Levels of Biological Organization
... Ferns, Lycophytes and horsetails Share features with Bryophytes Have rudimentary root and vascular system Seed producing plants (Gymnosperms and angiosperms) Gymnosperms (naked seed) includes conifers Produce cone-like structure Wind pollinated- pollen reach exposed reproductive struct ...
... Ferns, Lycophytes and horsetails Share features with Bryophytes Have rudimentary root and vascular system Seed producing plants (Gymnosperms and angiosperms) Gymnosperms (naked seed) includes conifers Produce cone-like structure Wind pollinated- pollen reach exposed reproductive struct ...
Functions of Plant Parts:
... • Identify major internal structures, external structures, methods of locomotion, methods of reproduction and stages of development of plants: flower pistil style filament pollen fruit ovary anther roots stem leaves stomata xylem phloem transpiration node ...
... • Identify major internal structures, external structures, methods of locomotion, methods of reproduction and stages of development of plants: flower pistil style filament pollen fruit ovary anther roots stem leaves stomata xylem phloem transpiration node ...
Hydrangea macrophylla
... rich rose-pink lacecap with sturdy pink-red stems, dark green leaves that turn rose-pink-purple in fall, and high mildew and Cercospora leaf spot resistance is a significant introduction in the tradition of the remontant flowering cultivars, Endless Summer™ and ‘Blushing Bride’. This introduction re ...
... rich rose-pink lacecap with sturdy pink-red stems, dark green leaves that turn rose-pink-purple in fall, and high mildew and Cercospora leaf spot resistance is a significant introduction in the tradition of the remontant flowering cultivars, Endless Summer™ and ‘Blushing Bride’. This introduction re ...
Diversity of Plants - Dublin City University
... Seedless vascular plants • All have phloem and xylem in the stem to transport sugars and water (tracheids only) • All have underground stem (rhizome) • All have essentially the same reproductive system with a dominant sporophyte ...
... Seedless vascular plants • All have phloem and xylem in the stem to transport sugars and water (tracheids only) • All have underground stem (rhizome) • All have essentially the same reproductive system with a dominant sporophyte ...
THINGS TO STUDY FOR THE FINAL EXAM
... 1. What organs do plants possess? Tissues? Cells? a. Compare and contrast the structures and functions of each. 2. How is the dependence (or lack thereof) on water reflected in the plants’ structures? 3. Compare and contrast pollination in the seed plants. 4. What are the organs of the embryo? a. Wh ...
... 1. What organs do plants possess? Tissues? Cells? a. Compare and contrast the structures and functions of each. 2. How is the dependence (or lack thereof) on water reflected in the plants’ structures? 3. Compare and contrast pollination in the seed plants. 4. What are the organs of the embryo? a. Wh ...
BWSR Featured Plant - Minnesota Board of Water and Soil Resources
... Maximilian’s Sunflower has tall, upright, hairy stems without much branching with the exception of where the flowers emerge. It has alternate leaves except at the base of the plant where the leaves are opposite. The leaves have white hairs on the surface and sparse to smooth teeth on the edges. The ...
... Maximilian’s Sunflower has tall, upright, hairy stems without much branching with the exception of where the flowers emerge. It has alternate leaves except at the base of the plant where the leaves are opposite. The leaves have white hairs on the surface and sparse to smooth teeth on the edges. The ...
Plants- Part One
... in the soil that are needed for plant growth Gas exchange- plants need CO2 for photosynthesis and O2 for respiration Movement of water and minerals- plants must be able to take in both water and minerals and transport them throughout. ...
... in the soil that are needed for plant growth Gas exchange- plants need CO2 for photosynthesis and O2 for respiration Movement of water and minerals- plants must be able to take in both water and minerals and transport them throughout. ...
4. Milkweed - Friess Lake School District
... What is unusual about the seedpods or seeds of this plant? The flower clusters form warty, greenish-white pots in August and September. Inside the pods are numerous dark brown seeds attached to long white, silky fibers. When the pod ripens and splits, the fibers dry and form parachutes in order to t ...
... What is unusual about the seedpods or seeds of this plant? The flower clusters form warty, greenish-white pots in August and September. Inside the pods are numerous dark brown seeds attached to long white, silky fibers. When the pod ripens and splits, the fibers dry and form parachutes in order to t ...
Unit 5 : Diversity of Life Content Outline: Plant Kingdom (5.6) – Part 1
... 2. They are small organisms made of few cells, materials move from cell to cell by absorption and diffusion. 3. They are collectively known as Bryophytes (mosses, liverworts, hornworts). 4. They live in damp locations. B. Vascular plants 1. The seedless vascular plants known as Pteriodophytes. 2. Va ...
... 2. They are small organisms made of few cells, materials move from cell to cell by absorption and diffusion. 3. They are collectively known as Bryophytes (mosses, liverworts, hornworts). 4. They live in damp locations. B. Vascular plants 1. The seedless vascular plants known as Pteriodophytes. 2. Va ...
O A RIGINAL RTICLE
... Observations show two types of secretive glands with short stalks. The first with unicellular globule head and the second is a multicellular oval head. The presence of these types of glands are dense in M. spicata. Covering trichomes are simple and more dense in M. pulegium with no more then two cel ...
... Observations show two types of secretive glands with short stalks. The first with unicellular globule head and the second is a multicellular oval head. The presence of these types of glands are dense in M. spicata. Covering trichomes are simple and more dense in M. pulegium with no more then two cel ...
Pests and Diseases
... Diseases • There are 3 conditions necessary for diseases in plants – host plant – disease causing organism or pathogen must be present – favorable environment for disease organism to develop ...
... Diseases • There are 3 conditions necessary for diseases in plants – host plant – disease causing organism or pathogen must be present – favorable environment for disease organism to develop ...
Insect Solutions PDF - Buffalo Bonsai Society
... FUNGUS GNATS – are tiny little black insects hovering around plants. The adults do no harm, other than annoyance, but the larvae in the soil can damage fine root hairs if in large numbers. They prefer dying plant roots and are an indication that the soil is being kept too wet (which kills the roots) ...
... FUNGUS GNATS – are tiny little black insects hovering around plants. The adults do no harm, other than annoyance, but the larvae in the soil can damage fine root hairs if in large numbers. They prefer dying plant roots and are an indication that the soil is being kept too wet (which kills the roots) ...
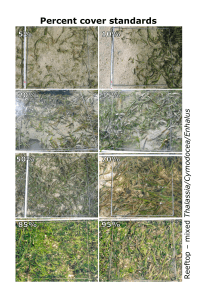
Species ID codes - Master.CDR - Seagrass
... Take the photograph from an angle as vertical as possible, which includes the entire quadrat frame, quadrat label and tape measure. Avoid having any shadows or patches of reflection off any water in the field of view. Check the photo taken box on datasheet for quadrat. Step 2. Describe sediment comp ...
... Take the photograph from an angle as vertical as possible, which includes the entire quadrat frame, quadrat label and tape measure. Avoid having any shadows or patches of reflection off any water in the field of view. Check the photo taken box on datasheet for quadrat. Step 2. Describe sediment comp ...
upper primary - Garth Cochrane
... Before moving into the clump of trees find a sunny open space and ask the students to note factors of the climate such as temperature, sunlight, wind and humidity. Once under the trees they will feel a reduction in the temperature, light and wind. An increase in humidity would be harder to notice. S ...
... Before moving into the clump of trees find a sunny open space and ask the students to note factors of the climate such as temperature, sunlight, wind and humidity. Once under the trees they will feel a reduction in the temperature, light and wind. An increase in humidity would be harder to notice. S ...
Plant Control and Hormones
... Plants are divided into groups based on: 1. whether or not they have vascular conducting tissues. Xylem – moves water from the roots up to the leaves Phloem – moves sugars made in the leaves down to the roots. 2. whether or not they make seeds. 3. whether or not they have flowers. The four groups ar ...
... Plants are divided into groups based on: 1. whether or not they have vascular conducting tissues. Xylem – moves water from the roots up to the leaves Phloem – moves sugars made in the leaves down to the roots. 2. whether or not they make seeds. 3. whether or not they have flowers. The four groups ar ...
BIOL 121
... One lineage gave rise to Bryophytes - plants that lack a xylem and phloem (non-vascular plants) mosses and their close relatives. Bryophytes have flagellated sperm which closely resemble those of the algal group, and which must swim to the eggs, so fertilization requires the plant be covered with wa ...
... One lineage gave rise to Bryophytes - plants that lack a xylem and phloem (non-vascular plants) mosses and their close relatives. Bryophytes have flagellated sperm which closely resemble those of the algal group, and which must swim to the eggs, so fertilization requires the plant be covered with wa ...
Carnivorous Plants and Insects
... •All traps are based on hairy leaves and folding •Hairs trap water droplets, insects drown in water •Bacteria decompose, nutrients absorbed into leaves •More water held, selective advantage pitfall traps •Bladder traps originate from aquatic plants with pitfall traps ...
... •All traps are based on hairy leaves and folding •Hairs trap water droplets, insects drown in water •Bacteria decompose, nutrients absorbed into leaves •More water held, selective advantage pitfall traps •Bladder traps originate from aquatic plants with pitfall traps ...
Nonvascular Plants
... Leaves called fronds found above ground and attached to a stem like petiole ...
... Leaves called fronds found above ground and attached to a stem like petiole ...
From Seed to Shining Seed
... of three node – composed of the leaf axil and bud opposite – leaf arrangement in which two leaves are attached at one level but on different sides of the stem ovary – where seeds develop at the base of a flower palmately compound – leaflets attached at the end of a stalk, spreading like fingers on a ...
... of three node – composed of the leaf axil and bud opposite – leaf arrangement in which two leaves are attached at one level but on different sides of the stem ovary – where seeds develop at the base of a flower palmately compound – leaflets attached at the end of a stalk, spreading like fingers on a ...
Life Cycle of Plants Study Guide
... ● Many plants grow from seeds. ● The plant parts that grow out of stems are leaves. ● All plant parts are made of cells. ● Chlorophyll gives plants their green color. ● A seed needs water to germinate. ● A young plant is a seedling. ● The underground parts of a plant is a plant that take in water an ...
... ● Many plants grow from seeds. ● The plant parts that grow out of stems are leaves. ● All plant parts are made of cells. ● Chlorophyll gives plants their green color. ● A seed needs water to germinate. ● A young plant is a seedling. ● The underground parts of a plant is a plant that take in water an ...
Plant Problems
... plants may be affected • May impact a large area • May have a noticeable pattern • Defined line from healthy to unhealthy tissue ...
... plants may be affected • May impact a large area • May have a noticeable pattern • Defined line from healthy to unhealthy tissue ...
aquatic plants of texas - AgriLife Extension County Offices
... distinguish from flat-stem pondweed. Distinctive yellow, star-shaped flowers provides basis for it’s common name. ARROWHEAD (Sagittaria spp.) Perennial, generally emergent plants growing from a rhizome with large leaves. Leaf shape can vary from blade to the broad lancelot form. Some underwater rose ...
... distinguish from flat-stem pondweed. Distinctive yellow, star-shaped flowers provides basis for it’s common name. ARROWHEAD (Sagittaria spp.) Perennial, generally emergent plants growing from a rhizome with large leaves. Leaf shape can vary from blade to the broad lancelot form. Some underwater rose ...
1 Plant Characteristics Booklet Student Name
... Roots are used to anchor the plant and absorb water & nutrients from the soil. The greater surface area of the root, the better it absorbs water & nutrients. ...
... Roots are used to anchor the plant and absorb water & nutrients from the soil. The greater surface area of the root, the better it absorbs water & nutrients. ...
Uglynest caterpillar
... wings and a wingspan of approximately 18–25 mm. Mature larvae are about 20 mm long and greenish yellow with black heads. Larvae pupate in the nest. Life history: Overwintered eggs begin to hatch in May. Larvae live together in dense nests of webbing, leaves and twigs, and may be present until Septem ...
... wings and a wingspan of approximately 18–25 mm. Mature larvae are about 20 mm long and greenish yellow with black heads. Larvae pupate in the nest. Life history: Overwintered eggs begin to hatch in May. Larvae live together in dense nests of webbing, leaves and twigs, and may be present until Septem ...
Phyllanthus fluitans - Florida Natural Areas Inventory
... Growth Habit: Floating Aquatic Origin: Central and South America ...
... Growth Habit: Floating Aquatic Origin: Central and South America ...
Leaf

A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant and is the principal lateral appendage of the stem. The leaves and stem together form the shoot. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves collectively.Typically a leaf is a thin, dorsiventrally flattened organ, borne above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Most leaves have distinctive upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) surfaces that differ in colour, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases) and other features. In most plant species, leaves are broad and flat. Such species are referred to as broad-leaved plants. Many gymnosperm species have thin needle-like leaves that can be advantageous in cold climates frequented by snow and frost. Leaves can also have other shapes and forms such as the scales in certain species of conifers. Some leaves are not above ground (such as bulb scales). Succulent plants often have thick juicy leaves, but some leaves are without major photosynthetic function and may be dead at maturity, as in some cataphylls, and spines). Furthermore, several kinds of leaf-like structures found in vascular plants are not totally homologous with them. Examples include flattened plant stems (called phylloclades and cladodes), and phyllodes (flattened leaf stems), both of which differ from leaves in their structure and origin. Many structures of non-vascular plants, and even of some lichens, which are not plants at all (in the sense of being members of the kingdom Plantae), look and function much like leaves. The primary site of photosynthesis in most leaves (palisade mesophyll) almost always occurs on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of Eucalyptus palisade occurs on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral.