Preattentive Filling-in of Visual Surfaces in Parietal Extinction
... influence of perceptual filling-in on extinction arises at the level of a 3D representation of visual surfaces. We used displays like those shown in Fig. 4, A through C. V.R.’s task was to detect the onset of black bars on either side of a central cube. In bilateral trials, the two bars were arrange ...
... influence of perceptual filling-in on extinction arises at the level of a 3D representation of visual surfaces. We used displays like those shown in Fig. 4, A through C. V.R.’s task was to detect the onset of black bars on either side of a central cube. In bilateral trials, the two bars were arrange ...
The basic nonuniformity of the cerebral cortex
... cerebral cortex, N, and the total cortical surface area, A) varied threefold from 42,710/mm2 in Macaca fascicularis to 129,670/ mm2 in Saimiri sp. (Table 1), with an average of 83,945 neurons/ mm2 across species. Despite this variation, these values as a whole were not significantly different from t ...
... cerebral cortex, N, and the total cortical surface area, A) varied threefold from 42,710/mm2 in Macaca fascicularis to 129,670/ mm2 in Saimiri sp. (Table 1), with an average of 83,945 neurons/ mm2 across species. Despite this variation, these values as a whole were not significantly different from t ...
Neural Interaction in Cat Primary Auditory Cortex. Dependence on
... the unilateral excitation and common input cases, decreased with recording depth. In contrast, for dual-electrode pairs, only the association index decreased with depth. 10. There was no change in the value of the correlation coefficient, p, nor in the percentage of significant correlations with CF ...
... the unilateral excitation and common input cases, decreased with recording depth. In contrast, for dual-electrode pairs, only the association index decreased with depth. 10. There was no change in the value of the correlation coefficient, p, nor in the percentage of significant correlations with CF ...
Organization of Visual Areas in Macaque and
... See abbreviation list for full names of areas. Data were registered to the atlas using a surface-based registration method in which geographic (gyral and sulcal) landmarks were used to constrain the registration (Van Essen et al., 2001b). Depending on the data source, this method was applied to comp ...
... See abbreviation list for full names of areas. Data were registered to the atlas using a surface-based registration method in which geographic (gyral and sulcal) landmarks were used to constrain the registration (Van Essen et al., 2001b). Depending on the data source, this method was applied to comp ...
Control of movement direction - Cognitive Science Research Group
... et al., 1998). Hatsopoulos and colleagues have shown that significant synchrony between directionally tuned neurons occurs clustered around the onset of movement (e.g., a time window of 400 ms) and may encode information distinct from that provided by firing rate modulations alone. The mechanism, wh ...
... et al., 1998). Hatsopoulos and colleagues have shown that significant synchrony between directionally tuned neurons occurs clustered around the onset of movement (e.g., a time window of 400 ms) and may encode information distinct from that provided by firing rate modulations alone. The mechanism, wh ...
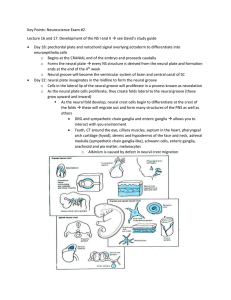
Key Points: Neuroscience Exam #2 Lecture 16 and 17: Development of
... o Closure of the neuropores coincides with the establishment of a vascular circulation for the neural tube. The walls of the neural tube thicken to form the brain and spinal cord o Anytime the neuropores do not close, you end up with an open NS and parts can be missing th 4 week (29 days): embryo un ...
... o Closure of the neuropores coincides with the establishment of a vascular circulation for the neural tube. The walls of the neural tube thicken to form the brain and spinal cord o Anytime the neuropores do not close, you end up with an open NS and parts can be missing th 4 week (29 days): embryo un ...
ap psych 2012 unit 3a and 3b
... 3. While mapping the motor cortex, researchers Foerster and Penfield found that a. although the mind's subsystems are localized in specific brain regions, the brain acts like a unified whole. b. damage to a specific area in the left frontal lobe disrupted speech ability. c. body areas requiring the ...
... 3. While mapping the motor cortex, researchers Foerster and Penfield found that a. although the mind's subsystems are localized in specific brain regions, the brain acts like a unified whole. b. damage to a specific area in the left frontal lobe disrupted speech ability. c. body areas requiring the ...
Affective neuroscience: the emergence of a discipline
... the relay of sensory inputs to the thalamus. Whereas the lemniscal nuclei (LEM) transmit only to the primary sensory cortex, the extralemniscal areas (EX) transmit to primary sensory and association regions of the cortex, as well as to the lateral nucleus of the amygdala. This region of the amygdala ...
... the relay of sensory inputs to the thalamus. Whereas the lemniscal nuclei (LEM) transmit only to the primary sensory cortex, the extralemniscal areas (EX) transmit to primary sensory and association regions of the cortex, as well as to the lateral nucleus of the amygdala. This region of the amygdala ...
Fact vs fiction—how paratextual information
... when participants evaluated real persons and concluded that real persons elicit more autobiographical memory retrieval as they have a higher personal relevance (see also Summerfield et al., 2009). However, as all those studies used slightly different materials across conditions, it cannot be exclude ...
... when participants evaluated real persons and concluded that real persons elicit more autobiographical memory retrieval as they have a higher personal relevance (see also Summerfield et al., 2009). However, as all those studies used slightly different materials across conditions, it cannot be exclude ...
Prediction in Human Decision Making
... Where P(a) is the probability of selecting action (a) at step (t); W(st,a) is the weight for action (a) in the current state; τ is a temperature parameter which controls the explorationexploitation tendency; and A is a set of all actions [15]. We have added a prediction part to the Actor-Critic stru ...
... Where P(a) is the probability of selecting action (a) at step (t); W(st,a) is the weight for action (a) in the current state; τ is a temperature parameter which controls the explorationexploitation tendency; and A is a set of all actions [15]. We have added a prediction part to the Actor-Critic stru ...
A proposed common neural mechanism for categorization and
... then the animals reported the match by releasing a touch bar; if the two directions were from different categories, the animals had to continue holding the touch bar. In this way neural signals before the onset of the test stimulus were dissociated from the form of the report, because at those t ...
... then the animals reported the match by releasing a touch bar; if the two directions were from different categories, the animals had to continue holding the touch bar. In this way neural signals before the onset of the test stimulus were dissociated from the form of the report, because at those t ...
- Wiley Online Library
... events from CD. Increased expression and abnormal localization of CD have been well described in the brain during aging, but less attention has been given to age-dependent changes in CE of the brain. Recently, CE was shown to be highly expressed in degenerating neurons and to be localized in the cor ...
... events from CD. Increased expression and abnormal localization of CD have been well described in the brain during aging, but less attention has been given to age-dependent changes in CE of the brain. Recently, CE was shown to be highly expressed in degenerating neurons and to be localized in the cor ...
The Motor Cortex and Descending Control of Movement
... macaques and then to apes, including humans, there has been a large increase in the number of direct connections to motoneurons. Other mammals such as cats have few if any direct connections (one exception is the racoon, which has both significant direct connections and good manual dexterity). Prima ...
... macaques and then to apes, including humans, there has been a large increase in the number of direct connections to motoneurons. Other mammals such as cats have few if any direct connections (one exception is the racoon, which has both significant direct connections and good manual dexterity). Prima ...
mechanisms of visual attention in the human cortex
... paired stimuli was reduced compared with that elicited by the single good stimulus. This result indicates that two stimuli present at the same time within a neuron’s RF are not processed independently, but rather that they interact with each other in a mutually suppressive way. This sensory suppress ...
... paired stimuli was reduced compared with that elicited by the single good stimulus. This result indicates that two stimuli present at the same time within a neuron’s RF are not processed independently, but rather that they interact with each other in a mutually suppressive way. This sensory suppress ...
Patterns of sensory intermodality relationships in the cerebral cortex
... sections were delineated according to the Nissl, AchE, distances from coronal sections, relying on previous parcelmyelin stains, and their relation to the pattern of callosal lation schemes (Donoghue and Wise, '82; Zilles, '85). As in the coronal sections, the lateral border of the connections. The ...
... sections were delineated according to the Nissl, AchE, distances from coronal sections, relying on previous parcelmyelin stains, and their relation to the pattern of callosal lation schemes (Donoghue and Wise, '82; Zilles, '85). As in the coronal sections, the lateral border of the connections. The ...
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR
... - many cortical areas involved in movements send their axons to __________________ , which also receive terminals from ______________ (dopamine); -caudate and putamen neurons then send their axons to ____________________; - in turn, GP axons contact the ________________, which feedback onto cortex t ...
... - many cortical areas involved in movements send their axons to __________________ , which also receive terminals from ______________ (dopamine); -caudate and putamen neurons then send their axons to ____________________; - in turn, GP axons contact the ________________, which feedback onto cortex t ...
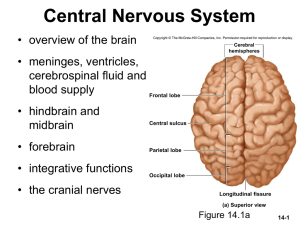
CNS Slide Show
... – bathes its external surface • buoyancy – allows brain to attain considerable size without being impaired by its own weight – if it rested heavily on floor of cranium, the pressure would kill the nervous tissue • protection – protects the brain from striking the cranium when the head is jolted – sh ...
... – bathes its external surface • buoyancy – allows brain to attain considerable size without being impaired by its own weight – if it rested heavily on floor of cranium, the pressure would kill the nervous tissue • protection – protects the brain from striking the cranium when the head is jolted – sh ...
Author`s personal copy
... maps represent their relevant sensory or motor dimensions continuously and completely. The second principle is that topographic and anatomical boundaries align with one another. These principles together form what we term, for simplicity, the standard model of topographic organization (see also [9,1 ...
... maps represent their relevant sensory or motor dimensions continuously and completely. The second principle is that topographic and anatomical boundaries align with one another. These principles together form what we term, for simplicity, the standard model of topographic organization (see also [9,1 ...
Heterotopic Transcallosal Projections Are Present throughout the
... techniques—has been performed that allows us to compare the organization of transcallosal connections in different functional regions of the mouse cortex including the primary motor and somatosensory cortices. Such a systematic analysis of inter-hemispheric connectivity is important as defects in th ...
... techniques—has been performed that allows us to compare the organization of transcallosal connections in different functional regions of the mouse cortex including the primary motor and somatosensory cortices. Such a systematic analysis of inter-hemispheric connectivity is important as defects in th ...
Behavioral and Cognitive Neuroscience
... character is any observable feature or attribute of an organism. A character could be a feature of the brain, such as the corpus callosum between the two cerebral hemispheres, or a feature of any other part of the body, or (as is often the case today) a molecule or a DNA sequence. By considering the ...
... character is any observable feature or attribute of an organism. A character could be a feature of the brain, such as the corpus callosum between the two cerebral hemispheres, or a feature of any other part of the body, or (as is often the case today) a molecule or a DNA sequence. By considering the ...
Cortical sensorimotor alterations classify clinical phenotype and
... interplay between disorder etiology and pathophysiology remains very limited. Specifically, it is unknown whether any of these reported brain abnormalities may be considered as a neuroimaging marker(s) for SD prediction and diagnostic differentiation. This is partly due to the fact that the majority o ...
... interplay between disorder etiology and pathophysiology remains very limited. Specifically, it is unknown whether any of these reported brain abnormalities may be considered as a neuroimaging marker(s) for SD prediction and diagnostic differentiation. This is partly due to the fact that the majority o ...
Learning Strengthens the Response of Primary Visual Cortex to
... that span both stimuli, spatial blurring of the hemodynamic response, noise in the localizer scan, or eye movements during scanning. For example, subjects may have occasionally fixated the middle location, thus moving it to the central location. The reduction in secondary response with learning was ...
... that span both stimuli, spatial blurring of the hemodynamic response, noise in the localizer scan, or eye movements during scanning. For example, subjects may have occasionally fixated the middle location, thus moving it to the central location. The reduction in secondary response with learning was ...
Current Challenges Facing the Translation of Brain
... et al., 2012) when compared to natural reaching movements. Thus, the ability to use a goal-tuned unit in posterior parietal cortex as a control source for decoding intent using motor imagery could serve as an informative alternative to decoders focused on motor cortex. There are several additional c ...
... et al., 2012) when compared to natural reaching movements. Thus, the ability to use a goal-tuned unit in posterior parietal cortex as a control source for decoding intent using motor imagery could serve as an informative alternative to decoders focused on motor cortex. There are several additional c ...
Neurological Principles and Rehabilitation of Action Disorders
... are implemented in tbe brain. Feed-forward control relies on 2 flavors of internal models: forward and inverse. Given the motor command, the forward model predicts the sensory consequence of this command, in effect mimicking the movements of the body in parallel with actual movements. A dramatic exa ...
... are implemented in tbe brain. Feed-forward control relies on 2 flavors of internal models: forward and inverse. Given the motor command, the forward model predicts the sensory consequence of this command, in effect mimicking the movements of the body in parallel with actual movements. A dramatic exa ...
ling411-19-Learning - OWL-Space
... For opposite hemisphere • Add 1 to figures for same hemisphere Probably, for any two columns anywhere in the cortex, whether functionally related or not, fewer than 6 degrees of separation ...
... For opposite hemisphere • Add 1 to figures for same hemisphere Probably, for any two columns anywhere in the cortex, whether functionally related or not, fewer than 6 degrees of separation ...
Cortical cooling
Neuroscientists generate various studies to help explain many of the complex connections and functions of the brain. Most studies utilize animal models that have varying degrees of comparison to the human brain; for example, small rodents are less comparable than non-human primates. One of the most definitive ways of determining which sections of the brain contribute to certain behavior or function is to deactivate a section of the brain and observe what behavior is altered. Investigators have a wide range of options for deactivating neural tissue, and one of the more recently developed methods being used is deactivation through cooling. Cortical cooling refers to the cooling methods restricted to the cerebral cortex, where most higher brain processes occur. Below is a list of current cooling methods, their advantages and limitations, and some studies that have used cooling to elucidate neural functions.