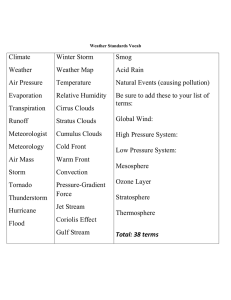
Weather Vocabulary
... Air Mass: a huge body of air that has similar temperature, humidity, and air pressure at any given height. Cold Front: forms when cold air moves under warm air which is less dense and pushes air up (produces thunderstorms heavy rain or snow). Convection Current: The circular movement of substances d ...
... Air Mass: a huge body of air that has similar temperature, humidity, and air pressure at any given height. Cold Front: forms when cold air moves under warm air which is less dense and pushes air up (produces thunderstorms heavy rain or snow). Convection Current: The circular movement of substances d ...
File
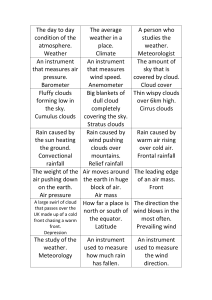
... Rain caused by Rain caused by the sun heating wind pushing the ground. clouds over Convectional mountains. rainfall Relief rainfall The weight of the Air moves around air pushing down the earth in huge on the earth. block of air. Air pressure Air mass A large swirl of cloud How far a place is that p ...
... Rain caused by Rain caused by the sun heating wind pushing the ground. clouds over Convectional mountains. rainfall Relief rainfall The weight of the Air moves around air pushing down the earth in huge on the earth. block of air. Air pressure Air mass A large swirl of cloud How far a place is that p ...
Chapter 12: Earth`s Atmosphere
... 1. The atmospheric layer directly above the troposphere 3. The atmospheric layer farthest from Earth's surface 4. When sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides combine with moisture in the atmosphere and form precipitation that has a pH lower than that of normal rainwater 6. Describes weather circulating ...
... 1. The atmospheric layer directly above the troposphere 3. The atmospheric layer farthest from Earth's surface 4. When sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides combine with moisture in the atmosphere and form precipitation that has a pH lower than that of normal rainwater 6. Describes weather circulating ...
Chapter 7 Science Study Guide Water can change state. What are
... Climate is yearlong and constant while weather changes day to day. A forecaster would study factors of weather on a daily basis and for climate they would analyze yearlong data. ...
... Climate is yearlong and constant while weather changes day to day. A forecaster would study factors of weather on a daily basis and for climate they would analyze yearlong data. ...
Meteorology Name Period _____ Ch. 9 pages 262
... 3. What is the source region for the air mass at point A? What is the source region for the air mass at point B? 4. Place the weather symbol for a thunderstorm on the map to show the probable location of thunderstorm. 5. Place the letter H on the map to indicate the area of high pressure – cool, cle ...
... 3. What is the source region for the air mass at point A? What is the source region for the air mass at point B? 4. Place the weather symbol for a thunderstorm on the map to show the probable location of thunderstorm. 5. Place the letter H on the map to indicate the area of high pressure – cool, cle ...
Atmospheric Gases
... The temperate zone temperatures are affected most by the changing seasons, but since the westerly wind belt is in that region, the weather systems during any season move from wind belt, the weather systems move across the country from west to east. Tropical weather systems, for example hurricanes, a ...
... The temperate zone temperatures are affected most by the changing seasons, but since the westerly wind belt is in that region, the weather systems during any season move from wind belt, the weather systems move across the country from west to east. Tropical weather systems, for example hurricanes, a ...
Providing meteorological services to the Canadian Armed
... MISSION STATEMENT The Canadian Forces Weather & Oceanographic Service (CFWOS) provides specialized meteorological & oceanographic (METOC) information for strategic, operational and tactical advantage on a global scale. ...
... MISSION STATEMENT The Canadian Forces Weather & Oceanographic Service (CFWOS) provides specialized meteorological & oceanographic (METOC) information for strategic, operational and tactical advantage on a global scale. ...
2.3- Winds and Ocean Currents
... heat around the globe. • Currents transfer heat around the planet through convection. ...
... heat around the globe. • Currents transfer heat around the planet through convection. ...
Wind Vane
... • Meteorology -the scientific study of Earth’s weather • Weather – the condition of the atmosphere at a certain time; includes temperature, and rainfall • High Pressure – anticyclone, equals low wind and dry clear conditions • Low Pressure = cyclone, high winds, wet stormy conditions • Hurricane – a ...
... • Meteorology -the scientific study of Earth’s weather • Weather – the condition of the atmosphere at a certain time; includes temperature, and rainfall • High Pressure – anticyclone, equals low wind and dry clear conditions • Low Pressure = cyclone, high winds, wet stormy conditions • Hurricane – a ...
Unit 2 Meteorology Test
... 19. More solar energy reaches the equatorial regions than the polar regions because the equatorial regions A are covered by a greater area of land. B have more vegetation to absorb sunlight. C have days with more hours of light. D receive sun rays closest to vertical. 20. Which diagram below is the ...
... 19. More solar energy reaches the equatorial regions than the polar regions because the equatorial regions A are covered by a greater area of land. B have more vegetation to absorb sunlight. C have days with more hours of light. D receive sun rays closest to vertical. 20. Which diagram below is the ...
how to collect meteorological data italy
... water fall from the clouds to the ground. The rain plays a very important role in the water cycle. Water evaporates from the oceans, condenses in the clouds and falls to the ground, then it returns to the ocean through groundwater and rivers, thus repeating the cycle. In this way water becomes avail ...
... water fall from the clouds to the ground. The rain plays a very important role in the water cycle. Water evaporates from the oceans, condenses in the clouds and falls to the ground, then it returns to the ocean through groundwater and rivers, thus repeating the cycle. In this way water becomes avail ...
metIstudyguide F14
... 2. What layer of atmosphere contains weather? 3. Which layer of atmosphere is most thin? 4. What is the most abundant gas in the atmosphere? 5. Put the following gases in order from most abundant to least: O2, N2, CO2, and Ar 6. Increased altitudes have _____________ pressure because _______________ ...
... 2. What layer of atmosphere contains weather? 3. Which layer of atmosphere is most thin? 4. What is the most abundant gas in the atmosphere? 5. Put the following gases in order from most abundant to least: O2, N2, CO2, and Ar 6. Increased altitudes have _____________ pressure because _______________ ...
01 - mrlongscience
... 17. Air rises as it is heated because it becomes less dense. 18. The temperature differences in the atmosphere result mainly from the way solar energy is absorbed. Some layers are warmer because they contain gases that absorb solar energy. 19. Secondary pollutants form when primary pollutants react ...
... 17. Air rises as it is heated because it becomes less dense. 18. The temperature differences in the atmosphere result mainly from the way solar energy is absorbed. Some layers are warmer because they contain gases that absorb solar energy. 19. Secondary pollutants form when primary pollutants react ...
Atmosphere
... Heating the Atmosphere Heat: the energy transferred from one object to another because of a direct difference in ...
... Heating the Atmosphere Heat: the energy transferred from one object to another because of a direct difference in ...
Chapter 1 - Weather Underground
... What is Meteorology? • First defined by Aristotle in Meteorologica • Meteors used to be everything that fell from the sky • Now, meteorology is the study of the atmosphere and its ...
... What is Meteorology? • First defined by Aristotle in Meteorologica • Meteors used to be everything that fell from the sky • Now, meteorology is the study of the atmosphere and its ...
Mathematicians save the planet!
... • For short forecasts, initial conditions and chaos are more important • For long forecasts – the effects of chaos average out – but the model results can change a lot if we get the amount of carbon dioxide emitted slightly wrong • So we can predict the temperature change in 50 years time, even if w ...
... • For short forecasts, initial conditions and chaos are more important • For long forecasts – the effects of chaos average out – but the model results can change a lot if we get the amount of carbon dioxide emitted slightly wrong • So we can predict the temperature change in 50 years time, even if w ...
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Atmosphere Weather: the state of the
... Climate includes average high and low conditions Climate includes record high and low conditions Weather and climate are expressed by six elements 1. temperature of the air 2. humidity of the air 3. type and amount of cloudiness 4. type and amount of precipitation 5. pressure exerted by the air 6. s ...
... Climate includes average high and low conditions Climate includes record high and low conditions Weather and climate are expressed by six elements 1. temperature of the air 2. humidity of the air 3. type and amount of cloudiness 4. type and amount of precipitation 5. pressure exerted by the air 6. s ...
The Structure of the Atmosphere
... disturb the atmosphere and masses of air flow horizontally from one latitude to another. These movements provide a background to the study of climate. ...
... disturb the atmosphere and masses of air flow horizontally from one latitude to another. These movements provide a background to the study of climate. ...
Weather-all-in-one-1
... disturb the atmosphere and masses of air flow horizontally from one latitude to another. These movements provide a background to the study of climate. ...
... disturb the atmosphere and masses of air flow horizontally from one latitude to another. These movements provide a background to the study of climate. ...
J.T. Reddick Middle School 6th Grade Earth Science Course
... Course: Unit 5 “Weather and Climate” Textbook: Prentice Hall Science Explorer – Georgia Earth Science (pages 392, 398-402, 404, 414-424, 432-464, and 472-479) Unit Overview: Meteorology is the study of the atmospheric conditions and weather in an area and how to forecast it. In this unit, students w ...
... Course: Unit 5 “Weather and Climate” Textbook: Prentice Hall Science Explorer – Georgia Earth Science (pages 392, 398-402, 404, 414-424, 432-464, and 472-479) Unit Overview: Meteorology is the study of the atmospheric conditions and weather in an area and how to forecast it. In this unit, students w ...
Weather

Weather is the state of the atmosphere, to the degree that it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. Weather, seen from an anthropological perspective, is something all humans in the world constantly experience through their senses, at least while being outside. There are socially and scientifically constructed understandings of what weather is, what makes it change, the effect it has on humans in different situations, etc. Therefore, weather is something people often communicate about.Most weather phenomena occur in the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather generally refers to day-to-day temperature and precipitation activity, whereas climate is the term for the statistics of atmospheric conditions over longer periods of time. When used without qualification, ""weather"" is generally understood to mean the weather of Earth.Weather is driven by air pressure (temperature and moisture) differences between one place and another. These pressure and temperature differences can occur due to the sun angle at any particular spot, which varies by latitude from the tropics. The strong temperature contrast between polar and tropical air gives rise to the jet stream. Weather systems in the mid-latitudes, such as extratropical cyclones, are caused by instabilities of the jet stream flow. Because the Earth's axis is tilted relative to its orbital plane, sunlight is incident at different angles at different times of the year. On Earth's surface, temperatures usually range ±40 °C (−40 °F to 100 °F) annually. Over thousands of years, changes in Earth's orbit can affect the amount and distribution of solar energy received by the Earth, thus influencing long-term climate and global climate change.Surface temperature differences in turn cause pressure differences. Higher altitudes are cooler than lower altitudes due to differences in compressional heating. Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere for a future time and a given location. The system is a chaotic system; so small changes to one part of the system can grow to have large effects on the system as a whole. Human attempts to control the weather have occurred throughout human history, and there is evidence that human activities such as agriculture and industry have modified weather patterns.Studying how the weather works on other planets has been helpful in understanding how weather works on Earth. A famous landmark in the Solar System, Jupiter's Great Red Spot, is an anticyclonic storm known to have existed for at least 300 years. However, weather is not limited to planetary bodies. A star's corona is constantly being lost to space, creating what is essentially a very thin atmosphere throughout the Solar System. The movement of mass ejected from the Sun is known as the solar wind.