Test Study Guide-cell processes_ homeostasis2
... SHORT ANSWER: Know the four things that cells need to maintain homeostasis: obtain and use energy, make new cells, exchange materials, and eliminate wastes Know that cells in multicellular organisms work together to maintain homeostasis for the entire organism. SHORT ANSWER: Know the main tran ...
... SHORT ANSWER: Know the four things that cells need to maintain homeostasis: obtain and use energy, make new cells, exchange materials, and eliminate wastes Know that cells in multicellular organisms work together to maintain homeostasis for the entire organism. SHORT ANSWER: Know the main tran ...
1-3 Studying Life: Read pages 16-22 carefully
... b. A multicellular organism may contain trillions of cells. c. A living thing that consists of a single cell is a multicellular organism. d. Organisms are made up of cells. 4. A type of asexual reproduction where a portion of the organism splits off to form a new organism is called _________________ ...
... b. A multicellular organism may contain trillions of cells. c. A living thing that consists of a single cell is a multicellular organism. d. Organisms are made up of cells. 4. A type of asexual reproduction where a portion of the organism splits off to form a new organism is called _________________ ...
Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems
... •Generalization: A group of cells working together make up tissues, a group of tissues working together make up organs, a group of organs working together make up an organ system, and a group of organ systems working together make up an organism. ...
... •Generalization: A group of cells working together make up tissues, a group of tissues working together make up organs, a group of organs working together make up an organ system, and a group of organ systems working together make up an organism. ...
Sex Differentiation
... Totipotent Inner Cell Mass Monozygotic (identical) twins Splitting of a single inner cell mass (totipotent) into two or three independent embryos ...
... Totipotent Inner Cell Mass Monozygotic (identical) twins Splitting of a single inner cell mass (totipotent) into two or three independent embryos ...
Week 2 Lecture Summarys copy
... Week 2- Prenatal Development and the Newborn Principles of prenatal development: -proximodistal sequence: growth occurs from the most interior parts of the body outwards -cephalocaudal sequence: growth occurs in a sequence from head to toe -mass-to- specific sequence: large structures and movements ...
... Week 2- Prenatal Development and the Newborn Principles of prenatal development: -proximodistal sequence: growth occurs from the most interior parts of the body outwards -cephalocaudal sequence: growth occurs in a sequence from head to toe -mass-to- specific sequence: large structures and movements ...
Unit V Outline
... point where they can survive on their own, and are born. iv. In mammals, fertilization takes place inside the females body, and the embryos typically develop within a structure called the womb, or uterus. v. The offspring are born in an underdeveloped condition and, for a period, feed on mothers mil ...
... point where they can survive on their own, and are born. iv. In mammals, fertilization takes place inside the females body, and the embryos typically develop within a structure called the womb, or uterus. v. The offspring are born in an underdeveloped condition and, for a period, feed on mothers mil ...
GCSE Cells Topic Learning Checklist
... Recall that stem cells from human embryos and adult bone marrow can be cloned and made to ...
... Recall that stem cells from human embryos and adult bone marrow can be cloned and made to ...
1-3 Studying Life
... b. A multicellular organism may contain trillions of cells. c. A living thing that consists of a single cell is a multicellular organism. d. Organisms are made up of cells. 4. A type of asexual reproduction where a portion of the organism splits off to form a new organism is called _________________ ...
... b. A multicellular organism may contain trillions of cells. c. A living thing that consists of a single cell is a multicellular organism. d. Organisms are made up of cells. 4. A type of asexual reproduction where a portion of the organism splits off to form a new organism is called _________________ ...
1-3_studying_life
... b. A multicellular organism may contain trillions of cells. c. A living thing that consists of a single cell is a multicellular organism. d. Organisms are made up of cells. 4. A type of asexual reproduction where a portion of the organism splits off to form a new organism is called _________________ ...
... b. A multicellular organism may contain trillions of cells. c. A living thing that consists of a single cell is a multicellular organism. d. Organisms are made up of cells. 4. A type of asexual reproduction where a portion of the organism splits off to form a new organism is called _________________ ...
stem cell
... organisms, multicellular organisms are made of many cells that are specialized to perform particular tasks. Multicellular organisms are made up of specialized cells that work together to make tissues, followed by organs, then organ systems, and finally an organism. ...
... organisms, multicellular organisms are made of many cells that are specialized to perform particular tasks. Multicellular organisms are made up of specialized cells that work together to make tissues, followed by organs, then organ systems, and finally an organism. ...
The History of Cell Biology
... of the cubicles or “cells” in which monks lived, so he called them cells. What Hooke had observed were actually the remains of dead plant cells. The first person to observe living cells was a Dutch trader, Anton van Leeuwenhoek. Although van Leeuwenhoek’s microscope was rather simple, in 1673 it was ...
... of the cubicles or “cells” in which monks lived, so he called them cells. What Hooke had observed were actually the remains of dead plant cells. The first person to observe living cells was a Dutch trader, Anton van Leeuwenhoek. Although van Leeuwenhoek’s microscope was rather simple, in 1673 it was ...
active reading worksheets
... of the cubicles or “cells” in which monks lived, so he called them cells. What Hooke had observed were actually the remains of dead plant cells. The first person to observe living cells was a Dutch trader, Anton van Leeuwenhoek. Although van Leeuwenhoek’s microscope was rather simple, in 1673 it was ...
... of the cubicles or “cells” in which monks lived, so he called them cells. What Hooke had observed were actually the remains of dead plant cells. The first person to observe living cells was a Dutch trader, Anton van Leeuwenhoek. Although van Leeuwenhoek’s microscope was rather simple, in 1673 it was ...
active reading worksheets
... of the cubicles or “cells” in which monks lived, so he called them cells. What Hooke had observed were actually the remains of dead plant cells. The first person to observe living cells was a Dutch trader, Anton van Leeuwenhoek. Although van Leeuwenhoek’s microscope was rather simple, in 1673 it was ...
... of the cubicles or “cells” in which monks lived, so he called them cells. What Hooke had observed were actually the remains of dead plant cells. The first person to observe living cells was a Dutch trader, Anton van Leeuwenhoek. Although van Leeuwenhoek’s microscope was rather simple, in 1673 it was ...
Cells and Systems Notes Topic 1 1. What are five characteristics that
... 5. What are the two types of microscopes and tell me which is the most powerful? ...
... 5. What are the two types of microscopes and tell me which is the most powerful? ...
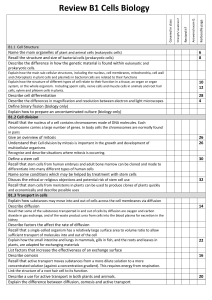
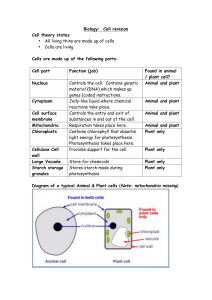
Biology Cell revision
... Groups of cells Complicated organisms (like you) are made of billion of cells. • A group of similar cells is called tissue. (e.g. muscle tissue) • A group of similar tissue is called an organ (e.g. heart) • A group of similar organs is called a system (e.g. circulatory system) • A group of systems i ...
... Groups of cells Complicated organisms (like you) are made of billion of cells. • A group of similar cells is called tissue. (e.g. muscle tissue) • A group of similar tissue is called an organ (e.g. heart) • A group of similar organs is called a system (e.g. circulatory system) • A group of systems i ...
SEVENTH GRADE LIFE SCIENCES THEME: LIFE AROUND US
... 1. Science Processes and Inquiry – The student will engage in investigations that lead to the discovery of science concepts. a. Use appropriate tools and technology to perform tests, collect and display data. b. Use a variety of resources to collect information for research. c. Select the most logic ...
... 1. Science Processes and Inquiry – The student will engage in investigations that lead to the discovery of science concepts. a. Use appropriate tools and technology to perform tests, collect and display data. b. Use a variety of resources to collect information for research. c. Select the most logic ...
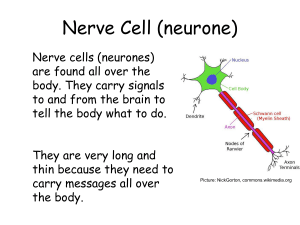
L4-specialised-cells-cards
... muscles they can stretch without being broken. They also contain small organelles called mitochondria which can release energy from food for movement ...
... muscles they can stretch without being broken. They also contain small organelles called mitochondria which can release energy from food for movement ...
National 5: Multicellular Organisms Summary
... impulses move along neurons. A synapse occurs between neurons, allowing chemicals to transfer from one neuron to another. Hormonal control Endocrine glands release hormones into the blood stream. Hormones are chemical messengers. Target tissues have cells with receptors for hormones, so only some ...
... impulses move along neurons. A synapse occurs between neurons, allowing chemicals to transfer from one neuron to another. Hormonal control Endocrine glands release hormones into the blood stream. Hormones are chemical messengers. Target tissues have cells with receptors for hormones, so only some ...
Living Systems
... different types of molecules including proteins, carbohydrates, and others. • Your body contains trillions of cells, each one a living system on its own. ...
... different types of molecules including proteins, carbohydrates, and others. • Your body contains trillions of cells, each one a living system on its own. ...
Sc 8 Unit 2 Topic 5 Notes WP
... - They can grow very large. - They can get their energy from a wide variety of foods. - Their cells are more efficient because they can specialize in their particular function and these specialized cells get grouped together and they can work with other cells performing the same function. Many plant ...
... - They can grow very large. - They can get their energy from a wide variety of foods. - Their cells are more efficient because they can specialize in their particular function and these specialized cells get grouped together and they can work with other cells performing the same function. Many plant ...
Chimera (genetics)

A chimera (also spelled chimaera) (from the creature Chimera in Greek mythology) is a single organism composed of genetically distinct cells. This can result in male and female organs, two blood types, or subtle variations in form. Animal chimeras are produced by the merger of multiple fertilized eggs. In plant chimeras, however, the distinct types of tissue may originate from the same zygote, and the difference is often due to mutation during ordinary cell division. Normally, chimerism is not visible on casual inspection; however, it has been detected in the course of proving parentage.Another way that chimerism can occur in animals is by organ transplantation, giving one individual tissues that developed from two genomes. For example, a bone marrow transplant can change someone's blood type.