Surface complementarity of buried protein residues
... content3. This is borne out by the fact that site-directed mutagenesis of these residues are generally destabilizing4,5 for the protein. Further sequence and structure comparison studies between naturally occurring homologous proteins show buried residues to mutate only among apolar amino acids5. In ...
... content3. This is borne out by the fact that site-directed mutagenesis of these residues are generally destabilizing4,5 for the protein. Further sequence and structure comparison studies between naturally occurring homologous proteins show buried residues to mutate only among apolar amino acids5. In ...
Dias nummer 1
... B-cell epitope prediction does not seem to make much sense as these only comprise app. 10% of the total number of epitopes and the linear prediction method does predict epitopes internally in the protein which obviously not are surface exposed. When we used two different models for predicting confor ...
... B-cell epitope prediction does not seem to make much sense as these only comprise app. 10% of the total number of epitopes and the linear prediction method does predict epitopes internally in the protein which obviously not are surface exposed. When we used two different models for predicting confor ...
Informatics Software Development and Computational Biology
... High-throughput proteomics is not possible without a sophisticated LIMS. The LIMS provides the foundation for all automated data collection, reduction, and analysis. Multiple LIMS systems are required (e.g., Y2H, Sequencing, Gene Cloning, Protein Pull-down, Mass Spec., etc. May collect very large am ...
... High-throughput proteomics is not possible without a sophisticated LIMS. The LIMS provides the foundation for all automated data collection, reduction, and analysis. Multiple LIMS systems are required (e.g., Y2H, Sequencing, Gene Cloning, Protein Pull-down, Mass Spec., etc. May collect very large am ...
The CamSol Method of Rational Design of Protein Mutants with
... thousands of amino acid substitutions or insertions to identify specific mutations that are predicted to maximally increase the solubility of a protein while preserving its fundamental properties, including its functional structure and binding affinity. The method requires the knowledge of the nativ ...
... thousands of amino acid substitutions or insertions to identify specific mutations that are predicted to maximally increase the solubility of a protein while preserving its fundamental properties, including its functional structure and binding affinity. The method requires the knowledge of the nativ ...
Hydrogen exchange mass spectrometry for the analysis of protein
... except for the amount of time the protein was exposed to D2O. C: Localized exchange information. Quenched samples (from part A, part B, or both) are digested with pepsin or another acid protease. The resulting peptides are analyzed with online HPLC-ESI-MS or with MALDI-MS. The resulting data analysi ...
... except for the amount of time the protein was exposed to D2O. C: Localized exchange information. Quenched samples (from part A, part B, or both) are digested with pepsin or another acid protease. The resulting peptides are analyzed with online HPLC-ESI-MS or with MALDI-MS. The resulting data analysi ...
Selenium incorporation using recombinant techniques
... anomalous scatterer into a protein is the fact that the resulting crystal will be used to obtain all data, making the heavy-atom derivative isomorphous with the protein structure. In the majority of cases, crystallization of an SeMet-labelled protein occurs under identical or very similar conditions ...
... anomalous scatterer into a protein is the fact that the resulting crystal will be used to obtain all data, making the heavy-atom derivative isomorphous with the protein structure. In the majority of cases, crystallization of an SeMet-labelled protein occurs under identical or very similar conditions ...
Sequence Entropy and the Absolute Rate of Amino Acid Substitutions
... that sequences from real proteins, as well as proteins from evolutionary simulations under selection for thermostability, tend to have a narrow range of stability values(23, 25-28). This stability range occurs where the decreasing effectiveness of selection for g ...
... that sequences from real proteins, as well as proteins from evolutionary simulations under selection for thermostability, tend to have a narrow range of stability values(23, 25-28). This stability range occurs where the decreasing effectiveness of selection for g ...
Dell`Orphano: SNP discovery
... • Filter 3 & 4: Addressed quality of each base call relative to its position and frequency in a contig. First 100 bases discarded. Consed view of a contig containing a high quality mismatch (A vs. T). The mismatch has been confirmed as a common SNP. ...
... • Filter 3 & 4: Addressed quality of each base call relative to its position and frequency in a contig. First 100 bases discarded. Consed view of a contig containing a high quality mismatch (A vs. T). The mismatch has been confirmed as a common SNP. ...
Localization of Protein-Protein lnteractions between Subunits of
... a second protein. If one of the segments of the second protein contains a region through which the new chimeric protein is able to properly self-associate, activity will be restored. We have used the h repressor (cl) as the first component in our assay system. The native h repressor is a homodimer o ...
... a second protein. If one of the segments of the second protein contains a region through which the new chimeric protein is able to properly self-associate, activity will be restored. We have used the h repressor (cl) as the first component in our assay system. The native h repressor is a homodimer o ...
Localization of Protein-Protein lnteractions between Subunits of
... a second protein. If one of the segments of the second protein contains a region through which the new chimeric protein is able to properly self-associate, activity will be restored. We have used the h repressor (cl) as the first component in our assay system. The native h repressor is a homodimer o ...
... a second protein. If one of the segments of the second protein contains a region through which the new chimeric protein is able to properly self-associate, activity will be restored. We have used the h repressor (cl) as the first component in our assay system. The native h repressor is a homodimer o ...
Lecture on BLAST
... custom position-specific score matrix • Bootstrapping results to find very related sequences • Megablast: • Search longer sequences with fewer differences • WU-BLAST: (Wash U BLAST) • Optimized, added features ...
... custom position-specific score matrix • Bootstrapping results to find very related sequences • Megablast: • Search longer sequences with fewer differences • WU-BLAST: (Wash U BLAST) • Optimized, added features ...
Slide 1
... COGs were delineated by comparing protein sequences encoded in 43 complete genomes representing 30 major phylogenetic lineages. Each Cluster has representatives of at least 3 lineages ...
... COGs were delineated by comparing protein sequences encoded in 43 complete genomes representing 30 major phylogenetic lineages. Each Cluster has representatives of at least 3 lineages ...
Proteins: Classification and Types
... Chymotrpsinogen in the native form with 245 amino acid chain. It becomes active (α-chymotrypsin) by removal of two dipeptides ( amino acid14-15, and amino acid -147-148) and cleaving the long chain 245 amino acid chain into three fragments (1-13, 16-146 and 149-245) which then get joined by disulfid ...
... Chymotrpsinogen in the native form with 245 amino acid chain. It becomes active (α-chymotrypsin) by removal of two dipeptides ( amino acid14-15, and amino acid -147-148) and cleaving the long chain 245 amino acid chain into three fragments (1-13, 16-146 and 149-245) which then get joined by disulfid ...
Sequencing the World of Possibilities for Energy & Environment
... Clusters of orthologous groups (COGs) COGs were delineated by comparing protein sequences encoded in 43 complete genomes representing 30 major phylogenetic lineages. Each Cluster has representatives of at least 3 lineages ...
... Clusters of orthologous groups (COGs) COGs were delineated by comparing protein sequences encoded in 43 complete genomes representing 30 major phylogenetic lineages. Each Cluster has representatives of at least 3 lineages ...
Gene encoding the group B streptococcal protein R4, its
... prototypic reference antisera for R4 in double-diffusion (results not shown). The trypsin-extracted R4 showed a precipitin result with anti-R4 antiserum for both controls. As the classic example of pepsin sensitivity for pepsin at pH2, no precipitin result was shown. At pH4, pH6 and pH8, however, pr ...
... prototypic reference antisera for R4 in double-diffusion (results not shown). The trypsin-extracted R4 showed a precipitin result with anti-R4 antiserum for both controls. As the classic example of pepsin sensitivity for pepsin at pH2, no precipitin result was shown. At pH4, pH6 and pH8, however, pr ...
Fluorescence Study of Bovine β-Lactoglobulin
... 10. Albani JR (2007) New insights in the interpretation of tryptophan fluorescence: origin of the fluorescence lifetime and characterization of a new fluorescence parameter in proteins: the emission to excitation ratio. J fluoresc 17: 406-417. 11. Albani JR (2009) Fluorescence lifetimes of tryptopha ...
... 10. Albani JR (2007) New insights in the interpretation of tryptophan fluorescence: origin of the fluorescence lifetime and characterization of a new fluorescence parameter in proteins: the emission to excitation ratio. J fluoresc 17: 406-417. 11. Albani JR (2009) Fluorescence lifetimes of tryptopha ...
New insight into plant intramembrane proteases
... plant and its responses to a changeable environment. Recent research has shown that proteases are not only engaged in quality control and protein turnover processes but also participate in the process which is known as regulated membrane proteolysis (RIP). Four families of integral membrane protease ...
... plant and its responses to a changeable environment. Recent research has shown that proteases are not only engaged in quality control and protein turnover processes but also participate in the process which is known as regulated membrane proteolysis (RIP). Four families of integral membrane protease ...
Chapter 5A Lecture
... Molecular oxygen (O2) is only slightly soluble in aqueous solution. It cannot be carried to tissues in sufficient quantity if it is simply dissolved in blood plasma. Diffusion of O2 through the tissues is also ineffective over distances of greater than a few millimeters. For these reasons the evolut ...
... Molecular oxygen (O2) is only slightly soluble in aqueous solution. It cannot be carried to tissues in sufficient quantity if it is simply dissolved in blood plasma. Diffusion of O2 through the tissues is also ineffective over distances of greater than a few millimeters. For these reasons the evolut ...
Full-Text PDF
... Antibiotics are agents that suppress bacterial growth or kill bacteria. The term “antibiotic” was introduced in 1942 by Waksman and his collaborators. At first, antibiotics included only microbially-originated chemical substances, which inhibit the growth or the metabolic activities of bacteria and ...
... Antibiotics are agents that suppress bacterial growth or kill bacteria. The term “antibiotic” was introduced in 1942 by Waksman and his collaborators. At first, antibiotics included only microbially-originated chemical substances, which inhibit the growth or the metabolic activities of bacteria and ...
Protein Foods
... o Complete: Animal sources of protein. These proteins contain all of the protein building blocks called amino acids that your body needs to grow and maintain tissue. o Incomplete: Plant sources of protein. These proteins are missing one or more amino acids; not all of the building blocks are there. ...
... o Complete: Animal sources of protein. These proteins contain all of the protein building blocks called amino acids that your body needs to grow and maintain tissue. o Incomplete: Plant sources of protein. These proteins are missing one or more amino acids; not all of the building blocks are there. ...
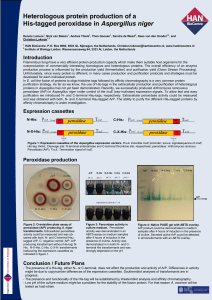
Heterologous protein production of a His-tagged peroxidase
... Filamentous fungi have a very efficient protein-production capacity which make them suitable host organisms for the overproduction of commercially interesting homologous and heterologous proteins. The overall efficiency of an enzyme production process is influenced by the production yield (fermentat ...
... Filamentous fungi have a very efficient protein-production capacity which make them suitable host organisms for the overproduction of commercially interesting homologous and heterologous proteins. The overall efficiency of an enzyme production process is influenced by the production yield (fermentat ...
A Survey of Left-handed Helices in Protein Structures
... residues whose f angles are all between 308 and 1308 and whose j angles are all between K508 and 1008. Subsequently, a non-redundant subset of the PDB (version of September, 2003) was generated with the PISCES server.18 To produce a large enough subset, relaxed criteria were used in the generation o ...
... residues whose f angles are all between 308 and 1308 and whose j angles are all between K508 and 1008. Subsequently, a non-redundant subset of the PDB (version of September, 2003) was generated with the PISCES server.18 To produce a large enough subset, relaxed criteria were used in the generation o ...
Homology modeling

Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the ""target"" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein (the ""template""). Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of an alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been shown that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure.Evolutionarily related proteins have similar sequences and naturally occurring homologous proteins have similar protein structure.It has been shown that three-dimensional protein structure is evolutionarily more conserved than would be expected on the basis of sequence conservation alone.The sequence alignment and template structure are then used to produce a structural model of the target. Because protein structures are more conserved than DNA sequences, detectable levels of sequence similarity usually imply significant structural similarity.The quality of the homology model is dependent on the quality of the sequence alignment and template structure. The approach can be complicated by the presence of alignment gaps (commonly called indels) that indicate a structural region present in the target but not in the template, and by structure gaps in the template that arise from poor resolution in the experimental procedure (usually X-ray crystallography) used to solve the structure. Model quality declines with decreasing sequence identity; a typical model has ~1–2 Å root mean square deviation between the matched Cα atoms at 70% sequence identity but only 2–4 Å agreement at 25% sequence identity. However, the errors are significantly higher in the loop regions, where the amino acid sequences of the target and template proteins may be completely different.Regions of the model that were constructed without a template, usually by loop modeling, are generally much less accurate than the rest of the model. Errors in side chain packing and position also increase with decreasing identity, and variations in these packing configurations have been suggested as a major reason for poor model quality at low identity. Taken together, these various atomic-position errors are significant and impede the use of homology models for purposes that require atomic-resolution data, such as drug design and protein–protein interaction predictions; even the quaternary structure of a protein may be difficult to predict from homology models of its subunit(s). Nevertheless, homology models can be useful in reaching qualitative conclusions about the biochemistry of the query sequence, especially in formulating hypotheses about why certain residues are conserved, which may in turn lead to experiments to test those hypotheses. For example, the spatial arrangement of conserved residues may suggest whether a particular residue is conserved to stabilize the folding, to participate in binding some small molecule, or to foster association with another protein or nucleic acid. Homology modeling can produce high-quality structural models when the target and template are closely related, which has inspired the formation of a structural genomics consortium dedicated to the production of representative experimental structures for all classes of protein folds. The chief inaccuracies in homology modeling, which worsen with lower sequence identity, derive from errors in the initial sequence alignment and from improper template selection. Like other methods of structure prediction, current practice in homology modeling is assessed in a biennial large-scale experiment known as the Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction, or CASP.