Another exAmple: expository mode
... stars. Young stars convert hydrogen to helium through a process known as nuclear fusion to produce light. As stars use up this hydrogen, in a process that takes billions of years, they pass through certain phases or stages. In each stage, the star’s brightness, temperature, and size change. The redg ...
... stars. Young stars convert hydrogen to helium through a process known as nuclear fusion to produce light. As stars use up this hydrogen, in a process that takes billions of years, they pass through certain phases or stages. In each stage, the star’s brightness, temperature, and size change. The redg ...
Spectra of stars
... The continuous spectrum originates from the surface of the star and the absorption lines are produced when light passes upwards and outwards through the tenuous upper layers of the star. By looking at the spectrum of a star astronomers can determine: (a) the temperature of the star (b) the velocity ...
... The continuous spectrum originates from the surface of the star and the absorption lines are produced when light passes upwards and outwards through the tenuous upper layers of the star. By looking at the spectrum of a star astronomers can determine: (a) the temperature of the star (b) the velocity ...
Use this form to take notes in class about stars
... 3. What causes the center of the “core” to heat up? ...
... 3. What causes the center of the “core” to heat up? ...
K - College of San Mateo
... G -Weaker Hydrogen, strong CaII, stronger NaI, many ionized and neutral metals, G-band is present ...
... G -Weaker Hydrogen, strong CaII, stronger NaI, many ionized and neutral metals, G-band is present ...
The Temperatures of Stars
... and eventually supervisor for the other women. Once the Draper survey began, Fleming was given the huge task of photographing, cataloging, and analyzing about 10,000 stars over 9 years. She developed her own labeling system for the spectra using the letters A-Q. At the time, no one understood the di ...
... and eventually supervisor for the other women. Once the Draper survey began, Fleming was given the huge task of photographing, cataloging, and analyzing about 10,000 stars over 9 years. She developed her own labeling system for the spectra using the letters A-Q. At the time, no one understood the di ...
Sammy Nagel · Annie Jump Cannon
... She discovered a system for describing how hot stars are. She used a mnemonic device to remember the letters. the letters were O B A F G K M. The mnemonic was "Oh, be a fine girlkiss me" The O is the hottest star. The M is the coolest star. G is the same as the sun. The hottest two stars are O and B ...
... She discovered a system for describing how hot stars are. She used a mnemonic device to remember the letters. the letters were O B A F G K M. The mnemonic was "Oh, be a fine girlkiss me" The O is the hottest star. The M is the coolest star. G is the same as the sun. The hottest two stars are O and B ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... • As it collapses, gravitational energy is again converted to thermal energy… • This heat allows fusion to occur in a shell of material surrounding the core… • Due to the higher central temperature, the star’s luminosity is greater than before… • This increased energy production causes the outer par ...
... • As it collapses, gravitational energy is again converted to thermal energy… • This heat allows fusion to occur in a shell of material surrounding the core… • Due to the higher central temperature, the star’s luminosity is greater than before… • This increased energy production causes the outer par ...
ppt
... If star wobbles with amplitude of 1 arc-second (1/3600th of a degree), then it is at distance of 1 parsec (definition of parsec). 1 pc = 3.26 light years. In general, ...
... If star wobbles with amplitude of 1 arc-second (1/3600th of a degree), then it is at distance of 1 parsec (definition of parsec). 1 pc = 3.26 light years. In general, ...
Stellar Spectra
... Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Multicolor photography --- Blue and Visual Plates allowed “colors” Objective Prism Spectra Realization that Spectral Type related to ...
... Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Multicolor photography --- Blue and Visual Plates allowed “colors” Objective Prism Spectra Realization that Spectral Type related to ...
General Astronomy - Stockton University
... how much hydrogen could be observed in their spectra. Later, Annie Jump Cannon would improve upon this work to develop a simpler classification system based on ...
... how much hydrogen could be observed in their spectra. Later, Annie Jump Cannon would improve upon this work to develop a simpler classification system based on ...
Physical properties of stars
... that are 1,000 times larger than our sun. pg. 450 Temperature: Surface temperatures range from 3000K to 30,000K Color is an indication of temperature. Blue hottest White Yellow Orange Red coolest Mass While the size of stars varies widely the mass does not. 15 times our Sun’s mass to .2 times our Su ...
... that are 1,000 times larger than our sun. pg. 450 Temperature: Surface temperatures range from 3000K to 30,000K Color is an indication of temperature. Blue hottest White Yellow Orange Red coolest Mass While the size of stars varies widely the mass does not. 15 times our Sun’s mass to .2 times our Su ...
StarType
... When you look at the stars you’ll notice that some are white, some are yellow, and some are red. Stars are classified according to their colors, ranging from electric blue for the hottest stars to dull red for the coolest stars. Early spectrometers identified emission lines in the stars’ spectrum fo ...
... When you look at the stars you’ll notice that some are white, some are yellow, and some are red. Stars are classified according to their colors, ranging from electric blue for the hottest stars to dull red for the coolest stars. Early spectrometers identified emission lines in the stars’ spectrum fo ...
STARS - AN INTRODUCTION
... Different types of gases make the star burn. They give off light and heat. The Sun is a medium sized star. It is bigger than all eight planets combined! However, there are stars a lot bigger than the Sun! The largest stars are called ...
... Different types of gases make the star burn. They give off light and heat. The Sun is a medium sized star. It is bigger than all eight planets combined! However, there are stars a lot bigger than the Sun! The largest stars are called ...
OP/IP27 Stars HR life of stars WS
... What makes a high mass star become a black hole instead of a neutron star? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ____________ ...
... What makes a high mass star become a black hole instead of a neutron star? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ____________ ...
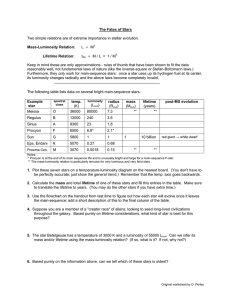
The Fates of Stars Mass-Luminosity Relation: Lifetime Relation:
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
source
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
A Brief History of Planetary Science
... Ionized atoms are represented with roman numerals (e.g. Ca II, calcium with 2 electrons missing) ...
... Ionized atoms are represented with roman numerals (e.g. Ca II, calcium with 2 electrons missing) ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Spectrometer: separates light into colors Each element has unique spectra Most stars are made of H, He, Fe, Na, Ca Color indicates surface temp of star: – Blue = hotter (30,000 C) – Red = cooler (3,500 C) ...
... Spectrometer: separates light into colors Each element has unique spectra Most stars are made of H, He, Fe, Na, Ca Color indicates surface temp of star: – Blue = hotter (30,000 C) – Red = cooler (3,500 C) ...
Hertzsprung2 - courses.psu.edu
... * Result of seeking correlations between observable properties of stars. * Correlates luminosity (or absolute magnitude) and temperature (or spectral type). ...
... * Result of seeking correlations between observable properties of stars. * Correlates luminosity (or absolute magnitude) and temperature (or spectral type). ...
Spectral Classification and the HR Diagram
... Pickering was unhappy with the work performed by his male employees and declared that his maid could do a better job than they did. In 1881, Pickering did hire his maid, Williamina Fleming (1857-1911), to do some mathematical calculations at the Harvard Observatory. Fleming was soon promoted to work ...
... Pickering was unhappy with the work performed by his male employees and declared that his maid could do a better job than they did. In 1881, Pickering did hire his maid, Williamina Fleming (1857-1911), to do some mathematical calculations at the Harvard Observatory. Fleming was soon promoted to work ...
OBAFGKM
... to star’s surface temperature ? • How do we measure brightness of stars: and why apparent vs absolute magnitudes? ...
... to star’s surface temperature ? • How do we measure brightness of stars: and why apparent vs absolute magnitudes? ...
Lecture 10: Stars
... Class self-demo of parallax & Your nose is the Sun & Your left eye is the Earth in January & Your right eye is the Earth in June Watch the apparent motion of your thumb against a distant reference point (repeat at arm’s length) Which “move” more -- closer or farther objects? ...
... Class self-demo of parallax & Your nose is the Sun & Your left eye is the Earth in January & Your right eye is the Earth in June Watch the apparent motion of your thumb against a distant reference point (repeat at arm’s length) Which “move” more -- closer or farther objects? ...
Section 2
... Section 2 Characteristics of stars By Antonia James, Hannah Rohrborn, Jada Staples ...
... Section 2 Characteristics of stars By Antonia James, Hannah Rohrborn, Jada Staples ...
Stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Light from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the rainbow of colors interspersed with absorption lines. Each line indicates an ion of a certain chemical element, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that ion. The relative abundance of the different ions varies with the temperature of the photosphere. The spectral class of a star is a short code summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature and density.Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system using the letters O, B, A, F, G, K, and M, a sequence from the hottest (O type) to the coolest (M type). Each letter class is then subdivided using a numeric digit with 0 being hottest and 9 being coolest (e.g. A8, A9, F0, F1 form a sequence from hotter to cooler). The sequence has been expanded with classes for other stars and star-like objects that do not fit in the classical system, such class D for white dwarfs and class C for carbon stars.In the MK system a luminosity class is added to the spectral class using Roman numerals. This is based on the width of certain absorption lines in the star's spectrum which vary with the density of the atmosphere and so distinguish giant stars from dwarfs. Luminosity class 0 or Ia+ stars for hypergiants, class I stars for supergiants, class II for bright giants, class III for regular giants, class IV for sub-giants, class V for main-sequence stars, class sd for sub-dwarfs, and class D for white dwarfs. The full spectral class for the Sun is then G2V, indicating a main-sequence star with a temperature around 5,800K.