Star Constellations
... outdoors at night, like shepherds, named the constellations. They told stories about them. Pictured below is one of the most easily recognized constellations ( Figure 1.1). The ancient Greeks thought this group of stars looked like a hunter. They named it Orion, after a great hunter in Greek mytholo ...
... outdoors at night, like shepherds, named the constellations. They told stories about them. Pictured below is one of the most easily recognized constellations ( Figure 1.1). The ancient Greeks thought this group of stars looked like a hunter. They named it Orion, after a great hunter in Greek mytholo ...
HW7-3
... (261) Learning to Look 1-2; Supp. Q. 4 (260) RQ 3: What is a brown dwarf? A brown dwarf is a “failed star.” They are balls of gas without fusion. The upper end of brown dwarfs is well defined: 8% M☉ = 80 Jupiters. There is a not-so-welldefined line between small brown dwarfs and large ...
... (261) Learning to Look 1-2; Supp. Q. 4 (260) RQ 3: What is a brown dwarf? A brown dwarf is a “failed star.” They are balls of gas without fusion. The upper end of brown dwarfs is well defined: 8% M☉ = 80 Jupiters. There is a not-so-welldefined line between small brown dwarfs and large ...
Document
... • High Mass stars often times explode! • This spreads all of the elements Hydrogen through Iron (which makes up our planets and other new stars) and forms all elements after Iron (up to element 92). ...
... • High Mass stars often times explode! • This spreads all of the elements Hydrogen through Iron (which makes up our planets and other new stars) and forms all elements after Iron (up to element 92). ...
guide to orion 3-d flythrough
... The central area of the nebula is called the Trapezium cluster. It is dominated by four young, massive stars in a kite-like arrangement. The brightest of these stars, which has a luminosity 100,000 times that of the Sun, provides the energy that creates the nebula as we see it. It produces a flood o ...
... The central area of the nebula is called the Trapezium cluster. It is dominated by four young, massive stars in a kite-like arrangement. The brightest of these stars, which has a luminosity 100,000 times that of the Sun, provides the energy that creates the nebula as we see it. It produces a flood o ...
15-1 Notes - westscidept
... use a ________________ to separate a star’s light into a spectrum. The spectrum gives information about the ______________ and temperature of a star. When a chemical element emits ________, only some colors in the spectrum appear. These are called ____________ lines. The __________ atmosphere of a s ...
... use a ________________ to separate a star’s light into a spectrum. The spectrum gives information about the ______________ and temperature of a star. When a chemical element emits ________, only some colors in the spectrum appear. These are called ____________ lines. The __________ atmosphere of a s ...
Barium Stars Observed with the Coude Echelle Spectrometer
... infrequent in early spectral subclasses (because I was searching lor objects related to ß Cephei and 53 Persei stars I did not observe latertypes). This is in line with observations by a group at the University of British Columbia in Vancouver 01 other early-type Be stars which could be the prograde ...
... infrequent in early spectral subclasses (because I was searching lor objects related to ß Cephei and 53 Persei stars I did not observe latertypes). This is in line with observations by a group at the University of British Columbia in Vancouver 01 other early-type Be stars which could be the prograde ...
Binary Star Systems - d_smith.lhseducators.com
... • An eclipsing binary system is a special type of spectroscopic binary, where the orbit of the two stars is edge-on to our line of sight. • We periodically see one star pass in front of or eclipse the other star. When this happens the total amount of light that we receive from the pair dims for a fe ...
... • An eclipsing binary system is a special type of spectroscopic binary, where the orbit of the two stars is edge-on to our line of sight. • We periodically see one star pass in front of or eclipse the other star. When this happens the total amount of light that we receive from the pair dims for a fe ...
BV Color Index and Temperature - The University of Texas at Dallas
... - an eclipsing binary star system in constellation Cepheus. - contains a red supergiant (A) which fills its Roche lobe when closest to its companion blue star, which appears to be on the main sequence Peculiar “double-dip” light curve of ...
... - an eclipsing binary star system in constellation Cepheus. - contains a red supergiant (A) which fills its Roche lobe when closest to its companion blue star, which appears to be on the main sequence Peculiar “double-dip” light curve of ...
GEARS Workshop Monday - Georgia Southern University
... of helium fusion. However, a big surprise was the presence of magnesium in similar quantities. This result may provide a key to the unique composition of H1504+65 and validate theoretical predictions that, if massive enough, some stars can extend their lives by tapping yet another energy source: the ...
... of helium fusion. However, a big surprise was the presence of magnesium in similar quantities. This result may provide a key to the unique composition of H1504+65 and validate theoretical predictions that, if massive enough, some stars can extend their lives by tapping yet another energy source: the ...
types of stars, luminosity, and brightness
... 5. The absolute brightness is the brightness that would be measured at a standard distance of 10 pc. Apparent brightness is the brightness of a star measured from Earth. 6. Absolute brightness is the luminosity of a star as it would be measured at 10 pc. Luminosity is the intrinsic energy per sec th ...
... 5. The absolute brightness is the brightness that would be measured at a standard distance of 10 pc. Apparent brightness is the brightness of a star measured from Earth. 6. Absolute brightness is the luminosity of a star as it would be measured at 10 pc. Luminosity is the intrinsic energy per sec th ...
Winter Stargazing - Trimble County Schools
... and looks like a silvery cloud. • It is filled with red giants, 100s of times brighter than the Sun. ...
... and looks like a silvery cloud. • It is filled with red giants, 100s of times brighter than the Sun. ...
www.aavso.org
... The accumulated charge in each pixel from photons falling on is measured. CCDs are very sensitive, respond to light over a wide range of wavelengths and can measure many stars at once, as compared to photomultiplier tubes which only measure one star at a time. ...
... The accumulated charge in each pixel from photons falling on is measured. CCDs are very sensitive, respond to light over a wide range of wavelengths and can measure many stars at once, as compared to photomultiplier tubes which only measure one star at a time. ...
elementary measuring stars
... The proper motion of a star refers to its annual displacement in the sky relative to a fixed coordinate grid. Proper motion angles are much larger than parallax angles. ...
... The proper motion of a star refers to its annual displacement in the sky relative to a fixed coordinate grid. Proper motion angles are much larger than parallax angles. ...
AN INTRODUCTION TO THE STARS AND CONSTELLATIONS
... Sky maps come in many types and shapes. Typical examples are the small, portable star wheel locator, the celestial globe with stellar objects distributed across the surface of a sphere, and the flat star map that is often published in astronomy magazines or mounted on the walls of classrooms. But th ...
... Sky maps come in many types and shapes. Typical examples are the small, portable star wheel locator, the celestial globe with stellar objects distributed across the surface of a sphere, and the flat star map that is often published in astronomy magazines or mounted on the walls of classrooms. But th ...
Constellations and Distances to Stars
... • The constellation Ursa Major contains the group of stars commonly called the Big Dipper. • The Big Dipper is not a constellation itself, but an asterism, which is a distinctive group of stars. • Another famous asterism is the Little Dipper in the constellation Ursa Minor. • The most famous star in ...
... • The constellation Ursa Major contains the group of stars commonly called the Big Dipper. • The Big Dipper is not a constellation itself, but an asterism, which is a distinctive group of stars. • Another famous asterism is the Little Dipper in the constellation Ursa Minor. • The most famous star in ...
Slide 1
... The mass loss rates for OB (and WR) stars are currently in question at the order-of-magnitude level ( see Fig 1 ) with profound implications for stellar evolution, mass loss processes across the HR diagram and the injection of enriched gas into the ISM. The recognition of clumped and/or porous radia ...
... The mass loss rates for OB (and WR) stars are currently in question at the order-of-magnitude level ( see Fig 1 ) with profound implications for stellar evolution, mass loss processes across the HR diagram and the injection of enriched gas into the ISM. The recognition of clumped and/or porous radia ...
Parallax, Event Horizon, HR diagrams equation
... Physics : distance to the stars and counting the stars "1 Light Year is the distance traveled by light in one year." 1 light year (ly) is equivalent to: 63,270 AU Closer stars could appear larger. More distant stars could be very large, but seem small. How can we tell which stars are farther away? ...
... Physics : distance to the stars and counting the stars "1 Light Year is the distance traveled by light in one year." 1 light year (ly) is equivalent to: 63,270 AU Closer stars could appear larger. More distant stars could be very large, but seem small. How can we tell which stars are farther away? ...
Stars
... •Almost all stars are so small they appear only as a point of light in the largest telescopes •A small number are big and close enough to determine their sizes directly through geometry ...
... •Almost all stars are so small they appear only as a point of light in the largest telescopes •A small number are big and close enough to determine their sizes directly through geometry ...
Apparent Magnitude
... of mass. For each star, the other is its companion star. A large percentage of stars are part of systems with at least two stars. Binary star systems are very important in astrophysics, because observing their mutual orbits allows their mass to be determined. The masses of many single stars can then ...
... of mass. For each star, the other is its companion star. A large percentage of stars are part of systems with at least two stars. Binary star systems are very important in astrophysics, because observing their mutual orbits allows their mass to be determined. The masses of many single stars can then ...
Teacher Guide Lives of Stars
... progresses, students develop an understanding of the most fundamental concepts in stellar astronomy. The most important ideas are repeated through out the play. At the conclusion of the activity, students will have an understanding of the main three types of stars (red, yellow, and blue stars) and t ...
... progresses, students develop an understanding of the most fundamental concepts in stellar astronomy. The most important ideas are repeated through out the play. At the conclusion of the activity, students will have an understanding of the main three types of stars (red, yellow, and blue stars) and t ...
Project Packet - Montville.net
... 2. What direction you should look and at what time 3. How high above the horizon you should look. Part 2 1. What does your constellation look like? 2. Draw a diagram or include an image in the space on the results pages. Part 3 Look up what stars are in your constellation. Use this link: http://en.w ...
... 2. What direction you should look and at what time 3. How high above the horizon you should look. Part 2 1. What does your constellation look like? 2. Draw a diagram or include an image in the space on the results pages. Part 3 Look up what stars are in your constellation. Use this link: http://en.w ...
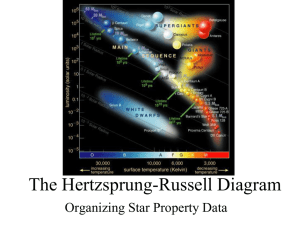
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Most Stars are “Main Sequence” Others are: White Dwarfs, Giants and Supergiants ...
... Most Stars are “Main Sequence” Others are: White Dwarfs, Giants and Supergiants ...
Notes_ stars and sun
... • A constellation is a group of visible stars that form a pattern. • They have been used for many different things. • The first use for constellations was probably religious. Many civilizations believed that the stars were how the gods told stories. • A more practical use for constellations was ...
... • A constellation is a group of visible stars that form a pattern. • They have been used for many different things. • The first use for constellations was probably religious. Many civilizations believed that the stars were how the gods told stories. • A more practical use for constellations was ...
Stars, Stellar classification, H
... These two stars have about the same luminosity -which one appears brighter? A. Alpha Centauri B. The Sun ...
... These two stars have about the same luminosity -which one appears brighter? A. Alpha Centauri B. The Sun ...
Basic Properties of Stars
... The Distances of Stars To give you an idea of the distances involved: the Sun is about 1 million miles in diameter. In other words, walking once around the Sun is equivalent to walking about 100 times around the Earth! But if you shrink the Sun into the size a ball bearing (about 1 cm in diameter) ...
... The Distances of Stars To give you an idea of the distances involved: the Sun is about 1 million miles in diameter. In other words, walking once around the Sun is equivalent to walking about 100 times around the Earth! But if you shrink the Sun into the size a ball bearing (about 1 cm in diameter) ...
Star catalogue

A star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient peoples, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from NASA's Astronomical Data Center.Completeness and accuracy is described by the weakest apparent magnitude V (largest number) and the accuracy of the positions.