in plants, at least two major factors have been wellcharacterized. These are Fission1, a tail-anchored membrane protein (hFis1 in mammals: Yoon et al., 2003; Stojanovski et al., 2004; Fis1p in yeast: Mozdy et al., 2000; Tieu and Nunnari, 2000; Fis1/BIGYIN in plants: Scott et al., 2006) and a ...
High-Molecular-Weight Forms of Tyrosinase and the
... TRP-2 migrated exclusively in a hig h - molecul ar-we ig ht form, as expected from its behavior on mol ecul ar sieve HPLC (Fig 1b, bottom). No TRP-2 was detected in association with th e peak of "free" tyrosinase from HPLC (Fig lb, lOp), Triton X-1 00 was used only in the initial phase of the purifi ...
... TRP-2 migrated exclusively in a hig h - molecul ar-we ig ht form, as expected from its behavior on mol ecul ar sieve HPLC (Fig 1b, bottom). No TRP-2 was detected in association with th e peak of "free" tyrosinase from HPLC (Fig lb, lOp), Triton X-1 00 was used only in the initial phase of the purifi ...
EMD Millipore Protease and Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktails
... phosphorylated by protein kinases that transfer a phosphate group to a specific protein, typically at serine, threonine, or tyrosine residues. The covalent attachment of a phosphoryl group changes the conformation of the protein and alters its ability to interact with a ligand. The phosphate group i ...
... phosphorylated by protein kinases that transfer a phosphate group to a specific protein, typically at serine, threonine, or tyrosine residues. The covalent attachment of a phosphoryl group changes the conformation of the protein and alters its ability to interact with a ligand. The phosphate group i ...
Co-translational Targeting and Translocation of the Amino Terminus
... partially dissociate the coupling between translation and translocation across the mammalian ER membrane. However, the targeting and translocation efficiencies were very low (24 – 27), suggesting that efficient translocation may only occur coupled to translation. To investigate translocation in a ma ...
... partially dissociate the coupling between translation and translocation across the mammalian ER membrane. However, the targeting and translocation efficiencies were very low (24 – 27), suggesting that efficient translocation may only occur coupled to translation. To investigate translocation in a ma ...
Nuclear Factor-κB Modulates the p53 Response in Neurons
... Neuronal death is controlled by a complex series of events, which include both pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic signals. To examine the fundamental signals induced by DNA damage, we have used the paradigm of cortical neuronal death initiated by exposure to the topoisomerase1 inhibitor, camptothecin. ...
... Neuronal death is controlled by a complex series of events, which include both pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic signals. To examine the fundamental signals induced by DNA damage, we have used the paradigm of cortical neuronal death initiated by exposure to the topoisomerase1 inhibitor, camptothecin. ...
Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson`s disease
... chain (rev. in refs. [60,61]). It consists of 14 central and up to 32 accessory subunits, which form an L-shaped complex with a membrane arm and a peripheral arm protruding into the mitochondrial matrix. Seven hydrophobic subunits forming the membrane central core are encoded by mitochondrial (mt) D ...
... chain (rev. in refs. [60,61]). It consists of 14 central and up to 32 accessory subunits, which form an L-shaped complex with a membrane arm and a peripheral arm protruding into the mitochondrial matrix. Seven hydrophobic subunits forming the membrane central core are encoded by mitochondrial (mt) D ...
Building and Breaking Bridges between Sister Chromatids
... tension, which is counteracted by cohesion between the sisters. No tension is generated if both sister kinetochores have been attached to microtubules from the same pole, known as syntelic attachment. (B) The cohesin cycle. Cohesin complexes are loaded onto chromosomes before the onset of DNA replic ...
... tension, which is counteracted by cohesion between the sisters. No tension is generated if both sister kinetochores have been attached to microtubules from the same pole, known as syntelic attachment. (B) The cohesin cycle. Cohesin complexes are loaded onto chromosomes before the onset of DNA replic ...
The AP-3 adaptor complex is required for vacuolar function
... mutant background, we observed swelling and vacuolization of PVC compartments visualized by PVC markers, such as GFP-RABF2b [34] (Figure 2E and 2F). Moreover, the swollen PVC phenotype in the pat4 mutant resembled the effect of wortmannin on the PVC morphology [10]. Taken together, these results ind ...
... mutant background, we observed swelling and vacuolization of PVC compartments visualized by PVC markers, such as GFP-RABF2b [34] (Figure 2E and 2F). Moreover, the swollen PVC phenotype in the pat4 mutant resembled the effect of wortmannin on the PVC morphology [10]. Taken together, these results ind ...
A. Work Accomplished by You and/or Others Cellular biology of
... Cellular biology of protein chaperones Protein molecular chaperones play critical roles in cellular biology. The family of proteins classified as molecular chaperones is large and diverse, but is united by a common characteristic – the ability to form transient yet productive interactions with a bro ...
... Cellular biology of protein chaperones Protein molecular chaperones play critical roles in cellular biology. The family of proteins classified as molecular chaperones is large and diverse, but is united by a common characteristic – the ability to form transient yet productive interactions with a bro ...
- Gastroenterology
... notable example is trypsinogen, which reaches the small intestine as precursor zymogen, is activated by brushborder enterokinase, and then acts as the master enzyme in activating other digestive proteases. A pivotal role of trypsin in the initiating events of pancreatitis can be assumed because tryp ...
... notable example is trypsinogen, which reaches the small intestine as precursor zymogen, is activated by brushborder enterokinase, and then acts as the master enzyme in activating other digestive proteases. A pivotal role of trypsin in the initiating events of pancreatitis can be assumed because tryp ...
Candidate Vaccine Neisseria meningitidis a to Genome
... Genome-derived neisserial Ag (GNA) 1870 is a meningococcal vaccine candidate that can be subdivided into three variants based on amino acid sequence variability. Variant group 1 accounts for ⬃60% of disease-producing group B isolates. The Ag went unrecognized until its discovery by genome mining bec ...
... Genome-derived neisserial Ag (GNA) 1870 is a meningococcal vaccine candidate that can be subdivided into three variants based on amino acid sequence variability. Variant group 1 accounts for ⬃60% of disease-producing group B isolates. The Ag went unrecognized until its discovery by genome mining bec ...
Sirtuins at a Glance - Journal of Cell Science
... 2009b; Zillikens et al., 2009a). Taken together, these findings provide strong evidence that SIRT1 has significant roles in metabolic diseases, such as type 2 diabetes and obesity, and controlling SIRT1 activity with nutrients or small molecules could be a valuable treatment strategy. Roles in infla ...
... 2009b; Zillikens et al., 2009a). Taken together, these findings provide strong evidence that SIRT1 has significant roles in metabolic diseases, such as type 2 diabetes and obesity, and controlling SIRT1 activity with nutrients or small molecules could be a valuable treatment strategy. Roles in infla ...
Suppressor of Hairless-independent events in
... effector of Notch since the expression of bHLH genes encoded by E(spl) depends on both Notch signaling and the presence of Su(H)-binding sites in the promoters (Jennings et al., 1994; Lecourtois and Schweisguth, 1995; Bailey and Posakony, 1995). Truncation of the extracellular domain of Notch result ...
... effector of Notch since the expression of bHLH genes encoded by E(spl) depends on both Notch signaling and the presence of Su(H)-binding sites in the promoters (Jennings et al., 1994; Lecourtois and Schweisguth, 1995; Bailey and Posakony, 1995). Truncation of the extracellular domain of Notch result ...
Physical interaction between pRb and cdk9/cyclinT2 complex
... 1993). The pocket region is also the binding site for other cellular factors lacking the LXCXE motif, such as E2F transcription factors (Stiegler and Giordano, 2001). Mutations in these pocket residues render pRb inactive or heavily impaired in controlling the cell cycle. The function to arrest the ...
... 1993). The pocket region is also the binding site for other cellular factors lacking the LXCXE motif, such as E2F transcription factors (Stiegler and Giordano, 2001). Mutations in these pocket residues render pRb inactive or heavily impaired in controlling the cell cycle. The function to arrest the ...
Apoptosome

The apoptosome is a large quaternary protein structure formed in the process of apoptosis. Its formation is triggered by the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria in response to an internal (intrinsic) or external (extrinsic) cell death stimulus. Stimuli can vary from DNA damage and viral infection to developmental cues such as those leading to the degradation of a tadpole's tail.In mammalian cells, once cytochrome c is released, it binds to the cytosolic protein Apaf-1 to facilitate the formation of apoptosome. An early biochemical study suggests a two-to-one ratio of cytochrome c to apaf-1 for apoptosome formation. However, recent structural studies suggest the cytochrome c to apaf-1 ratio is one-to-one. It has also been shown that the nucleotide dATP as third component binds to apaf-1, however its exact role is still debated. The mammalian apoptosome had never been crystallized, but a human APAF-1/cytochrome-c apoptosome has been imaged at lower (2 nm) resolution by cryogenic transmission electron microscopy 10 years ago, revealing a wheel-like particle with 7-fold symmetry. Recently, a medium resolution (9.5 Ångström) structure of human apoptosome was also solved by cryo-electron microscopy, which allows unambiguous inference for positions of all the APAF-1 domains (CARD, NBARC and WD40) and cytochrome c. There is also now a crystal structure of the monomeric, inactive Apaf-1 subunit (PDB 3SFZ). Once formed, the apoptosome can then recruit and activate the inactive pro-caspase-9. Once activated, this initiator caspase can then activate effector caspases and trigger a cascade of events leading to apoptosis.