PHYSICS 015
... not the products of the nuclear reactions deep within the core! It is almost pure H + He. The escaping material eventually merges into the interstellar medium, and is available to be used in other stars that may form later. ...
... not the products of the nuclear reactions deep within the core! It is almost pure H + He. The escaping material eventually merges into the interstellar medium, and is available to be used in other stars that may form later. ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe
... • Main SequenceRed GiantWhite Dwarf • The H-R diagram shows the relationship of a star’s surface temperature and its absolute magnitude. • A white dwarf is is a star that has used up all of its hydrogen and is the leftover center of an older star. • Class F stars are yellow-white • The majority of ...
... • Main SequenceRed GiantWhite Dwarf • The H-R diagram shows the relationship of a star’s surface temperature and its absolute magnitude. • A white dwarf is is a star that has used up all of its hydrogen and is the leftover center of an older star. • Class F stars are yellow-white • The majority of ...
Slide 1
... light of particular wavelengths by the atoms in the outer part of the star. See Figure 1 (B). Depending on the pattern of spectroscopic absorption and emission lines, stars may be grouped into particular spectral types. The traditional spectral types are denoted by the letters O, B, A, F, G, K and M ...
... light of particular wavelengths by the atoms in the outer part of the star. See Figure 1 (B). Depending on the pattern of spectroscopic absorption and emission lines, stars may be grouped into particular spectral types. The traditional spectral types are denoted by the letters O, B, A, F, G, K and M ...
Chapter 21
... Notes Classifying Stars Stars are classified by: Color and Temperature What color stars are the hottest? _____________ Coolest? ______________ Size The sun is a medium-sized star. Stars that are much larger than the sun are called ______________ or __________________. Composition – The chemica ...
... Notes Classifying Stars Stars are classified by: Color and Temperature What color stars are the hottest? _____________ Coolest? ______________ Size The sun is a medium-sized star. Stars that are much larger than the sun are called ______________ or __________________. Composition – The chemica ...
Create a HR Diagram - EarthSpaceScience
... Objective: Use that Table of stars and plot them on the Empty H-R diagram based on Luminosity and Spectral Class. Use circles or shading to correctly label the Main Sequence, Giants, and Dwarfs. Then use your diagram to answer the questions. Stars: Star Name ...
... Objective: Use that Table of stars and plot them on the Empty H-R diagram based on Luminosity and Spectral Class. Use circles or shading to correctly label the Main Sequence, Giants, and Dwarfs. Then use your diagram to answer the questions. Stars: Star Name ...
22 Stellar Remnant/HR Diagram
... • Flux also indicates Temperature • Temperature indicates color • We measure color ...
... • Flux also indicates Temperature • Temperature indicates color • We measure color ...
The HR Diagram and Stars Worksheet
... b. Page 626 – Use colored pencils to add and label the band that represents Main Sequence stars. c. Page 626 – Use colored pencils to label the following areas: Blue Giants, Red Super Giants, Red Giants, Red Dwarfs, White Dwarfs d. Page 626 - Label the following stars: Spica, Vega, Sun, Proxima Cent ...
... b. Page 626 – Use colored pencils to add and label the band that represents Main Sequence stars. c. Page 626 – Use colored pencils to label the following areas: Blue Giants, Red Super Giants, Red Giants, Red Dwarfs, White Dwarfs d. Page 626 - Label the following stars: Spica, Vega, Sun, Proxima Cent ...
Stellar Spectra
... Classification (cont’d) • Annie Jump Cannon arranged the spectra of stars in a sequence which corresponds to the temperatures. • Classified over 500,000 stars! • The spectral sequence is: O, B, A, F, G, K, M (RNS) hotter ------------> cooler • A temperature sequence. ...
... Classification (cont’d) • Annie Jump Cannon arranged the spectra of stars in a sequence which corresponds to the temperatures. • Classified over 500,000 stars! • The spectral sequence is: O, B, A, F, G, K, M (RNS) hotter ------------> cooler • A temperature sequence. ...
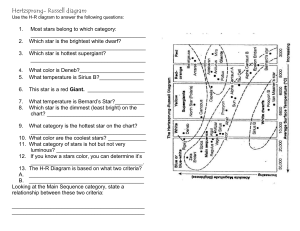
Hertzsprung - Russel Diagram
... 10. What color are the coolest stars? _____________ 11. What category of stars is hot but not very luminous? ______________________________ 12. If you know a stars color, you can determine it’s ______________________________________. 13. The H-R Diagram is based on what two criteria? A. ____________ ...
... 10. What color are the coolest stars? _____________ 11. What category of stars is hot but not very luminous? ______________________________ 12. If you know a stars color, you can determine it’s ______________________________________. 13. The H-R Diagram is based on what two criteria? A. ____________ ...
Part 2 Answer Key
... Star Clusters are multiple star systems bound together by the force of gravity. Star Clusters can be divided into two main groups. One group is called Globular Clusters. They contain many stars and gravity holds them tightly together. They swarm just outside the galaxy and form a halo or bulge. We k ...
... Star Clusters are multiple star systems bound together by the force of gravity. Star Clusters can be divided into two main groups. One group is called Globular Clusters. They contain many stars and gravity holds them tightly together. They swarm just outside the galaxy and form a halo or bulge. We k ...
JPL Small-Body Database Browser
... The hottest stars have temperatures ~30,000K. The coolest stars have temperatures ~3,000K. ...
... The hottest stars have temperatures ~30,000K. The coolest stars have temperatures ~3,000K. ...
A Universe of Dwarfs and Giants
... classed as proper stars. A star must produce its own light. These objects are either very dim or even black when looked at in visible light. The little they radiate is mainly infra-red light. Brown dwarfs can be thought of as failed stars; much bigger than a planet but just not big enough to make it ...
... classed as proper stars. A star must produce its own light. These objects are either very dim or even black when looked at in visible light. The little they radiate is mainly infra-red light. Brown dwarfs can be thought of as failed stars; much bigger than a planet but just not big enough to make it ...
Temperature
... • Ionized gases at a star’s surface absorb specific frequencies of light. – Dark lines in a star’s spectrum ...
... • Ionized gases at a star’s surface absorb specific frequencies of light. – Dark lines in a star’s spectrum ...
Astrophysics
... system which ranks them in order of surface temperature (the letters were re-ordered from an older system): ...
... system which ranks them in order of surface temperature (the letters were re-ordered from an older system): ...
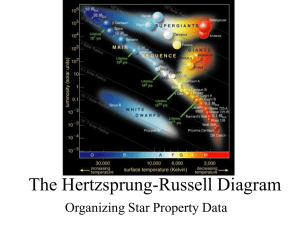
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
Extension worksheet – Topic 6 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... Extension Worksheet – Option E, Worksheet 2, HL only ...
... Extension Worksheet – Option E, Worksheet 2, HL only ...
Lecture 11 - Stars and Atomic Spectra
... Photon energy • Up to now, we have been discussing the wavelength of light as determining it color • However, light comes in discrete packets called photons and the energy of each photon is set by its color or wavelength • From Einstein, we known that the photon energy is inversely proportional to ...
... Photon energy • Up to now, we have been discussing the wavelength of light as determining it color • However, light comes in discrete packets called photons and the energy of each photon is set by its color or wavelength • From Einstein, we known that the photon energy is inversely proportional to ...
Stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Light from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the rainbow of colors interspersed with absorption lines. Each line indicates an ion of a certain chemical element, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that ion. The relative abundance of the different ions varies with the temperature of the photosphere. The spectral class of a star is a short code summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature and density.Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system using the letters O, B, A, F, G, K, and M, a sequence from the hottest (O type) to the coolest (M type). Each letter class is then subdivided using a numeric digit with 0 being hottest and 9 being coolest (e.g. A8, A9, F0, F1 form a sequence from hotter to cooler). The sequence has been expanded with classes for other stars and star-like objects that do not fit in the classical system, such class D for white dwarfs and class C for carbon stars.In the MK system a luminosity class is added to the spectral class using Roman numerals. This is based on the width of certain absorption lines in the star's spectrum which vary with the density of the atmosphere and so distinguish giant stars from dwarfs. Luminosity class 0 or Ia+ stars for hypergiants, class I stars for supergiants, class II for bright giants, class III for regular giants, class IV for sub-giants, class V for main-sequence stars, class sd for sub-dwarfs, and class D for white dwarfs. The full spectral class for the Sun is then G2V, indicating a main-sequence star with a temperature around 5,800K.














![Test ticket - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010793453_1-3f96ef5ee7d4646c2142d92e4dc3c3f6-300x300.png)