3 Gamma-Ray Detectors
... preferred for detailed spectroscopy, such as the analysis of the complex low-energy gamma-ray and x-ray spectra of uranium and plutonium. Because of their high resolution, semiconductor detectors are relatively sensitive to performance degradation from radiation damage. The amount of damage produced ...
... preferred for detailed spectroscopy, such as the analysis of the complex low-energy gamma-ray and x-ray spectra of uranium and plutonium. Because of their high resolution, semiconductor detectors are relatively sensitive to performance degradation from radiation damage. The amount of damage produced ...
Questions - Clever Teach
... (iii) One theory of the origin of the Universe predicted that there should be cosmic background radiation with a wavelength of about 1 mm. Explain why scientists had to wait until the development of space flight before they could study this radiation in detail. ...
... (iii) One theory of the origin of the Universe predicted that there should be cosmic background radiation with a wavelength of about 1 mm. Explain why scientists had to wait until the development of space flight before they could study this radiation in detail. ...
The Milky Way Model - University of Chicago
... closely packed stars, was it part of the Earth’s atmosphere or at great astronomical distances? These days, looking up at the sky from even a small city or suburb, the Milky Way isn’t even visible anymore due to light pollution and has lost its hold on imagination of most people on Earth. Yet at the ...
... closely packed stars, was it part of the Earth’s atmosphere or at great astronomical distances? These days, looking up at the sky from even a small city or suburb, the Milky Way isn’t even visible anymore due to light pollution and has lost its hold on imagination of most people on Earth. Yet at the ...
Galaxies (and stars) in the far infrared: results from the AKARI All
... Supply of metals to the interstellar space II: final life stages of stars The death of light stars : planetary nebulae (PNe) Stars with masses similar to the Sun run out the hydrogen in the core, change their equilibrium structure and expand, and become cool huge stars (red giant branch stars: RGBs ...
... Supply of metals to the interstellar space II: final life stages of stars The death of light stars : planetary nebulae (PNe) Stars with masses similar to the Sun run out the hydrogen in the core, change their equilibrium structure and expand, and become cool huge stars (red giant branch stars: RGBs ...
4 Distances in Astronomy
... 0:500 , which can sometimes be reduced to about 0:0100 by averaging over many measurements. This corresponds to a distance of about 300 ly. Spacebased telescopes can do better (see the discussion of Hipparcos below), but so far the most distant stars for which parallax has been measured reliably are ...
... 0:500 , which can sometimes be reduced to about 0:0100 by averaging over many measurements. This corresponds to a distance of about 300 ly. Spacebased telescopes can do better (see the discussion of Hipparcos below), but so far the most distant stars for which parallax has been measured reliably are ...
Chapter 31 - The Galaxy & Universe
... 1. The outcome of the Universe depends on the amount (density) of material in it. a) Less than critical density (10-26 kg/m3) results in open Universe. ...
... 1. The outcome of the Universe depends on the amount (density) of material in it. a) Less than critical density (10-26 kg/m3) results in open Universe. ...
M101: The Pinwheel Galaxy
... understand about galaxies.You can use these statements to evaluate your students’ misconceptions. Ask students to volunteer their ideas, or collect their papers, compile a list of misconceptions, and discuss them with the class. Ask students to review the galaxy image on the front of the “M101: The ...
... understand about galaxies.You can use these statements to evaluate your students’ misconceptions. Ask students to volunteer their ideas, or collect their papers, compile a list of misconceptions, and discuss them with the class. Ask students to review the galaxy image on the front of the “M101: The ...
X-Ray Telescope
... Now we have TeV emission, we will be able to determine the Emax. Older SNRs should be studied more for proton acceleration study. ...
... Now we have TeV emission, we will be able to determine the Emax. Older SNRs should be studied more for proton acceleration study. ...
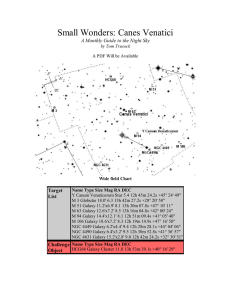
Small Wonders: Canes Venatici
... the differences seen when moving between different size scopes. Can you spot the large HII region visually? ...
... the differences seen when moving between different size scopes. Can you spot the large HII region visually? ...
ACTIVE GALAXIES
... • Head-tail radio galaxies arise when jets are bent by the ram-pressure of gas as the host galaxy moves through it. • For powerful sources only one jet is seen: this is because of RELATIVISTIC DOPPER BOOSTING: the approaching jet appears MUCH brighter than an intrinsically equal receding jet since m ...
... • Head-tail radio galaxies arise when jets are bent by the ram-pressure of gas as the host galaxy moves through it. • For powerful sources only one jet is seen: this is because of RELATIVISTIC DOPPER BOOSTING: the approaching jet appears MUCH brighter than an intrinsically equal receding jet since m ...
Staring Back to Cosmic Dawn - UC-HiPACC
... z8_GND_5296, appears red due to its extreme redshift. It’s forming stars at a rate about 100 times greater than our Milky Way. ...
... z8_GND_5296, appears red due to its extreme redshift. It’s forming stars at a rate about 100 times greater than our Milky Way. ...
Astronomy 112: The Physics of Stars Class 18 Notes: Neutron Stars
... as the magnetic field. The period, which is simply P = 2π/ω, decreases by the same factor. As with the magnetic field, we’re not exactly sure what rotation rates should be for massive star cores, but we can guess based on white dwarfs. The fastest rotating of these, which are probably the youngest a ...
... as the magnetic field. The period, which is simply P = 2π/ω, decreases by the same factor. As with the magnetic field, we’re not exactly sure what rotation rates should be for massive star cores, but we can guess based on white dwarfs. The fastest rotating of these, which are probably the youngest a ...
SPACETIME SINGULARITIES: The STORY of BLACK HOLES
... the GR equations, but that much more important, they were almost inevitable. To put this another way - no matter what kind of universe one had, there had to be singularities in it somewhere! This purely theoretical work coincided roughly with several other developments, all in the 1960’s, as follows ...
... the GR equations, but that much more important, they were almost inevitable. To put this another way - no matter what kind of universe one had, there had to be singularities in it somewhere! This purely theoretical work coincided roughly with several other developments, all in the 1960’s, as follows ...
D109-08x
... on our overall understanding of galaxy evolution. Since these extreme galaxies exist, then there are obviously physical mechanisms available for their formation and/or current evolutionary state. In some cases these mechanism involve gravitational/hydrodynamical interactions with the environment/IGM ...
... on our overall understanding of galaxy evolution. Since these extreme galaxies exist, then there are obviously physical mechanisms available for their formation and/or current evolutionary state. In some cases these mechanism involve gravitational/hydrodynamical interactions with the environment/IGM ...
T Einstein’s Mirage Paul L. Schechter
... academic curiosities, far too unlikely to actually be observed. But in 1979what appeared to be a close pair of virtually identical quasars was observed. Quasars are very bright distant sources, so light from them sometimes passes near galaxies on its way to us. The suspicion that they were the multi ...
... academic curiosities, far too unlikely to actually be observed. But in 1979what appeared to be a close pair of virtually identical quasars was observed. Quasars are very bright distant sources, so light from them sometimes passes near galaxies on its way to us. The suspicion that they were the multi ...
MOPTOP
... relativistic plasma dynamics) in such transient sources as blazars, active galactic nuclei, X-ray binaries and gamma ray bursts (GRBs) (see Jermak et al 2016 for an example of studying linear polarisation in blazars). As an example, use of polarimetry as a diagnostic tool in time domain programs has ...
... relativistic plasma dynamics) in such transient sources as blazars, active galactic nuclei, X-ray binaries and gamma ray bursts (GRBs) (see Jermak et al 2016 for an example of studying linear polarisation in blazars). As an example, use of polarimetry as a diagnostic tool in time domain programs has ...
Supernovae and supernova remnants
... this phase comes from the following series of radioactive decays: 56Ni (7 days) → 56Co (77 days) → 56Fe. This decay series will keep the supernova bright for several months. The ejecta, rich in heavier elements, will eventually form another generation of stars and planets. The ejecta first expand at ...
... this phase comes from the following series of radioactive decays: 56Ni (7 days) → 56Co (77 days) → 56Fe. This decay series will keep the supernova bright for several months. The ejecta, rich in heavier elements, will eventually form another generation of stars and planets. The ejecta first expand at ...
24.1 Hubble`s Galaxy Classification
... Variation in shape among barred-spiral galaxies. The variation from SBa to SBc is similar to that for the spirals in Figure 24.2, except that now the spiral arms begin at either end of a bar through the galactic center. In frame (c), the bright star is a foreground object in our own Galaxy; the obje ...
... Variation in shape among barred-spiral galaxies. The variation from SBa to SBc is similar to that for the spirals in Figure 24.2, except that now the spiral arms begin at either end of a bar through the galactic center. In frame (c), the bright star is a foreground object in our own Galaxy; the obje ...
Gamma-ray burst

Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are flashes of gamma rays associated with extremely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the brightest electromagnetic events known to occur in the universe. Bursts can last from ten milliseconds to several hours. The initial burst is usually followed by a longer-lived ""afterglow"" emitted at longer wavelengths (X-ray, ultraviolet, optical, infrared, microwave and radio).Most observed GRBs are believed to consist of a narrow beam of intense radiation released during a supernova or hypernova as a rapidly rotating, high-mass star collapses to form a neutron star, quark star, or black hole. A subclass of GRBs (the ""short"" bursts) appear to originate from a different process – this may be due to the merger of binary neutron stars. The cause of the precursor burst observed in some of these short events may be due to the development of a resonance between the crust and core of such stars as a result of the massive tidal forces experienced in the seconds leading up to their collision, causing the entire crust of the star to shatter.The sources of most GRBs are billions of light years away from Earth, implying that the explosions are both extremely energetic (a typical burst releases as much energy in a few seconds as the Sun will in its entire 10-billion-year lifetime) and extremely rare (a few per galaxy per million years). All observed GRBs have originated from outside the Milky Way galaxy, although a related class of phenomena, soft gamma repeater flares, are associated with magnetars within the Milky Way. It has been hypothesized that a gamma-ray burst in the Milky Way, pointing directly towards the Earth, could cause a mass extinction event.GRBs were first detected in 1967 by the Vela satellites, a series of satellites designed to detect covert nuclear weapons tests. Hundreds of theoretical models were proposed to explain these bursts in the years following their discovery, such as collisions between comets and neutron stars. Little information was available to verify these models until the 1997 detection of the first X-ray and optical afterglows and direct measurement of their redshifts using optical spectroscopy, and thus their distances and energy outputs. These discoveries, and subsequent studies of the galaxies and supernovae associated with the bursts, clarified the distance and luminosity of GRBs. These facts definitively placed them in distant galaxies and also connected long GRBs with the explosion of massive stars, the only possible source for the energy outputs observed.