The Structure of Proteins
... stance is known to have the cyclol structure; but teins, under special conditions, in solution and in an indirect calculation can be made in many wa;% the crystal, we attribute to definite stabilizing namely, (1) hydrogen bonds between such as the following. One hexamethylenetetra- fa~tors;2~12~ min ...
... stance is known to have the cyclol structure; but teins, under special conditions, in solution and in an indirect calculation can be made in many wa;% the crystal, we attribute to definite stabilizing namely, (1) hydrogen bonds between such as the following. One hexamethylenetetra- fa~tors;2~12~ min ...
Comparative study of pathogenesis-related protein - NOPR
... as well as for resistance to protease degradation24. Molecular Modelling ...
... as well as for resistance to protease degradation24. Molecular Modelling ...
plotfold
... Using energy minimization criteria, any predicted "optimal" secondary structure for an RNA or DNA molecule depends on the model of folding and the specific folding energies used to calculate that structure. Different optimal foldings may be calculated if the folding energies are changed even slightl ...
... Using energy minimization criteria, any predicted "optimal" secondary structure for an RNA or DNA molecule depends on the model of folding and the specific folding energies used to calculate that structure. Different optimal foldings may be calculated if the folding energies are changed even slightl ...
pdbe.org
... short β-strand between the domains. This interaction explains why the Candida adhesins preferentially bind free C-termini of proteins: the buried positive charge on the lysine is neutralised by the negative charge from the substrate. The adhesin cannot bind peptides without a C-terminal carboxylate ...
... short β-strand between the domains. This interaction explains why the Candida adhesins preferentially bind free C-termini of proteins: the buried positive charge on the lysine is neutralised by the negative charge from the substrate. The adhesin cannot bind peptides without a C-terminal carboxylate ...
Page 1 Proteins - Made up of amino acid monomers (yep, you got it
... describe the formation of a peptide bond; understand the meaning of the terms primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure and their importance in the structure of enzymes; understand that condensation and hydrolysis reactions are involved in the synthesis and degradation of polypeptides an ...
... describe the formation of a peptide bond; understand the meaning of the terms primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure and their importance in the structure of enzymes; understand that condensation and hydrolysis reactions are involved in the synthesis and degradation of polypeptides an ...
PPTX
... • This might be achieved by assigning confidence scores to different levels of the complex by which it collapses/expands… ...
... • This might be achieved by assigning confidence scores to different levels of the complex by which it collapses/expands… ...
Document
... The Hirschberg algorithm (Hirschberg, 1975) reduces the space requirements of a standard alignment algorithm from O(n2) to O(n) while leaving the time complexity O(n2), via a recursive procedure in which a decoding pass is made over the two halves of the matrix to determine the crossing point of the ...
... The Hirschberg algorithm (Hirschberg, 1975) reduces the space requirements of a standard alignment algorithm from O(n2) to O(n) while leaving the time complexity O(n2), via a recursive procedure in which a decoding pass is made over the two halves of the matrix to determine the crossing point of the ...
Guidelines for Abstract Submission
... N-terminal region. In order to identify residues important for chloroplast and/or mitochondria targeting, we introduced point mutations and deletions into conserved residues of RBP1b TS, and evaluated their effect in the relative mitochondria/chloroplast targeting, using a novel GFP quantitative app ...
... N-terminal region. In order to identify residues important for chloroplast and/or mitochondria targeting, we introduced point mutations and deletions into conserved residues of RBP1b TS, and evaluated their effect in the relative mitochondria/chloroplast targeting, using a novel GFP quantitative app ...
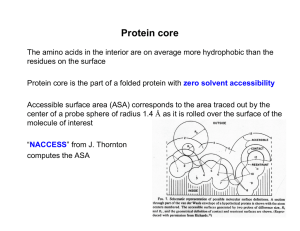
Protein core - Acsu.buffalo.edu
... Simple hydrophobic interaction can contribute more to stability than buried salt bridges, while offering conformational specificity required for function However, internal salt bridges may confer specificity by discriminating against alternate conformations ...
... Simple hydrophobic interaction can contribute more to stability than buried salt bridges, while offering conformational specificity required for function However, internal salt bridges may confer specificity by discriminating against alternate conformations ...
manual PURExpress In Vitro Protein Synthesis Kit E6800
... PCR products, linear, or circular plasmid DNA can be used as the template DNA with PURExpress. While higher yields are often obtained with circular plasmid DNA as the template, PCR products can generate acceptable yields and can provide many timesaving advantages. The use of PCR to prepare template ...
... PCR products, linear, or circular plasmid DNA can be used as the template DNA with PURExpress. While higher yields are often obtained with circular plasmid DNA as the template, PCR products can generate acceptable yields and can provide many timesaving advantages. The use of PCR to prepare template ...
Change linear sequence of genera in Psittacidae
... 30 genera of Neotropical parrots. The well-supported nodes that affect our sequence are • Deroptyus and Pionites are sisters (100% Bayesian support, 100% ML bootstrap support) • Myiopsitta and Brotogeris are sisters (100% Bayesian support, 100% ML bootstrap support) • Nannopsittaca and Bolborhynchus ...
... 30 genera of Neotropical parrots. The well-supported nodes that affect our sequence are • Deroptyus and Pionites are sisters (100% Bayesian support, 100% ML bootstrap support) • Myiopsitta and Brotogeris are sisters (100% Bayesian support, 100% ML bootstrap support) • Nannopsittaca and Bolborhynchus ...
Protein Ubiquitination
... important role in protein folding. Chaperons safeguard the folding of nascent chains. ...
... important role in protein folding. Chaperons safeguard the folding of nascent chains. ...
NCBI Protein Structure
... - foldit - http://fold.it/portal/info/science These three sites are very in-depth and are meant to provide you with explanations of your protein’s chemistry. The serve as references - you are not expected to master the material. Refer the ‘Objectives’ section (above) to see what level of chemical de ...
... - foldit - http://fold.it/portal/info/science These three sites are very in-depth and are meant to provide you with explanations of your protein’s chemistry. The serve as references - you are not expected to master the material. Refer the ‘Objectives’ section (above) to see what level of chemical de ...
Early states during protein folding - The Astbury Centre for Structural
... able to detect all the species populated during folding and to characterise their structural, dynamic and spectroscopic properties in as much detail, and at as high a resolution, as possible. Whilst this can be readily achieved for the native state using NMR or X-ray methods, the transient nature, c ...
... able to detect all the species populated during folding and to characterise their structural, dynamic and spectroscopic properties in as much detail, and at as high a resolution, as possible. Whilst this can be readily achieved for the native state using NMR or X-ray methods, the transient nature, c ...
Nucleotide sequence of the 3h-terminal two
... (ORF1b), HSP70 homologue (ORF4), a putative HSP90 homologue (ORF5), CP (ORF6) and CPd (ORF7) were identified. In general, the genome organization of GLRaV-3 is consistent with that expected for a typical monopartite closterovirus (Dolja et al., 1994). Our analysis of ORF1a shows that it is incomplet ...
... (ORF1b), HSP70 homologue (ORF4), a putative HSP90 homologue (ORF5), CP (ORF6) and CPd (ORF7) were identified. In general, the genome organization of GLRaV-3 is consistent with that expected for a typical monopartite closterovirus (Dolja et al., 1994). Our analysis of ORF1a shows that it is incomplet ...
Nucleotide sequence of the 3h-terminal two
... (ORF1b), HSP70 homologue (ORF4), a putative HSP90 homologue (ORF5), CP (ORF6) and CPd (ORF7) were identified. In general, the genome organization of GLRaV-3 is consistent with that expected for a typical monopartite closterovirus (Dolja et al., 1994). Our analysis of ORF1a shows that it is incomplet ...
... (ORF1b), HSP70 homologue (ORF4), a putative HSP90 homologue (ORF5), CP (ORF6) and CPd (ORF7) were identified. In general, the genome organization of GLRaV-3 is consistent with that expected for a typical monopartite closterovirus (Dolja et al., 1994). Our analysis of ORF1a shows that it is incomplet ...
Q5B - ICH
... II. Rationale for Analysis of the Expression Construct The purpose of analysing the expression construct is to establish that the correct coding sequence of the product has been incorporated into the host cell and is maintained during culture to the end of production. The genetic sequence of recombi ...
... II. Rationale for Analysis of the Expression Construct The purpose of analysing the expression construct is to establish that the correct coding sequence of the product has been incorporated into the host cell and is maintained during culture to the end of production. The genetic sequence of recombi ...
SINGAPORE’S R&D FRAMEWORK and the TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT
... a Built-In Biomolecular Cavity Database (10,000 Protein and Nucleic Acid Entries) ...
... a Built-In Biomolecular Cavity Database (10,000 Protein and Nucleic Acid Entries) ...
the extent of population exposure to assess clinical safety
... II. Rationale for Analysis of the Expression Construct The purpose of analysing the expression construct is to establish that the correct coding sequence of the product has been incorporated into the host cell and is maintained during culture to the end of production. The genetic sequence of recombi ...
... II. Rationale for Analysis of the Expression Construct The purpose of analysing the expression construct is to establish that the correct coding sequence of the product has been incorporated into the host cell and is maintained during culture to the end of production. The genetic sequence of recombi ...
Automatic identification of topic boundaries in
... Pairwise Sequence comparison: sequence alignment is a crucial operation in bioinformatics, and genetics research. Typically a scoring function is used to rank different alignments so that biologically plausible alignments score higher. Sequence alignments are used to probe sequence databases for sim ...
... Pairwise Sequence comparison: sequence alignment is a crucial operation in bioinformatics, and genetics research. Typically a scoring function is used to rank different alignments so that biologically plausible alignments score higher. Sequence alignments are used to probe sequence databases for sim ...
Gene Section PTPN14 (protein tyrosine phosphatase, non receptor type 14) -
... Localisation to the golgi apparatus in epithelial cell types (Wyatt and Khew-Goodall, 2008) and mitochondria in human sperm has also been reported (Chao et al., 2011). ...
... Localisation to the golgi apparatus in epithelial cell types (Wyatt and Khew-Goodall, 2008) and mitochondria in human sperm has also been reported (Chao et al., 2011). ...
Homology modeling

Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the ""target"" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein (the ""template""). Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of an alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been shown that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure.Evolutionarily related proteins have similar sequences and naturally occurring homologous proteins have similar protein structure.It has been shown that three-dimensional protein structure is evolutionarily more conserved than would be expected on the basis of sequence conservation alone.The sequence alignment and template structure are then used to produce a structural model of the target. Because protein structures are more conserved than DNA sequences, detectable levels of sequence similarity usually imply significant structural similarity.The quality of the homology model is dependent on the quality of the sequence alignment and template structure. The approach can be complicated by the presence of alignment gaps (commonly called indels) that indicate a structural region present in the target but not in the template, and by structure gaps in the template that arise from poor resolution in the experimental procedure (usually X-ray crystallography) used to solve the structure. Model quality declines with decreasing sequence identity; a typical model has ~1–2 Å root mean square deviation between the matched Cα atoms at 70% sequence identity but only 2–4 Å agreement at 25% sequence identity. However, the errors are significantly higher in the loop regions, where the amino acid sequences of the target and template proteins may be completely different.Regions of the model that were constructed without a template, usually by loop modeling, are generally much less accurate than the rest of the model. Errors in side chain packing and position also increase with decreasing identity, and variations in these packing configurations have been suggested as a major reason for poor model quality at low identity. Taken together, these various atomic-position errors are significant and impede the use of homology models for purposes that require atomic-resolution data, such as drug design and protein–protein interaction predictions; even the quaternary structure of a protein may be difficult to predict from homology models of its subunit(s). Nevertheless, homology models can be useful in reaching qualitative conclusions about the biochemistry of the query sequence, especially in formulating hypotheses about why certain residues are conserved, which may in turn lead to experiments to test those hypotheses. For example, the spatial arrangement of conserved residues may suggest whether a particular residue is conserved to stabilize the folding, to participate in binding some small molecule, or to foster association with another protein or nucleic acid. Homology modeling can produce high-quality structural models when the target and template are closely related, which has inspired the formation of a structural genomics consortium dedicated to the production of representative experimental structures for all classes of protein folds. The chief inaccuracies in homology modeling, which worsen with lower sequence identity, derive from errors in the initial sequence alignment and from improper template selection. Like other methods of structure prediction, current practice in homology modeling is assessed in a biennial large-scale experiment known as the Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction, or CASP.