Weather Tools
... • Wind speed is an important part of weather. • An anemometer is a weather tool that measures wind speed. ...
... • Wind speed is an important part of weather. • An anemometer is a weather tool that measures wind speed. ...
5-SG - TeacherWeb
... saturation, dew point - calculating RH and DP using ESRT - using DP and temp to forecast precip. ...
... saturation, dew point - calculating RH and DP using ESRT - using DP and temp to forecast precip. ...
Eyewitness
... 7. What is the word for a strong Japanese wind? 8. How fast can debris travel in a tornado? 9. Weather forecasting is good for how many hours ahead? 10. How long has it been for some parts of the South American desert since it has gotten rain? 11. Does cold or warm air hold more water? 12. How many ...
... 7. What is the word for a strong Japanese wind? 8. How fast can debris travel in a tornado? 9. Weather forecasting is good for how many hours ahead? 10. How long has it been for some parts of the South American desert since it has gotten rain? 11. Does cold or warm air hold more water? 12. How many ...
Blog 2017_ Week 4 Jan 30
... and water affect climate and weather. Analyze and interpret data to compare and contrast the of Earth’s atmospheric layers (including the ozone layer) and greenhouse gases. (Clarification statement: Earth’s atmospheric layers include the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and thermosphere.) SE64 ...
... and water affect climate and weather. Analyze and interpret data to compare and contrast the of Earth’s atmospheric layers (including the ozone layer) and greenhouse gases. (Clarification statement: Earth’s atmospheric layers include the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and thermosphere.) SE64 ...
File
... – Big picture first, then drill down to local. You can’t make an accurate forecast without understanding the big picture. (We call this the forecast funnel) ...
... – Big picture first, then drill down to local. You can’t make an accurate forecast without understanding the big picture. (We call this the forecast funnel) ...
Unit 8: Earth`s Oceans and Atmosphere
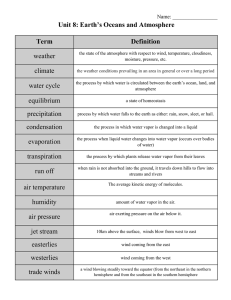
... the state of the atmosphere with respect to wind, temperature, cloudiness, moisture, pressure, etc. ...
... the state of the atmosphere with respect to wind, temperature, cloudiness, moisture, pressure, etc. ...
Weather Lab Powerpoint Charts
... Atmosphere Temperature Wind Humidity Precipitation Air pressure Fronts ...
... Atmosphere Temperature Wind Humidity Precipitation Air pressure Fronts ...
Notes 1-12-17 Diagrams
... Weather Map of the United States from the Weather Channel An important tool for predicting the weather If you know the changes in air pressure and the direction of the wind, you can predict the weather It appears the Northeast is experiences some type of snow storm Low pressure usually means a storm ...
... Weather Map of the United States from the Weather Channel An important tool for predicting the weather If you know the changes in air pressure and the direction of the wind, you can predict the weather It appears the Northeast is experiences some type of snow storm Low pressure usually means a storm ...
Sping-EXTREME WEATHER – Jigsaw Spring
... Countries that have the same seasons as us and those that are different. Southern hemisphere countries and how they have the opposite season to us. Weather diaries – starting point/introduction to. ...
... Countries that have the same seasons as us and those that are different. Southern hemisphere countries and how they have the opposite season to us. Weather diaries – starting point/introduction to. ...
Weather and Climate - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets
... 11. The state of the earth's atmosphere at a certain time and place is called http://www.helpteaching.com/tests/159771/weather-and-climate ...
... 11. The state of the earth's atmosphere at a certain time and place is called http://www.helpteaching.com/tests/159771/weather-and-climate ...
Bill Nye Wind Worksheet
... 2. The balloon swelled because warm air takes up more space and shrinks because cold air takes up (more or less) ...
... 2. The balloon swelled because warm air takes up more space and shrinks because cold air takes up (more or less) ...
EPO4 Atmosphere, weather, and climate
... 8. Fill the gaps. The _______________ _______________ can be a map with symbols and temperatures or a table. Spain has a _______________ _______________, with a _______________ _______________ in the Canary Islands. _______________ _______________ have the most precipitation. This takes the fo ...
... 8. Fill the gaps. The _______________ _______________ can be a map with symbols and temperatures or a table. Spain has a _______________ _______________, with a _______________ _______________ in the Canary Islands. _______________ _______________ have the most precipitation. This takes the fo ...
Twenty Questions
... Water droplets in the atmosphere are pushed up into cooler layers of the atmosphere, over and over until pellets form and finally fall to the Earth ...
... Water droplets in the atmosphere are pushed up into cooler layers of the atmosphere, over and over until pellets form and finally fall to the Earth ...
The atmosphere! - Studentportalen
... middle. The mesosphere extends from about 50#km to 80 or 85#km. Temperature decreasing with height." ...
... middle. The mesosphere extends from about 50#km to 80 or 85#km. Temperature decreasing with height." ...
Comparison of the Ionospheric Effects of the Space Weather and
... 2 Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal University, Kaliningrad, Russia ...
... 2 Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal University, Kaliningrad, Russia ...
Investigation 1 Study Guide - Hewlett
... the amount of matter in an object or a substance such as rock, a glass of water, or a volume of air. Mass is measured in grams. 4. Air is matter and has mass. It is a mixture of gases that make up Earth’s atmosphere. Nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%) are the main permanent gases in the air. It also co ...
... the amount of matter in an object or a substance such as rock, a glass of water, or a volume of air. Mass is measured in grams. 4. Air is matter and has mass. It is a mixture of gases that make up Earth’s atmosphere. Nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%) are the main permanent gases in the air. It also co ...
Chapter 24 Concept Review
... a. temperature and precipitation. b. high temperature and low temperature. c. season and temperature. d. season and precipitation. ______ 8. City climates are sometimes a few degrees warmer than surrounding rural climates because pavement and buildings a. block winds. b. prevent the movement of clou ...
... a. temperature and precipitation. b. high temperature and low temperature. c. season and temperature. d. season and precipitation. ______ 8. City climates are sometimes a few degrees warmer than surrounding rural climates because pavement and buildings a. block winds. b. prevent the movement of clou ...
Goal 3 Weather and Climate vocab
... Global winds at the poles of the earth. These global winds sometimes affect our weather during the ...
... Global winds at the poles of the earth. These global winds sometimes affect our weather during the ...
Chapter01c
... Water vapor, which normally occupies less than 4 percent in a volume of air near the surface, can condense into liquid cloud droplets or transform into delicate ice crystals. Water is the only substance in our atmosphere that is found naturally as a gas (water vapor), as a liquid (water) and as a so ...
... Water vapor, which normally occupies less than 4 percent in a volume of air near the surface, can condense into liquid cloud droplets or transform into delicate ice crystals. Water is the only substance in our atmosphere that is found naturally as a gas (water vapor), as a liquid (water) and as a so ...
Quiz 1 Study List
... Weather: is the condition of Earth's atmosphere at a given time in a given place. Atmosphere: is the layer of air surrounding Earth. Troposphere: lies next to Earths surface and is the lowest layer of the atmosphere. The atmospheric pressure is higher due to gravitational forces. This is the layer w ...
... Weather: is the condition of Earth's atmosphere at a given time in a given place. Atmosphere: is the layer of air surrounding Earth. Troposphere: lies next to Earths surface and is the lowest layer of the atmosphere. The atmospheric pressure is higher due to gravitational forces. This is the layer w ...
METEOROLOGY PART II REVIEW S13
... 11. Name an area on Earth that you’d expect to be dominated by… -- low-pressure systems: -- high-pressure systems: 12. How do clouds impact the Earth’s temperature during the day and night? ...
... 11. Name an area on Earth that you’d expect to be dominated by… -- low-pressure systems: -- high-pressure systems: 12. How do clouds impact the Earth’s temperature during the day and night? ...
seasonality-elementary
... 2-3.2 Recall weather terminology (including temperature, wind direction, wind speed, and precipitation as rain, snow, sleet, and hail). 2-3.3 Illustrate the weather conditions of different seasons. 2-3.4 Carry out procedures to measure and record daily weather conditions (including temperature, prec ...
... 2-3.2 Recall weather terminology (including temperature, wind direction, wind speed, and precipitation as rain, snow, sleet, and hail). 2-3.3 Illustrate the weather conditions of different seasons. 2-3.4 Carry out procedures to measure and record daily weather conditions (including temperature, prec ...
Weather

Weather is the state of the atmosphere, to the degree that it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. Weather, seen from an anthropological perspective, is something all humans in the world constantly experience through their senses, at least while being outside. There are socially and scientifically constructed understandings of what weather is, what makes it change, the effect it has on humans in different situations, etc. Therefore, weather is something people often communicate about.Most weather phenomena occur in the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather generally refers to day-to-day temperature and precipitation activity, whereas climate is the term for the statistics of atmospheric conditions over longer periods of time. When used without qualification, ""weather"" is generally understood to mean the weather of Earth.Weather is driven by air pressure (temperature and moisture) differences between one place and another. These pressure and temperature differences can occur due to the sun angle at any particular spot, which varies by latitude from the tropics. The strong temperature contrast between polar and tropical air gives rise to the jet stream. Weather systems in the mid-latitudes, such as extratropical cyclones, are caused by instabilities of the jet stream flow. Because the Earth's axis is tilted relative to its orbital plane, sunlight is incident at different angles at different times of the year. On Earth's surface, temperatures usually range ±40 °C (−40 °F to 100 °F) annually. Over thousands of years, changes in Earth's orbit can affect the amount and distribution of solar energy received by the Earth, thus influencing long-term climate and global climate change.Surface temperature differences in turn cause pressure differences. Higher altitudes are cooler than lower altitudes due to differences in compressional heating. Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere for a future time and a given location. The system is a chaotic system; so small changes to one part of the system can grow to have large effects on the system as a whole. Human attempts to control the weather have occurred throughout human history, and there is evidence that human activities such as agriculture and industry have modified weather patterns.Studying how the weather works on other planets has been helpful in understanding how weather works on Earth. A famous landmark in the Solar System, Jupiter's Great Red Spot, is an anticyclonic storm known to have existed for at least 300 years. However, weather is not limited to planetary bodies. A star's corona is constantly being lost to space, creating what is essentially a very thin atmosphere throughout the Solar System. The movement of mass ejected from the Sun is known as the solar wind.