Harts Tongue Fern
... The Bruce Trail Conservancy is continually acquiring and conserving land along the Niagara Escarpment, including areas where the Hart’s Tongue Fern can be found. Ontario has the bulk of North Americas population and most are found along the Niagara Escarpment. According to the Ministry of Natural ...
... The Bruce Trail Conservancy is continually acquiring and conserving land along the Niagara Escarpment, including areas where the Hart’s Tongue Fern can be found. Ontario has the bulk of North Americas population and most are found along the Niagara Escarpment. According to the Ministry of Natural ...
Plant descriptions
... flowers. Leaves vary in shape, some deeply notched, other not notched at all. Leaves arranged opposite each other on the twig. Terminal leaves often curled up into galls containing larvae of an insect. Also at site 109 (between thimbleberry). Bush with masses of white flowers which stay on as dried ...
... flowers. Leaves vary in shape, some deeply notched, other not notched at all. Leaves arranged opposite each other on the twig. Terminal leaves often curled up into galls containing larvae of an insect. Also at site 109 (between thimbleberry). Bush with masses of white flowers which stay on as dried ...
Types of Plants Notes - Teacher Copy
... vi Stores energy as starch B. Plant kingdom is divided into four groups based on: i ...
... vi Stores energy as starch B. Plant kingdom is divided into four groups based on: i ...
Study of Momordica charantia L. species grown on the specific
... area (LA) of a sample of leaves using regression analysis. Results and discussion Momordica charantia L. species presents a rapidly growing rate, final height of one plant being of 2,5-3 m, in some cases reaching even 4-5 m. Climbing pubescent stem posseses simple tendrils. The number of main copse ...
... area (LA) of a sample of leaves using regression analysis. Results and discussion Momordica charantia L. species presents a rapidly growing rate, final height of one plant being of 2,5-3 m, in some cases reaching even 4-5 m. Climbing pubescent stem posseses simple tendrils. The number of main copse ...
Children`s Discovery Guide NW NATIVE PLANT GARDEN at Point
... Conifer: A tree or shrub bearing cones and evergreen leaves (also called needles). From the Latin words, conus (cone) + ferre (to bear). Deciduous: A tree or shrub which loses its leaves in the fall, growing new leaves the following spring. From the Latin word deciduus (falling). Evergreen: A plant ...
... Conifer: A tree or shrub bearing cones and evergreen leaves (also called needles). From the Latin words, conus (cone) + ferre (to bear). Deciduous: A tree or shrub which loses its leaves in the fall, growing new leaves the following spring. From the Latin word deciduus (falling). Evergreen: A plant ...
22.1 - What Is a Plant? alternation of generations
... sapwood- in a woody stem, the layer of secondary phloem that surrounds the heartwood; usually active in fluid transport bark- tissues that are found outside the vascular cambium, including the phloem, cork cambium, and cork 23.4- Leaves blade- thin, flattened part of plant leaf petiole- thin stalk t ...
... sapwood- in a woody stem, the layer of secondary phloem that surrounds the heartwood; usually active in fluid transport bark- tissues that are found outside the vascular cambium, including the phloem, cork cambium, and cork 23.4- Leaves blade- thin, flattened part of plant leaf petiole- thin stalk t ...
Document
... - reproduce with spores - diagram shows spores growing in clusters called sori on the back of the frond of the fern ...
... - reproduce with spores - diagram shows spores growing in clusters called sori on the back of the frond of the fern ...
ss 1 biology - Danbo International Schools
... b. Bryophyta – They are called Bryophytes. They possess rhizoids or false root e.g moss plant. c. Tracheophyta – They are usually called Tracheophytes. They are also known as vascular plant e.g fern DIVISION OF TRACHEOPHYTA The divisions include: 1. Pteridophyta 2. Spermatophyta (seed plant) (the sp ...
... b. Bryophyta – They are called Bryophytes. They possess rhizoids or false root e.g moss plant. c. Tracheophyta – They are usually called Tracheophytes. They are also known as vascular plant e.g fern DIVISION OF TRACHEOPHYTA The divisions include: 1. Pteridophyta 2. Spermatophyta (seed plant) (the sp ...
Orchid-tree yellowing? Nutrients or/and Lace Bugs?
... storage because the leaves dropped early. There are other species of lace bugs that are host specific and will not attack other plants. However, the cotton lace bug is not a finicky eater and has a wide host range including citrus, hibiscus, lima beans, Annona species, egg plant and even royal palm. ...
... storage because the leaves dropped early. There are other species of lace bugs that are host specific and will not attack other plants. However, the cotton lace bug is not a finicky eater and has a wide host range including citrus, hibiscus, lima beans, Annona species, egg plant and even royal palm. ...
Common cocklebur
... and narrow. The first leaf pair is opposite; subsequent leaves are alternate. Leaves Common cocklebur seedling. are triangular (widest at base) with toothed margins and 3 prominent veins, and are rough to touch. Stems Green stems have purple or brown Common cocklebur stem. spots, are erect and branc ...
... and narrow. The first leaf pair is opposite; subsequent leaves are alternate. Leaves Common cocklebur seedling. are triangular (widest at base) with toothed margins and 3 prominent veins, and are rough to touch. Stems Green stems have purple or brown Common cocklebur stem. spots, are erect and branc ...
Diversity of Plants
... 1. most numerous of all of the non-seed plants in number and variety 2. Exhibits fronds - large pinnate leaf-like structures (not true leaves) that grow from the base of the plant a. When fronds first form, they are called fiddleheads, which are tightly coiled fronds resembling the top of a violin. ...
... 1. most numerous of all of the non-seed plants in number and variety 2. Exhibits fronds - large pinnate leaf-like structures (not true leaves) that grow from the base of the plant a. When fronds first form, they are called fiddleheads, which are tightly coiled fronds resembling the top of a violin. ...
Why Plants Need Phosphorus (Missouri)
... ponent of membranes that surround each other parts of the cell and in other plant parts. plant cell and organelle. Inside the cell, genet- This phosphate/triose phosphate exchange ic information in the form of DNA and RNA reaction is critical for proper movement of molecules contains P as an integra ...
... ponent of membranes that surround each other parts of the cell and in other plant parts. plant cell and organelle. Inside the cell, genet- This phosphate/triose phosphate exchange ic information in the form of DNA and RNA reaction is critical for proper movement of molecules contains P as an integra ...
pest_diseases
... • Warm temperatures and moist conditions in greenhouse plant production make most horticulture plant diseases worse because of environmental conditions that support diseasecausing pathogens ...
... • Warm temperatures and moist conditions in greenhouse plant production make most horticulture plant diseases worse because of environmental conditions that support diseasecausing pathogens ...
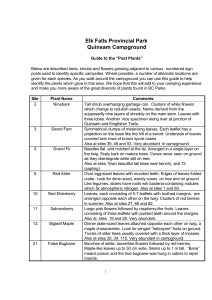
Jetbead (Rhodotypos scandens) - New Jersey Invasive Species
... NJ Status: Emerging Stage 2 - Uncommon (may be regionally abundant). It is highly threatening to natural communities. All detected occurrences should be eradicated. ...
... NJ Status: Emerging Stage 2 - Uncommon (may be regionally abundant). It is highly threatening to natural communities. All detected occurrences should be eradicated. ...
Ch 21 PPT
... Male and female cones on same tree Scalelike leaves with cutin Evergreen – lose leaves throughout the year ...
... Male and female cones on same tree Scalelike leaves with cutin Evergreen – lose leaves throughout the year ...
Diversity of Plants
... 4 Alternation of _____________ describes the two distinct life cycles of plants from a haploid to diploid genome. (11) ...
... 4 Alternation of _____________ describes the two distinct life cycles of plants from a haploid to diploid genome. (11) ...
Kingdom_Plantae_Notes
... waterproof, protective layer. Vascular tissue conducts materials throughout plant. o Xylem These cells are dead at maturity. The hollow cells form a continuous channel through the plant from the roots to the leaves and conduct water and minerals upward from the roots. They have hard walls whic ...
... waterproof, protective layer. Vascular tissue conducts materials throughout plant. o Xylem These cells are dead at maturity. The hollow cells form a continuous channel through the plant from the roots to the leaves and conduct water and minerals upward from the roots. They have hard walls whic ...
The tissues main that are found in a mesophytic leaf are epidermal
... lamina; it consists of a large surface area for photosynthesis but is only 0.3mm thick it composes of four thin tissues of layers with veins at intervals. Leaves most important task is photosynthesis that why leaves are flat and wide. So the most important tissue in a leaf is the palisade and the sp ...
... lamina; it consists of a large surface area for photosynthesis but is only 0.3mm thick it composes of four thin tissues of layers with veins at intervals. Leaves most important task is photosynthesis that why leaves are flat and wide. So the most important tissue in a leaf is the palisade and the sp ...
Botany for Arborists - Street Tree Seminar
... Leaves are often the primary site of photosynthesis. ...
... Leaves are often the primary site of photosynthesis. ...
Review - Plant Systems 15
... 8. Why are plants green? Cells contain chloroplasts which have chlorophyll which reflects light to make plant look green 9. Where does most of the photosynthesis take place in the leaf? Palisade mesophyll. Why? Closest tissue to the sun. 10. Fill in the following boxes as either vascular or nonvascu ...
... 8. Why are plants green? Cells contain chloroplasts which have chlorophyll which reflects light to make plant look green 9. Where does most of the photosynthesis take place in the leaf? Palisade mesophyll. Why? Closest tissue to the sun. 10. Fill in the following boxes as either vascular or nonvascu ...
Shisham (Dalbergia sissoo)
... or light brown in colour. Leaves of the shisham are compound and each leaflet is light green and thin initially, turning slightly rough and dark green with age. Three or five leaflets form one leaf, each roughly heart-shaped with a finely drawn-out short tip. They are arranged alternately on the lea ...
... or light brown in colour. Leaves of the shisham are compound and each leaflet is light green and thin initially, turning slightly rough and dark green with age. Three or five leaflets form one leaf, each roughly heart-shaped with a finely drawn-out short tip. They are arranged alternately on the lea ...
1 www.ugaextension.com
... • Botanical Names – Applied by botanist using the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature • They seem difficult to learn & use since they are written in Latin • They are precise – one name for each plant following the International Code • The names also reflect the classification of the plants, ...
... • Botanical Names – Applied by botanist using the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature • They seem difficult to learn & use since they are written in Latin • They are precise – one name for each plant following the International Code • The names also reflect the classification of the plants, ...
Leaf

A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant and is the principal lateral appendage of the stem. The leaves and stem together form the shoot. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves collectively.Typically a leaf is a thin, dorsiventrally flattened organ, borne above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Most leaves have distinctive upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) surfaces that differ in colour, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases) and other features. In most plant species, leaves are broad and flat. Such species are referred to as broad-leaved plants. Many gymnosperm species have thin needle-like leaves that can be advantageous in cold climates frequented by snow and frost. Leaves can also have other shapes and forms such as the scales in certain species of conifers. Some leaves are not above ground (such as bulb scales). Succulent plants often have thick juicy leaves, but some leaves are without major photosynthetic function and may be dead at maturity, as in some cataphylls, and spines). Furthermore, several kinds of leaf-like structures found in vascular plants are not totally homologous with them. Examples include flattened plant stems (called phylloclades and cladodes), and phyllodes (flattened leaf stems), both of which differ from leaves in their structure and origin. Many structures of non-vascular plants, and even of some lichens, which are not plants at all (in the sense of being members of the kingdom Plantae), look and function much like leaves. The primary site of photosynthesis in most leaves (palisade mesophyll) almost always occurs on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of Eucalyptus palisade occurs on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral.