African Violets Can Bloom All Year Long By Joan
... As your violets get older, the lower row of leaves usually dies off. Removing the dead leaves tends to make the plant look as if it has a neck. When this happens, it is time to repot. Take the plant out of the container and gently brush off as much soil as possible from the root ball. Take off any o ...
... As your violets get older, the lower row of leaves usually dies off. Removing the dead leaves tends to make the plant look as if it has a neck. When this happens, it is time to repot. Take the plant out of the container and gently brush off as much soil as possible from the root ball. Take off any o ...
Topic 13 - OoCities
... substances. Root system is simple and sometimes functions as an anchoring device since absorption is carried out by all other parts of the plant. ...
... substances. Root system is simple and sometimes functions as an anchoring device since absorption is carried out by all other parts of the plant. ...
PIGNUT CONTROL PROGRAM
... The plant has deep roots on which develop nut-like tubers 10 to 15 inches below the surface and are difficult to remove from the soil. This plant is a herb, the stems of which are 8 to 12 inches high, with a tuft of leaves at the base. The leaves are twice divided, 3 to 5 inches long, and there are ...
... The plant has deep roots on which develop nut-like tubers 10 to 15 inches below the surface and are difficult to remove from the soil. This plant is a herb, the stems of which are 8 to 12 inches high, with a tuft of leaves at the base. The leaves are twice divided, 3 to 5 inches long, and there are ...
our Flyer - Pierce County Noxious Weed Control Board
... An aquatic weed from the Haloragaceae Family, Variable– Leaf Milfoil spreads primarily through vegetative fragments, although it may also reproduce via seed production. Variable leaf milfoil is a submersed, rooted aquatic plant, that has both submerged and emergent leaves growing from a stout re ...
... An aquatic weed from the Haloragaceae Family, Variable– Leaf Milfoil spreads primarily through vegetative fragments, although it may also reproduce via seed production. Variable leaf milfoil is a submersed, rooted aquatic plant, that has both submerged and emergent leaves growing from a stout re ...
PLANT FORM AND FUNCTION
... have parasitic roots. These are Haustoria and they penetrate into the xylem and phloem vascular tissue of a host plant allowing the parasite to grow without the investment in growth of the tree trunk to reach light or roots that have to reach the ground for water. Parasitic plant with ...
... have parasitic roots. These are Haustoria and they penetrate into the xylem and phloem vascular tissue of a host plant allowing the parasite to grow without the investment in growth of the tree trunk to reach light or roots that have to reach the ground for water. Parasitic plant with ...
File
... Vascular bundles are arranged in a circle in the middle of the stem surrounding a central pith. To the outside of the vascular bundles is the cortex which is covered by a single layer of epidermis cells. The xylem orientated towards the middle of the stem and the phloem towards the outside. ...
... Vascular bundles are arranged in a circle in the middle of the stem surrounding a central pith. To the outside of the vascular bundles is the cortex which is covered by a single layer of epidermis cells. The xylem orientated towards the middle of the stem and the phloem towards the outside. ...
CLASSIFICATION ppt revision
... • They all contain chloroplasts, so that they can carry out photosynthesis. • They all have cell walls made of cellulose. • They all use photosynthesis to create their own food. • They store carbohydrates as starch or sucrose. ...
... • They all contain chloroplasts, so that they can carry out photosynthesis. • They all have cell walls made of cellulose. • They all use photosynthesis to create their own food. • They store carbohydrates as starch or sucrose. ...
Woody Plants Database
... 'Moonshadow' - wavy leaves bright yellow with a thin green margin; grows 1' - 2' tall and remains dense and compact ...
... 'Moonshadow' - wavy leaves bright yellow with a thin green margin; grows 1' - 2' tall and remains dense and compact ...
Ch. 22 Plant Diversity ppt
... Plants are multicellular eukaryotes that have cell walls made of cellulose They develop from multicellular embryos & carry out photosynthesis using the green pigments chlorophyll a & b ...
... Plants are multicellular eukaryotes that have cell walls made of cellulose They develop from multicellular embryos & carry out photosynthesis using the green pigments chlorophyll a & b ...
Tropicanna® Canna 4.6MB - Landscaping With Tesselaar Plants
... In garden beds: grows to 4’ (1.2 m) high in the first year, grows up to 6’ (2 m) high in subsequent years in USDA Zones 7 and above if undisturbed (not lifted), after growing season. In containers: will grow 3’ (9 m) high or more, can be cut back any time to force new growth. Plant in a large pot, 2 ...
... In garden beds: grows to 4’ (1.2 m) high in the first year, grows up to 6’ (2 m) high in subsequent years in USDA Zones 7 and above if undisturbed (not lifted), after growing season. In containers: will grow 3’ (9 m) high or more, can be cut back any time to force new growth. Plant in a large pot, 2 ...
FA-3
... Photosynthesis: In some desert plants, leaves are absent or reduced to spines. Here, the stem performs photosynthesis to synthesise food. Supportive structures: In climbing plants, stems are modified sometimes into structures which twine around the support. Leaves Leaves are the structures which dev ...
... Photosynthesis: In some desert plants, leaves are absent or reduced to spines. Here, the stem performs photosynthesis to synthesise food. Supportive structures: In climbing plants, stems are modified sometimes into structures which twine around the support. Leaves Leaves are the structures which dev ...
Chapter 22 Worksheet - Hamilton Local Schools
... f. tissue that carries water upward from the roots to other parts of the plant ...
... f. tissue that carries water upward from the roots to other parts of the plant ...
Gas Exchange in Plants
... In the roots and stem gas exchange occurs in the outer layer of cells Lenticels break though the bark (on woody plants) and allow air to diffuse though Within the plant diffusion is used in the spongy ...
... In the roots and stem gas exchange occurs in the outer layer of cells Lenticels break though the bark (on woody plants) and allow air to diffuse though Within the plant diffusion is used in the spongy ...
The Plant Kingdom - UNT's College of Education
... Apical Meristem (Produces new cells for growth) Zone of Elongation (Cells elongate allowing the root to grow longer) Zone of Maturation (Cells develop into tissues) ...
... Apical Meristem (Produces new cells for growth) Zone of Elongation (Cells elongate allowing the root to grow longer) Zone of Maturation (Cells develop into tissues) ...
Plant Responses: Hormones
... today, living fossil – Class Cycadopsida – Cycads; found in tropics – Class Pinopsida – cone bearers; 9 families contain over 300 species, evergreens: pines, spruce, hemlocks, firs What does Vasuclar Tissue mean? Means they have xylem (water) and phloem (sugar) to transport water up from the ground ...
... today, living fossil – Class Cycadopsida – Cycads; found in tropics – Class Pinopsida – cone bearers; 9 families contain over 300 species, evergreens: pines, spruce, hemlocks, firs What does Vasuclar Tissue mean? Means they have xylem (water) and phloem (sugar) to transport water up from the ground ...
Photosynthesis - Shelton State
... -photolysis= -electron transport chain -involves two pathways for e- to flow Noncyclic Electron Flow Light Rxn: -occurs in plants & algae - e- originate with H2O and end with NADPH -both photosystems are involved -Noncyclic Photosphosphorylation ...
... -photolysis= -electron transport chain -involves two pathways for e- to flow Noncyclic Electron Flow Light Rxn: -occurs in plants & algae - e- originate with H2O and end with NADPH -both photosystems are involved -Noncyclic Photosphosphorylation ...
Infection process of Plectosporium alismatis on host and non
... and S. graminea Inoculate with spore suspension of RH97 ...
... and S. graminea Inoculate with spore suspension of RH97 ...
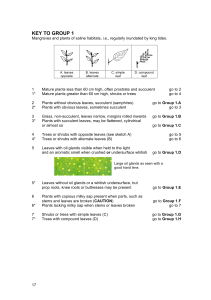
Section 1-Maggie-final_AM
... This plant grows from 3-20 m tall and has thick peg-like roots or pneumatophores which poke up through the mud. Leaves opposite, slightly reflexed at the tip, apex acute to obtuse. Flowers large with numerous long white stamens followed by a cupular fruit more than 2 cm diameter, greenish, sepals pe ...
... This plant grows from 3-20 m tall and has thick peg-like roots or pneumatophores which poke up through the mud. Leaves opposite, slightly reflexed at the tip, apex acute to obtuse. Flowers large with numerous long white stamens followed by a cupular fruit more than 2 cm diameter, greenish, sepals pe ...
Plant Project Rubrics
... Where they are found---around water so plant won’t dry out Way of transporting materials---no roots, stems, or leaves so absorb water and nutrients directly from their surroundings. Process of sexual reproduction---water needed for sperm to swim to egg 2. Bryophytes (Mosses & Liverworts) (non ...
... Where they are found---around water so plant won’t dry out Way of transporting materials---no roots, stems, or leaves so absorb water and nutrients directly from their surroundings. Process of sexual reproduction---water needed for sperm to swim to egg 2. Bryophytes (Mosses & Liverworts) (non ...
Chapter 9A
... -rootstock consists of non-elongating small amount ofvertical stem relatively undifferentiated shoot apical meristem (bearing roots below) but vertically oriented bearing leaf spines, and a massive quantity stem characteristic of cactus family, of thick, fleshy ...
... -rootstock consists of non-elongating small amount ofvertical stem relatively undifferentiated shoot apical meristem (bearing roots below) but vertically oriented bearing leaf spines, and a massive quantity stem characteristic of cactus family, of thick, fleshy ...
Leaf

A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant and is the principal lateral appendage of the stem. The leaves and stem together form the shoot. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves collectively.Typically a leaf is a thin, dorsiventrally flattened organ, borne above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Most leaves have distinctive upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) surfaces that differ in colour, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases) and other features. In most plant species, leaves are broad and flat. Such species are referred to as broad-leaved plants. Many gymnosperm species have thin needle-like leaves that can be advantageous in cold climates frequented by snow and frost. Leaves can also have other shapes and forms such as the scales in certain species of conifers. Some leaves are not above ground (such as bulb scales). Succulent plants often have thick juicy leaves, but some leaves are without major photosynthetic function and may be dead at maturity, as in some cataphylls, and spines). Furthermore, several kinds of leaf-like structures found in vascular plants are not totally homologous with them. Examples include flattened plant stems (called phylloclades and cladodes), and phyllodes (flattened leaf stems), both of which differ from leaves in their structure and origin. Many structures of non-vascular plants, and even of some lichens, which are not plants at all (in the sense of being members of the kingdom Plantae), look and function much like leaves. The primary site of photosynthesis in most leaves (palisade mesophyll) almost always occurs on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of Eucalyptus palisade occurs on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral.