Stellar Evolution - Hays High Indians
... – Small low mass stars can take billions of years to form – More massive stars can completely form in a few hundred thousand years ...
... – Small low mass stars can take billions of years to form – More massive stars can completely form in a few hundred thousand years ...
The Milky Way - Midlandstech
... Evolution off the Main Sequence: Expansion into a Red Giant When the hydrogen in the core is completely ...
... Evolution off the Main Sequence: Expansion into a Red Giant When the hydrogen in the core is completely ...
The Milky Way - 清華大學物理系歡迎頁 Welcome to
... Evolution off the Main Sequence: Expansion into a Red Giant When the hydrogen in the core is completely ...
... Evolution off the Main Sequence: Expansion into a Red Giant When the hydrogen in the core is completely ...
Day 1: How to Describe the Sky The Motions of the Stars
... • One evening at midnight, you observe Leo high in the Southern sky. Virgo is to the East of Leo and Cancer is to the West. One month earlier, which of these constellations was high in the Southern sky at midnight? • A: Leo • B: Virgo • C: Cancer ...
... • One evening at midnight, you observe Leo high in the Southern sky. Virgo is to the East of Leo and Cancer is to the West. One month earlier, which of these constellations was high in the Southern sky at midnight? • A: Leo • B: Virgo • C: Cancer ...
Toys Watch the Sky - The Sun is a close star
... centre of our Solar System. The Sun is located in an outer spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy, approximately 28,000 light-years from the galaxy's centre. (One light year is about 10 million million km.) In comparison with other stars, our Sun is very ordinary – it’s an average sized (1.4 million km ...
... centre of our Solar System. The Sun is located in an outer spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy, approximately 28,000 light-years from the galaxy's centre. (One light year is about 10 million million km.) In comparison with other stars, our Sun is very ordinary – it’s an average sized (1.4 million km ...
Scientists discover surprising importance of `I Love Q` for
... Yunes, assistant professor in MSU's Department of This is the first time that Yunes and Yagi have Physics. published their work in "Science," the world's leading journal of scientific research, global news The reason – discovered by Yunes and postdoctoral scholar Kent Yagi—is almost universal and co ...
... Yunes, assistant professor in MSU's Department of This is the first time that Yunes and Yagi have Physics. published their work in "Science," the world's leading journal of scientific research, global news The reason – discovered by Yunes and postdoctoral scholar Kent Yagi—is almost universal and co ...
What color are stars?
... Monitoring how binary stars move provide information about stellar masses ...
... Monitoring how binary stars move provide information about stellar masses ...
Astro 210 Lecture 4 Sept. 4, 2013 Announcements: • PS 1 available
... Q: how is BB color related to temperature? ...
... Q: how is BB color related to temperature? ...
proper motion
... The Sun-centered model of the solar system laid out by Copernicus in De Revolutionibus (1543) made a very specific prediction: that the nearby stars should exhibit parallax shifts with respect to the distant background of stars. Tycho Brahe improved positional measures from +/- 10 arc minutes to as ...
... The Sun-centered model of the solar system laid out by Copernicus in De Revolutionibus (1543) made a very specific prediction: that the nearby stars should exhibit parallax shifts with respect to the distant background of stars. Tycho Brahe improved positional measures from +/- 10 arc minutes to as ...
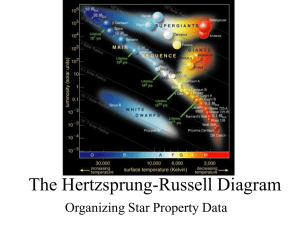
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Most Stars are “Main Sequence” Others are: White Dwarfs, Giants and Supergiants ...
... Most Stars are “Main Sequence” Others are: White Dwarfs, Giants and Supergiants ...
Stars: Their Life and Afterlife
... that SNRs must expand to much larger sizes before sweeping up enough mass to radiate appreciably in the radio – and by then, they are so large that their surface brightness (radio light emitted per unit area) is very low. This may be one reason why we see fewer SNRs in radio than expected from the r ...
... that SNRs must expand to much larger sizes before sweeping up enough mass to radiate appreciably in the radio – and by then, they are so large that their surface brightness (radio light emitted per unit area) is very low. This may be one reason why we see fewer SNRs in radio than expected from the r ...
Document
... • All MS stars to the left have already used up their H fuel and are gone. • The position of the hottest, brightest star on a cluster’s main sequence is called the main sequence turnoff point. ...
... • All MS stars to the left have already used up their H fuel and are gone. • The position of the hottest, brightest star on a cluster’s main sequence is called the main sequence turnoff point. ...
Distance measures - ScienceEducationatNewPaltz
... move across the sky relative to other stars in a definite direction over time. This is called proper motion and must be accounted for when determining parallaxes. If you study the parallax diagram you will see that the greatest baseline ground-based astronomers can obtain is by observing the star at ...
... move across the sky relative to other stars in a definite direction over time. This is called proper motion and must be accounted for when determining parallaxes. If you study the parallax diagram you will see that the greatest baseline ground-based astronomers can obtain is by observing the star at ...
Ch. 15 Notes
... – Easily identifiable by the three stars of his belt during the fall and winter – Betelgeuse, the hunter’s right shoulder, is a red supergiant star. If it was in our sun’s place it would extend to the orbit of Jupiter. It will explode in a supernova explosion sometime in the next 1000 years. When th ...
... – Easily identifiable by the three stars of his belt during the fall and winter – Betelgeuse, the hunter’s right shoulder, is a red supergiant star. If it was in our sun’s place it would extend to the orbit of Jupiter. It will explode in a supernova explosion sometime in the next 1000 years. When th ...
The correct answers are written in bold, italic and underlined. The
... The most massive stars are the most luminous, while less massive stars are distributed down the ZAMS. 2. On the main sequence of the Hertsprung-Russell diagram of a very young cluster, where will the most massive stars be found? • At the very bottom of the main sequence, massive stars being cool bec ...
... The most massive stars are the most luminous, while less massive stars are distributed down the ZAMS. 2. On the main sequence of the Hertsprung-Russell diagram of a very young cluster, where will the most massive stars be found? • At the very bottom of the main sequence, massive stars being cool bec ...
General Astronomy - Stockton University
... reach peak brightness, and in fact more than one flare can occur at time. It may turn out that most red dwarfs are flare stars, and that red dwarfs without violent flare activity are the exception rather than the rule. The first known flare stars (V1396 Cygni and AT Microscopii) were discovered in 1 ...
... reach peak brightness, and in fact more than one flare can occur at time. It may turn out that most red dwarfs are flare stars, and that red dwarfs without violent flare activity are the exception rather than the rule. The first known flare stars (V1396 Cygni and AT Microscopii) were discovered in 1 ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... The masses can be found from M1+M2 (suns) = a(AU)3 / P(yr)2 (individual masses can be gotten if you have a signal from both stars) The orbital period comes from watching the stars, or the periodic variation of their velocity or brightness. To get orbital semimajor axis, you need either the parallax ...
... The masses can be found from M1+M2 (suns) = a(AU)3 / P(yr)2 (individual masses can be gotten if you have a signal from both stars) The orbital period comes from watching the stars, or the periodic variation of their velocity or brightness. To get orbital semimajor axis, you need either the parallax ...
Stars and Constellations Power Point
... We live in the Milky Way galaxy. The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy. It has about 200 billion stars, and lots of gas and dust. All the stars in the Milky Way have their own motion, some are moving towards the sun while others are moving away from our sun. Our Sun is halfway to the edge of an arm, revo ...
... We live in the Milky Way galaxy. The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy. It has about 200 billion stars, and lots of gas and dust. All the stars in the Milky Way have their own motion, some are moving towards the sun while others are moving away from our sun. Our Sun is halfway to the edge of an arm, revo ...
Microsoft Power Point version
... The age of a cluster is equal to the main-sequence lifetime of hottest and most luminous main-sequence stars remaining in the cluster. On an HR diagram of the cluster, these stars sit farthest to the upper left, defining the main-sequence turnoff point of the cluster. ...
... The age of a cluster is equal to the main-sequence lifetime of hottest and most luminous main-sequence stars remaining in the cluster. On an HR diagram of the cluster, these stars sit farthest to the upper left, defining the main-sequence turnoff point of the cluster. ...
16. Properties of Stars
... A star’s luminosity is the total power (energy per unit time) that it radiates into space. It can be calculated from a star’s measured apparent brightness and distance, using the luminosity-distance formula: apparent brightness = luminosity / (4 × distance2). The distance to nearby stars can be meas ...
... A star’s luminosity is the total power (energy per unit time) that it radiates into space. It can be calculated from a star’s measured apparent brightness and distance, using the luminosity-distance formula: apparent brightness = luminosity / (4 × distance2). The distance to nearby stars can be meas ...
Stages of stars - University of Dayton
... gaseous shell, this gas that surrounds the core is called a Planetary Nebula. ...
... gaseous shell, this gas that surrounds the core is called a Planetary Nebula. ...
Characteristics of Stars
... • Astronomers use spectrographs to determine elements found in stars • Spectrograph- a device that breaks light into colors and produces an images of the resulting spectrum. • Most large telescopes have spectrographs to analyze light • Read page 112 ...
... • Astronomers use spectrographs to determine elements found in stars • Spectrograph- a device that breaks light into colors and produces an images of the resulting spectrum. • Most large telescopes have spectrographs to analyze light • Read page 112 ...
Star catalogue

A star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient peoples, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from NASA's Astronomical Data Center.Completeness and accuracy is described by the weakest apparent magnitude V (largest number) and the accuracy of the positions.