unit 12 — abnormal psychology
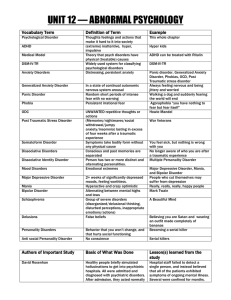
... fear with no warning Persistent irrational fear UNWANTED repetitive thoughts or actions (Memories/nightmares/social withdrawal/jumpy anxiety/insomnia) lasting in excess of four weeks after a traumatic experience Symptoms take bodily form without any physical cause Conscious and past memories are sep ...
... fear with no warning Persistent irrational fear UNWANTED repetitive thoughts or actions (Memories/nightmares/social withdrawal/jumpy anxiety/insomnia) lasting in excess of four weeks after a traumatic experience Symptoms take bodily form without any physical cause Conscious and past memories are sep ...
File - Pharmacology (HOME)
... Life changes Holmes & Rahe, 1967 Social Readjustment Rating Scale: measures stress with life changes and categorized them (mild with 30% chance of physical manifestation; moderate 50%, high 80%) Stress as Transaction Lazarus, 1991 Stress includes life changes and everyday. Process of complex ...
... Life changes Holmes & Rahe, 1967 Social Readjustment Rating Scale: measures stress with life changes and categorized them (mild with 30% chance of physical manifestation; moderate 50%, high 80%) Stress as Transaction Lazarus, 1991 Stress includes life changes and everyday. Process of complex ...
PSY 111 Practice Quiz Psychological Disorders Answers will be
... (4) In a major depressive episode, 5 of the 9 symptoms must be occurring for at least (a) 5 days. (b) 2 weeks. (c) 2 months. (d) 1 year. (5) When depressive symptoms are less severe and occur for period of 2 years or more, this is called (a) manic disorder. (b) bipolar disorder. (c) dissociative dis ...
... (4) In a major depressive episode, 5 of the 9 symptoms must be occurring for at least (a) 5 days. (b) 2 weeks. (c) 2 months. (d) 1 year. (5) When depressive symptoms are less severe and occur for period of 2 years or more, this is called (a) manic disorder. (b) bipolar disorder. (c) dissociative dis ...
I - Arizona Capital Representation Project
... In the face of danger people predictably attempt to defend themselves from the impending harm. Symptoms of hyperarousal are characteristic of the body’s natural ‘fight or flight’ defense mechanism. The sympathetic nervous system, the body’s emergency response system, takes over. The activation of th ...
... In the face of danger people predictably attempt to defend themselves from the impending harm. Symptoms of hyperarousal are characteristic of the body’s natural ‘fight or flight’ defense mechanism. The sympathetic nervous system, the body’s emergency response system, takes over. The activation of th ...
Home Is Where The Heart Is
... • >50% have physical health problems • >50% have experienced violence or abuse from family/partner • 41% rough sleepers have been involved in prostitution • 45% are mothers ...
... • >50% have physical health problems • >50% have experienced violence or abuse from family/partner • 41% rough sleepers have been involved in prostitution • 45% are mothers ...
Neurotic disorders - Farrell`s Class Page
... • The amnesia is usually centered on traumatic events, such as accidents, combat experiences, or unexpected bereavements, and used to be partial and ...
... • The amnesia is usually centered on traumatic events, such as accidents, combat experiences, or unexpected bereavements, and used to be partial and ...
Somatoform Disorders
... Presence of physical symptoms that suggest a general medical condition Symptoms not fully explained by medical condition Not due to substances or other mental disorders Somatoform Disorders can be clustered into 2 larger categories: Classical hysterical disorders – somatization disorder, CD, ...
... Presence of physical symptoms that suggest a general medical condition Symptoms not fully explained by medical condition Not due to substances or other mental disorders Somatoform Disorders can be clustered into 2 larger categories: Classical hysterical disorders – somatization disorder, CD, ...
When a Friend or Loved One Has Been Traumatized
... others. It is also important that these supporters can understand their loved ones' reactions as well as their own, so they can help them through the difficult times that accompany and follow traumatic events, and also take care of themselves. Natural responses to traumatic events It is natural for ...
... others. It is also important that these supporters can understand their loved ones' reactions as well as their own, so they can help them through the difficult times that accompany and follow traumatic events, and also take care of themselves. Natural responses to traumatic events It is natural for ...
Presentation
... Stage 3: Integration Not the end of therapy, but the stage that most resembles therapy with nondissociative people. Loneliness, mourning the loss of ‘others’ inside. ‘who am I?’ questions, learning to relate as a whole person, from the inside out, finding meaning and purpose, working on relat ...
... Stage 3: Integration Not the end of therapy, but the stage that most resembles therapy with nondissociative people. Loneliness, mourning the loss of ‘others’ inside. ‘who am I?’ questions, learning to relate as a whole person, from the inside out, finding meaning and purpose, working on relat ...
Life Events - Adult
... that produced feelings of fear, helplessness or horror, the total number of episodes reported and the event that caused the most distress. The Traumatic Life Events Questionnaire (TLEQ) was selected because it is a widely used, validated protocol with demonstrated reliability and validity. The The T ...
... that produced feelings of fear, helplessness or horror, the total number of episodes reported and the event that caused the most distress. The Traumatic Life Events Questionnaire (TLEQ) was selected because it is a widely used, validated protocol with demonstrated reliability and validity. The The T ...
OCD: Anxiety, rituals, co-morbidity or altered state? Treatment
... The importance of knowing the details of each OC action resulting from trauma are “essential” for dealing with any kind of repetitive OCBP (Obsessive Compulsive Behavior Pattern). Once the looping sets in, the ego-state that is responsible for the rituals, takes over and disenables the core personal ...
... The importance of knowing the details of each OC action resulting from trauma are “essential” for dealing with any kind of repetitive OCBP (Obsessive Compulsive Behavior Pattern). Once the looping sets in, the ego-state that is responsible for the rituals, takes over and disenables the core personal ...
Towards an understanding of the molecular basis
... the Korean and Vietnam Wars more than 80% of the soldiers with ASD returned to combat. While psychiatrists did a remarkable job in understanding and successfully treating ASD, I think they were also one of the primary causes of the high percentage of Vietnam and Korean Wars veterans affected by PTSD ...
... the Korean and Vietnam Wars more than 80% of the soldiers with ASD returned to combat. While psychiatrists did a remarkable job in understanding and successfully treating ASD, I think they were also one of the primary causes of the high percentage of Vietnam and Korean Wars veterans affected by PTSD ...
Anxiety Disorders
... preoccupation with one’s health despite the fact that genuine symptoms of the disorder are lacking ...
... preoccupation with one’s health despite the fact that genuine symptoms of the disorder are lacking ...
Mental Health/Wellness
... person’s pattern of thoughts, feelings and actions interfere with daily life (schizophrenia) Somatoform disorder- Person has symptoms of a disease but no physical cause can be found (hypochondria = misinterpreted aches and pains as illness). ...
... person’s pattern of thoughts, feelings and actions interfere with daily life (schizophrenia) Somatoform disorder- Person has symptoms of a disease but no physical cause can be found (hypochondria = misinterpreted aches and pains as illness). ...
... social and other functioning. If symptoms last beyond a month following the traumatic event, PTSD may ensue. These adverse effects do not always disappear with time. Acute stress management is focused on ensuring safety and providing support, including assessment of coping resources and support netw ...
psychology - TeacherWeb
... Example: Sometimes it feels and smells like someone has screwed a quarter-pound hamburger into my head and arms and legs and if you shine a headlight inside it will drill you. CLANG ASSOCIATION: psychotic speech in which words are rhymed. Example: You wear clothes and how much does this watch cost? ...
... Example: Sometimes it feels and smells like someone has screwed a quarter-pound hamburger into my head and arms and legs and if you shine a headlight inside it will drill you. CLANG ASSOCIATION: psychotic speech in which words are rhymed. Example: You wear clothes and how much does this watch cost? ...
Dissociative Disorders
... A. Sudden, unexpected travel away from home or one’s customary place of work, with inability to recall one’s past B. Confusion about personal identity or assumption of a new identity (partial or complete) C. Not better explained by a another mental disorder and is not due to a GMC or substance D. Sy ...
... A. Sudden, unexpected travel away from home or one’s customary place of work, with inability to recall one’s past B. Confusion about personal identity or assumption of a new identity (partial or complete) C. Not better explained by a another mental disorder and is not due to a GMC or substance D. Sy ...
Mental & Physical Health Slides
... Describe the psychological disorders that are found across cultures. Identify the role that culture plays in the diagnosis of psychological disorders. Identify the role that culture plays in the expressed symptoms and course of psychological disorders. ...
... Describe the psychological disorders that are found across cultures. Identify the role that culture plays in the diagnosis of psychological disorders. Identify the role that culture plays in the expressed symptoms and course of psychological disorders. ...
A Review of Two Instruments and Clinical Recommendations
... sexual abuse correlate with adult psychiatric disturbances and suicidal ideation. In addition to childhood traumatic events, many adults also experience trauma in the form of automobile accidents, intimate partner violence, rape, natural disasters, and combat, to name a few. A diagnosis of Posttraum ...
... sexual abuse correlate with adult psychiatric disturbances and suicidal ideation. In addition to childhood traumatic events, many adults also experience trauma in the form of automobile accidents, intimate partner violence, rape, natural disasters, and combat, to name a few. A diagnosis of Posttraum ...
Psychological Disorders Review Sheet (Chapter 15)
... argues disorders are maladaptive behaviors LEARNED from inappropriate rewards and/or punishments. ...
... argues disorders are maladaptive behaviors LEARNED from inappropriate rewards and/or punishments. ...
Chapter 7 - IPFW.edu
... actual or threatened sexual violation, in one or more of the following ways: experiencing the event personally, witnessing the event, learning that a violent or accidental death or threat of death occurred to a close other, or experiencing repeated or extreme exposure to aversive details of the even ...
... actual or threatened sexual violation, in one or more of the following ways: experiencing the event personally, witnessing the event, learning that a violent or accidental death or threat of death occurred to a close other, or experiencing repeated or extreme exposure to aversive details of the even ...
What is Dissociation? - University of Delaware
... Assumption of a new identity May last: hours to months Prevalence estimated: 1 in 500 Usually in response to stressor ...
... Assumption of a new identity May last: hours to months Prevalence estimated: 1 in 500 Usually in response to stressor ...
A Framework for How Personality Disorders Develop
... People with personality disorders and their families will often tell stories of childhood developmental struggles, of profound experiences with shame (or Herculean efforts to avoid shame), with terror or with great sadness, and stories of painful themes of abandonment, disregard, deprivation or othe ...
... People with personality disorders and their families will often tell stories of childhood developmental struggles, of profound experiences with shame (or Herculean efforts to avoid shame), with terror or with great sadness, and stories of painful themes of abandonment, disregard, deprivation or othe ...
When you just can`t forget
... as an observer, or in reports is exposed to major threats such as death, serious injury or sexual violence. ...
... as an observer, or in reports is exposed to major threats such as death, serious injury or sexual violence. ...
Anxiety Disorder
... Types of Phobias • One type of phobia, called specific phobia, can involve fear of an object (like an elevator) or a situation (like public speaking) that poses little or no danger. • Social Phobias can involve fear of being embarrassed, looked at, or made fun of in social or work situations • With ...
... Types of Phobias • One type of phobia, called specific phobia, can involve fear of an object (like an elevator) or a situation (like public speaking) that poses little or no danger. • Social Phobias can involve fear of being embarrassed, looked at, or made fun of in social or work situations • With ...