Plant ID - Midwest Aquatic Plant Management Society
... This undesirable exotic, also known as Crisp Pondweed, bears a waxy cuticle on its upper leaves making them stiff and somewhat brittle. The leaves have been described as resembling lasagna noodles, but upon close inspection a row of “teeth” can be seen to line the margins. Growing in dense mats near ...
... This undesirable exotic, also known as Crisp Pondweed, bears a waxy cuticle on its upper leaves making them stiff and somewhat brittle. The leaves have been described as resembling lasagna noodles, but upon close inspection a row of “teeth” can be seen to line the margins. Growing in dense mats near ...
Viburnum trilobum compactum
... turning a medium green as they mature. Color returns to these maple like leaves in the fall providing a nice show in the garden. The flowers, typical of viburnums, may not show up on this plant until it is well established. It has an upright growth habit when young, becoming rounder with age. Genera ...
... turning a medium green as they mature. Color returns to these maple like leaves in the fall providing a nice show in the garden. The flowers, typical of viburnums, may not show up on this plant until it is well established. It has an upright growth habit when young, becoming rounder with age. Genera ...
Najas guadalupensis (Spreng.) Magnus subsp. guadalupensis
... lateral shoot (lower leaf), simple with sheath, sessile, without stipules; sheaths at node slightly dimorphic, open, roundish, of cauline leaf fully sheathing and ca. 3 mm long, of bract partially sheathing and ca. 2 mm long, minutely serrate (= 1-celled teeth) on margins, the teeth aging brownish, ...
... lateral shoot (lower leaf), simple with sheath, sessile, without stipules; sheaths at node slightly dimorphic, open, roundish, of cauline leaf fully sheathing and ca. 3 mm long, of bract partially sheathing and ca. 2 mm long, minutely serrate (= 1-celled teeth) on margins, the teeth aging brownish, ...
e. Clustered, staled sporangia called sori
... b. Groups of vascular tissues scattered throughout the stem c. Groups of vascular tissues in a ring d. Flower parts mostly in threes or multiples of three e. Seeds with one cotyledon 13. Primary growth in plants results from activity of a. Apical meristems b. Lateral meristems c. Vascular cambium d. ...
... b. Groups of vascular tissues scattered throughout the stem c. Groups of vascular tissues in a ring d. Flower parts mostly in threes or multiples of three e. Seeds with one cotyledon 13. Primary growth in plants results from activity of a. Apical meristems b. Lateral meristems c. Vascular cambium d. ...
6 th Grade Science Ms. Koennecke Growing and
... Basic Parts of Plants 1. Leaves: take in carbon dioxide & sunlight to be used in photosynthesis 2. Stems: support branches, leaves, & flowers 3. Roots: secures plant in place, absorbs minerals & water, stores energy ...
... Basic Parts of Plants 1. Leaves: take in carbon dioxide & sunlight to be used in photosynthesis 2. Stems: support branches, leaves, & flowers 3. Roots: secures plant in place, absorbs minerals & water, stores energy ...
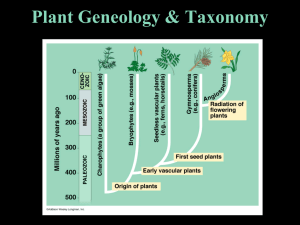
Plant Geneology & Taxonomy
... – Leaves are needle-like or scaly – Do not produce flowers – Many produce cones to protect seeds - conifers – Seeds not enclosed in fruit – Stems are woody • Example: ...
... – Leaves are needle-like or scaly – Do not produce flowers – Many produce cones to protect seeds - conifers – Seeds not enclosed in fruit – Stems are woody • Example: ...
Gunnera manicatab315
... noticed this giant perennial. In the right conditions, the leaves of Gunnera manicata can grow up to 6’ across on stalks up to 8’ tall. However, more often they get to be only 3’ across and 4’ high in our region. All top growth dies to the ground every year. The leaves are deeply lobed and covered i ...
... noticed this giant perennial. In the right conditions, the leaves of Gunnera manicata can grow up to 6’ across on stalks up to 8’ tall. However, more often they get to be only 3’ across and 4’ high in our region. All top growth dies to the ground every year. The leaves are deeply lobed and covered i ...
Printable
... Availability: somewhat available, may have to go out of the region to find the plant Description Height: 3 to 15 feet Spread: 3 to 4 feet Plant habit: round Plant density: moderate Growth rate: slow Texture: coarse Foliage Leaf arrangement: alternate Leaf type: simple Trunk/bark/branches: usually wi ...
... Availability: somewhat available, may have to go out of the region to find the plant Description Height: 3 to 15 feet Spread: 3 to 4 feet Plant habit: round Plant density: moderate Growth rate: slow Texture: coarse Foliage Leaf arrangement: alternate Leaf type: simple Trunk/bark/branches: usually wi ...
docx - STAO
... lamp. The blue food colouring will not enter the area of the leaf covered by petroleum jelly because transpiration is prevented in these areas and therefore water will not evaporate from the leaf. Consequently, water is not drawn up in response to the loss of water from the stomata. If microscopes a ...
... lamp. The blue food colouring will not enter the area of the leaf covered by petroleum jelly because transpiration is prevented in these areas and therefore water will not evaporate from the leaf. Consequently, water is not drawn up in response to the loss of water from the stomata. If microscopes a ...
Teacher Demo/Student Activity: Transpiration
... lamp. The blue food colouring will not enter the area of the leaf covered by petroleum jelly because transpiration is prevented in these areas and therefore water will not evaporate from the leaf. Consequently, water is not drawn up in response to the loss of water from the stomata. If microscopes a ...
... lamp. The blue food colouring will not enter the area of the leaf covered by petroleum jelly because transpiration is prevented in these areas and therefore water will not evaporate from the leaf. Consequently, water is not drawn up in response to the loss of water from the stomata. If microscopes a ...
toetoe - Trees for Survival
... spring and summer, while the pampas flowers in the autumn. Pampas also has tightly curled dead leaves at its base, and the leaves snap readily when given a sharp tug (toetoe leaves do not). ...
... spring and summer, while the pampas flowers in the autumn. Pampas also has tightly curled dead leaves at its base, and the leaves snap readily when given a sharp tug (toetoe leaves do not). ...
50. Sumac - Friess Lake School District
... The leaves are sharply toothed on the edges with their dark green sides above and their paler sides below. The leaves turn scarlet in autumn. What type of flowers bloom on this plant? What do the seedpods or seeds look like? The flowers are in dense panicles or spikes 5-30 cm long. Each flower is ve ...
... The leaves are sharply toothed on the edges with their dark green sides above and their paler sides below. The leaves turn scarlet in autumn. What type of flowers bloom on this plant? What do the seedpods or seeds look like? The flowers are in dense panicles or spikes 5-30 cm long. Each flower is ve ...
Dipladenia / Mandevilla - The Von Trapp Greenhouse
... Mandevilla sanderi (dipladenia) and Mandevilla x amabilis (mandevilla) are easy care tropical plants native to Brazil. Both thrive in full, blazing hot sun and reward the gardener with a profusion of bright blooms that do not require deadheading. They are drought tolerant and are therefore the perfe ...
... Mandevilla sanderi (dipladenia) and Mandevilla x amabilis (mandevilla) are easy care tropical plants native to Brazil. Both thrive in full, blazing hot sun and reward the gardener with a profusion of bright blooms that do not require deadheading. They are drought tolerant and are therefore the perfe ...
Puzzle - UBC Blogs
... light energy and pass excited electrons to acceptor molecules 25 ________________proton gradient drives ATP synthesis ...
... light energy and pass excited electrons to acceptor molecules 25 ________________proton gradient drives ATP synthesis ...
1 Plant Morphology
... distinguish between a compound leaf and a branch with several leaves, you must locate the axillary bud or buds which will occur in the axil of a leaf but not in the axil of a leaflet. ...
... distinguish between a compound leaf and a branch with several leaves, you must locate the axillary bud or buds which will occur in the axil of a leaf but not in the axil of a leaflet. ...
Information Sheet Giant Hog Weed DESCRIPTION Stems: Flowering
... Stems: Flowering stems up to 5m high and up to 10cm in diameter, hollow except at the nodes; both stems and petioles having obvious reddish-purple flecks throughout and sometimes nearly solid purple near the base; lower stem often very rough with sharp-pointed, irregularly-spaced bumps. Leaves: Leaf ...
... Stems: Flowering stems up to 5m high and up to 10cm in diameter, hollow except at the nodes; both stems and petioles having obvious reddish-purple flecks throughout and sometimes nearly solid purple near the base; lower stem often very rough with sharp-pointed, irregularly-spaced bumps. Leaves: Leaf ...
Central Forests - Science Olympiad
... General tips on arrangement are: 1. The Audubon Field Guide is arranged according to the family arrangement within the Orders of Trees and Shrubs. 2. Gymnosperms are followed by angiosperms with dicots first and then monocots. 3. Species are arranged alphabetically within the family by ...
... General tips on arrangement are: 1. The Audubon Field Guide is arranged according to the family arrangement within the Orders of Trees and Shrubs. 2. Gymnosperms are followed by angiosperms with dicots first and then monocots. 3. Species are arranged alphabetically within the family by ...
Caesalpinia pulcherrima (Dwarf Poinciana) Size/Shape
... Caesalpinia pulcherrima (Dwarf Poinciana) The dwarf Poinciana is a fast growing large shrub or small tree Leaves are bright green bi-pinnate feathery. Flowers are very showy yellow and orange in the middle appearing throughout the year. The fruits are pod. Makes a good specimen and used as barrier. ...
... Caesalpinia pulcherrima (Dwarf Poinciana) The dwarf Poinciana is a fast growing large shrub or small tree Leaves are bright green bi-pinnate feathery. Flowers are very showy yellow and orange in the middle appearing throughout the year. The fruits are pod. Makes a good specimen and used as barrier. ...
Botany Presentation - St. Lucie County Extension Office
... Leaf and Stem Arrangement A stem has nodes and internodes. Nodes are where leaves or buds are attached. ...
... Leaf and Stem Arrangement A stem has nodes and internodes. Nodes are where leaves or buds are attached. ...
Red-eyed Wattle
... Also known as the ‘Western Coastal Wattle’. This Acacia species is found in sandy and limestone soils along the coast from Eneabba to the Great Australian Bight where it extends into South Australia. It is a problem weed in South Africa where it has been introduced. Its scientific name, Acacia cyclo ...
... Also known as the ‘Western Coastal Wattle’. This Acacia species is found in sandy and limestone soils along the coast from Eneabba to the Great Australian Bight where it extends into South Australia. It is a problem weed in South Africa where it has been introduced. Its scientific name, Acacia cyclo ...
Dandelion
... Related species T. formosana Plant Distribution Widespread in temperate Asia, Europe, and North America Botanical Features Biennial or perennial herb, containing white milky juice; stems short and narrow; leaves oblong, spatulate or oblanceolate, 5-40 x 1-10 cm, nearly entire to pinnately lobed, sta ...
... Related species T. formosana Plant Distribution Widespread in temperate Asia, Europe, and North America Botanical Features Biennial or perennial herb, containing white milky juice; stems short and narrow; leaves oblong, spatulate or oblanceolate, 5-40 x 1-10 cm, nearly entire to pinnately lobed, sta ...
Plant Structures
... The stem is the plant structure that holds up the leaves. Leaves need sunlight in order to make food. The stem holds the leaves in position to capture as much of the Sun's energy as possible. The stem also is able to grow, making the plant taller and wider. The stems of trees can grow very tall. Th ...
... The stem is the plant structure that holds up the leaves. Leaves need sunlight in order to make food. The stem holds the leaves in position to capture as much of the Sun's energy as possible. The stem also is able to grow, making the plant taller and wider. The stems of trees can grow very tall. Th ...
Osmanthus burkwoodii
... group, hedge, solitary Habitat : finely toothed, pointy leaves that are covered with white down when they shoot in spring. In autumn the foliage colours a beautiful red, orange or yellow. Height : 100 - 200 cm ...
... group, hedge, solitary Habitat : finely toothed, pointy leaves that are covered with white down when they shoot in spring. In autumn the foliage colours a beautiful red, orange or yellow. Height : 100 - 200 cm ...
Examining Plant Structures and Functions
... made of one primary root with a number of small secondary roots. ...
... made of one primary root with a number of small secondary roots. ...
Leaf

A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant and is the principal lateral appendage of the stem. The leaves and stem together form the shoot. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves collectively.Typically a leaf is a thin, dorsiventrally flattened organ, borne above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Most leaves have distinctive upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) surfaces that differ in colour, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases) and other features. In most plant species, leaves are broad and flat. Such species are referred to as broad-leaved plants. Many gymnosperm species have thin needle-like leaves that can be advantageous in cold climates frequented by snow and frost. Leaves can also have other shapes and forms such as the scales in certain species of conifers. Some leaves are not above ground (such as bulb scales). Succulent plants often have thick juicy leaves, but some leaves are without major photosynthetic function and may be dead at maturity, as in some cataphylls, and spines). Furthermore, several kinds of leaf-like structures found in vascular plants are not totally homologous with them. Examples include flattened plant stems (called phylloclades and cladodes), and phyllodes (flattened leaf stems), both of which differ from leaves in their structure and origin. Many structures of non-vascular plants, and even of some lichens, which are not plants at all (in the sense of being members of the kingdom Plantae), look and function much like leaves. The primary site of photosynthesis in most leaves (palisade mesophyll) almost always occurs on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of Eucalyptus palisade occurs on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral.