The Different Jobs of Cells
... B. Types of Plant Cells • Plants have different type of cells in their leaves, roots, and stems • Root Cells are block shaped and do not ...
... B. Types of Plant Cells • Plants have different type of cells in their leaves, roots, and stems • Root Cells are block shaped and do not ...
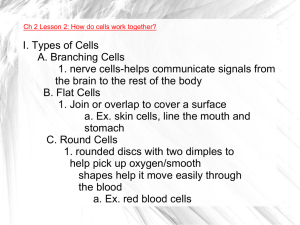
I. Types of Cells A. Branching Cells 1. nerve cells
... 1. Join or overlap to cover a surface a. Ex. skin cells, line the mouth and stomach C. Round Cells 1. rounded discs with two dimples to help pick up oxygen/smooth shapes help it move easily through the blood a. Ex. red blood cells ...
... 1. Join or overlap to cover a surface a. Ex. skin cells, line the mouth and stomach C. Round Cells 1. rounded discs with two dimples to help pick up oxygen/smooth shapes help it move easily through the blood a. Ex. red blood cells ...
N5- Unit 2 MO1-Cells, tissues, organs, stem cells and meristems 1
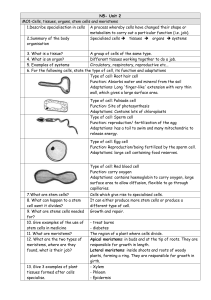
... Adaptations: contains haemoglobin to carry oxygen, large surface area to allow diffusion, flexible to go through capillaries. 7.What are stem cells? 8. What can happen to a stem cell went it divides? 9. What are stems cells needed for? 10. Give examples of the use of stem cells in medicine 11. What ...
... Adaptations: contains haemoglobin to carry oxygen, large surface area to allow diffusion, flexible to go through capillaries. 7.What are stem cells? 8. What can happen to a stem cell went it divides? 9. What are stems cells needed for? 10. Give examples of the use of stem cells in medicine 11. What ...
Living Systems PowerPoint Notes
... __________________ organisms. Multicellular organisms have _____________ _____________ – (humans have many trillion cells). The cells must remain a part of the organism’s body to _____________. Your body is made up of many _____________ _____________ of cells. You have skin cells, Organisms that are ...
... __________________ organisms. Multicellular organisms have _____________ _____________ – (humans have many trillion cells). The cells must remain a part of the organism’s body to _____________. Your body is made up of many _____________ _____________ of cells. You have skin cells, Organisms that are ...
I`m Bigger Than You
... I’m Bigger Than You An organ, such as the heart, is made up of groups of tissues that work together to perform a specific function. The heart is a pump that keeps blood flowing throughout the body. The heart is primarily made up of muscle tissue, but also contains connective and nerve tissue. Howeve ...
... I’m Bigger Than You An organ, such as the heart, is made up of groups of tissues that work together to perform a specific function. The heart is a pump that keeps blood flowing throughout the body. The heart is primarily made up of muscle tissue, but also contains connective and nerve tissue. Howeve ...
Investigation 1 “Living Cells” Big Ideas
... 2. How do cells get the things they need to survive? a. The circulatory system delivers water, sugar, and oxygen to cells and carries waste carbon dioxide away from the cells. 3. What is the general path taken by blood through the circulatory system? a. From the body to the right atrium of the heart ...
... 2. How do cells get the things they need to survive? a. The circulatory system delivers water, sugar, and oxygen to cells and carries waste carbon dioxide away from the cells. 3. What is the general path taken by blood through the circulatory system? a. From the body to the right atrium of the heart ...
National 4/5 Biology - Multicelluar Organisms
... * Cells will vary in size, shape, and structure * - this allows these cells to perform different functions ...
... * Cells will vary in size, shape, and structure * - this allows these cells to perform different functions ...
Fertilization
... Embryo splits into two during the early stages of development Have identical genes and must be of the same sex (Incidence: about 3 in every 1000 births) ...
... Embryo splits into two during the early stages of development Have identical genes and must be of the same sex (Incidence: about 3 in every 1000 births) ...
Semester 1 Exam Study Guide
... Hooke- observed cork cells Leeuwenhoek- observed bacteria and protists Schleiden- studied plant cells Schwann- studied animal cells Virchow- Discovered that all cells come from living things; cell theory Janssen – first compound microscope ...
... Hooke- observed cork cells Leeuwenhoek- observed bacteria and protists Schleiden- studied plant cells Schwann- studied animal cells Virchow- Discovered that all cells come from living things; cell theory Janssen – first compound microscope ...
Cell Theory Organelles Brain Cells Need a Tissue?
... This structure contains at least two types of tissues that work together to perform a specific ...
... This structure contains at least two types of tissues that work together to perform a specific ...
levels of organization directed reading
... into five categories: cells, tissues, organs, systems, organism. When we are organizing these parts, you can consider them as levels or parts of a whole. Organisms are made of multiple systems; each system is composed of different organs; each organ can be divided into different tissues; each tissue ...
... into five categories: cells, tissues, organs, systems, organism. When we are organizing these parts, you can consider them as levels or parts of a whole. Organisms are made of multiple systems; each system is composed of different organs; each organ can be divided into different tissues; each tissue ...
7A Cells
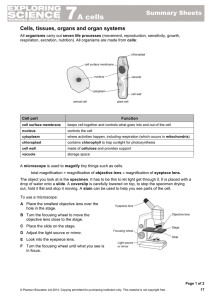
... Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems All organisms carry out seven life processes (movement, reproduction, sensitivity, growth, respiration, excretion, nutrition). All organisms are made from cells: ...
... Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems All organisms carry out seven life processes (movement, reproduction, sensitivity, growth, respiration, excretion, nutrition). All organisms are made from cells: ...
KS3 Science - Benjamin Britten School
... Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems All organisms carry out seven life processes (movement, reproduction, sensitivity, growth, respiration, excretion, nutrition). All organisms are made from cells: ...
... Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems All organisms carry out seven life processes (movement, reproduction, sensitivity, growth, respiration, excretion, nutrition). All organisms are made from cells: ...
3. What two organelles are unique to plant cells? • cell wall: ______
... Which system is responsible for filtering chemical waste from the blood (other than CO2)? Use the organs in this system to explain. ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ...
... Which system is responsible for filtering chemical waste from the blood (other than CO2)? Use the organs in this system to explain. ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ...
7A cells
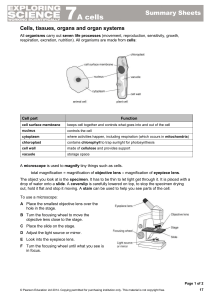
... Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems All organisms carry out seven life processes (movement, reproduction, sensitivity, growth, respiration, excretion, nutrition). All organisms are made from cells: ...
... Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems All organisms carry out seven life processes (movement, reproduction, sensitivity, growth, respiration, excretion, nutrition). All organisms are made from cells: ...
KS3 Science
... Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems All organisms carry out seven life processes (movement, reproduction, sensitivity, growth, respiration, excretion, nutrition). All organisms are made from cells: ...
... Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems All organisms carry out seven life processes (movement, reproduction, sensitivity, growth, respiration, excretion, nutrition). All organisms are made from cells: ...
Unit A - apel slice
... 1. Cells that work together to carry out a function make up a _____. 2. The group of organs and tissues that exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs is the _____. 3. A group of organs that work together to carry out life processes is an _____. 4. Tissues that work with your skeleton to help ...
... 1. Cells that work together to carry out a function make up a _____. 2. The group of organs and tissues that exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs is the _____. 3. A group of organs that work together to carry out life processes is an _____. 4. Tissues that work with your skeleton to help ...
Cell Theory
... Cells carry genetic material passed to daughter cells during cellular division. All cells are essentially the same in chemical composition. Energy flow (metabolism and biochemistry) occurs within cells. ...
... Cells carry genetic material passed to daughter cells during cellular division. All cells are essentially the same in chemical composition. Energy flow (metabolism and biochemistry) occurs within cells. ...
Chimera (genetics)

A chimera (also spelled chimaera) (from the creature Chimera in Greek mythology) is a single organism composed of genetically distinct cells. This can result in male and female organs, two blood types, or subtle variations in form. Animal chimeras are produced by the merger of multiple fertilized eggs. In plant chimeras, however, the distinct types of tissue may originate from the same zygote, and the difference is often due to mutation during ordinary cell division. Normally, chimerism is not visible on casual inspection; however, it has been detected in the course of proving parentage.Another way that chimerism can occur in animals is by organ transplantation, giving one individual tissues that developed from two genomes. For example, a bone marrow transplant can change someone's blood type.