Topological quantum memory
... fundamental quantum gate,11 assuming that decoherence is the only source of error. This estimate of the accuracy threshold is obtained by analyzing the efficacy of a concatenated code, a hierarchy of codes within codes, and it is based on many assumptions, which we will elaborate in Sec. II. For now ...
... fundamental quantum gate,11 assuming that decoherence is the only source of error. This estimate of the accuracy threshold is obtained by analyzing the efficacy of a concatenated code, a hierarchy of codes within codes, and it is based on many assumptions, which we will elaborate in Sec. II. For now ...
The Rutherford Memorial Lecture 1958 Reminiscences
... So far, the primary object of the discussions within the Manchester group wag *theimmediate consequences of the discovery of the atomic nucleus. The general programme of interpreting the accumulated experience about the ordinary physical a n d chemical properties of matter on the basis of the Ruther ...
... So far, the primary object of the discussions within the Manchester group wag *theimmediate consequences of the discovery of the atomic nucleus. The general programme of interpreting the accumulated experience about the ordinary physical a n d chemical properties of matter on the basis of the Ruther ...
Solid-State Century
... Goldstein, Kilby nurtured his idea in a laboratory that he had to himself for a hot summer month while his colleagues were all on vacation. By the mid-1960s another hero, Gordon Moore (also profiled in this issue) noticed that the number of transistors that could be put on a chip was doubling every ...
... Goldstein, Kilby nurtured his idea in a laboratory that he had to himself for a hot summer month while his colleagues were all on vacation. By the mid-1960s another hero, Gordon Moore (also profiled in this issue) noticed that the number of transistors that could be put on a chip was doubling every ...
Technologies and Designs for Electronic Nanocomputers
... microelectronic device designs must be replaced with new designs that take advantage of the quantum mechanical effects that dominate on such a small scale. There are a number of obstacles to making molecularscale electronic computer devices. What will they “look” like? Upon what operating principles ...
... microelectronic device designs must be replaced with new designs that take advantage of the quantum mechanical effects that dominate on such a small scale. There are a number of obstacles to making molecularscale electronic computer devices. What will they “look” like? Upon what operating principles ...
Smooth Scaling of Valence Electronic Properties in Fullerenes: From
... though, containing many atoms and electrons, accurate quantum theoretical treatments are difficult and computationally intensive. Measurements of the electronic properties of the isolated molecules are similarly challenging [2, 3]. On the other hand, the regular, quasispherical structures of these p ...
... though, containing many atoms and electrons, accurate quantum theoretical treatments are difficult and computationally intensive. Measurements of the electronic properties of the isolated molecules are similarly challenging [2, 3]. On the other hand, the regular, quasispherical structures of these p ...
AbMinPRL - University of Strathclyde
... There are two remaining problems in the AbrahamMinkowski dilemma: why is it that the experiments supporting one or other of these momenta give the results that they do and how can we correctly identify the momenta in a dispersive medium [19]? Explaining these, we suggest, completes the resolution of ...
... There are two remaining problems in the AbrahamMinkowski dilemma: why is it that the experiments supporting one or other of these momenta give the results that they do and how can we correctly identify the momenta in a dispersive medium [19]? Explaining these, we suggest, completes the resolution of ...
Quantum Mechanics of Many-Particle Systems: Atoms, Molecules
... ‘Big Bang’, when all the particles in the present Universe were contained in a small ‘ball’ which exploded – the interactions between them driving them apart to form the Expanding Universe we still have around us today. The first part of the chapter tells the story, as best we know it, from the tim ...
... ‘Big Bang’, when all the particles in the present Universe were contained in a small ‘ball’ which exploded – the interactions between them driving them apart to form the Expanding Universe we still have around us today. The first part of the chapter tells the story, as best we know it, from the tim ...
Aalborg Universitet The effect of time-dependent coupling on non-equilibrium steady states
... coupled system, the state does not depend at all on the switching. Moreover, we show that the stationary charge current has the same invariant property, and derive the Landau-Lifschitz and Landauer-Büttiker formulas. 1. Introduction The goal of this paper is to construct and study non equilibrium s ...
... coupled system, the state does not depend at all on the switching. Moreover, we show that the stationary charge current has the same invariant property, and derive the Landau-Lifschitz and Landauer-Büttiker formulas. 1. Introduction The goal of this paper is to construct and study non equilibrium s ...
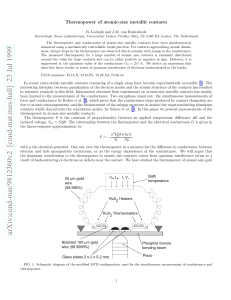
Thermopower of atomic-size metallic contacts
... remains equal to the substrate temperature and we assume that the actual temperature difference over the contact is a fixed fraction, α, of the measured temperature difference. We then determine this fraction by comparing the measured large-contact thermopower as a function of temperature with liter ...
... remains equal to the substrate temperature and we assume that the actual temperature difference over the contact is a fixed fraction, α, of the measured temperature difference. We then determine this fraction by comparing the measured large-contact thermopower as a function of temperature with liter ...
Particle Physics Part III Major Option 2008
... Empirically, the strong force is short range and therefore know that the physical gluons are confined. The colour singlet state does not exist in nature ! NOTE: this is not entirely ad hoc. In the context of gauge field theory (see minor option) the strong interaction arises from a fundamental SU( ...
... Empirically, the strong force is short range and therefore know that the physical gluons are confined. The colour singlet state does not exist in nature ! NOTE: this is not entirely ad hoc. In the context of gauge field theory (see minor option) the strong interaction arises from a fundamental SU( ...
arXiv:quant-ph/0202122 v1 21 Feb 2002
... of interest. The promise of new technologies like safe cryptography and new “super computers”, capable of handling otherwise untractable problems, has excited not only researchers from many different fields like physicists, mathematicians and computer scientists, but also a large public audience. On a ...
... of interest. The promise of new technologies like safe cryptography and new “super computers”, capable of handling otherwise untractable problems, has excited not only researchers from many different fields like physicists, mathematicians and computer scientists, but also a large public audience. On a ...
Electrostatic Formula
... For a capacitor U = ½ QV since it is easier to add charge at first and progressively gets more difficult C = Q CV = Q therefore U =1/2 QV= ½ CV2 V C = Q V = Q therefore U = ½ QV = ½ Q2 V C C ...
... For a capacitor U = ½ QV since it is easier to add charge at first and progressively gets more difficult C = Q CV = Q therefore U =1/2 QV= ½ CV2 V C = Q V = Q therefore U = ½ QV = ½ Q2 V C C ...
ORAMs in a Quantum World - Cryptology ePrint Archive
... patterns, even by allowing the adaptive execution of polynomially many learning queries. To our knowledge, this is the first time that these notions are defined in a homogeneous framework that allows for a formal treatment of any ORAM construction, without going to formal extremes that make it usele ...
... patterns, even by allowing the adaptive execution of polynomially many learning queries. To our knowledge, this is the first time that these notions are defined in a homogeneous framework that allows for a formal treatment of any ORAM construction, without going to formal extremes that make it usele ...
... chips rapidly decreases. Once the size of individual elements reach a certain critical level, their behavior and properties are no longer governed by classical physics, but rather by quantum mechanics. Another motivation was put forward by Richard P. Feynman [Feynman, 1982], who was among the first ...
Neutrino Oscillations
... Time evolution of the pendulums Lower frequency normal mode Higher frequency normal mode The basic physics behind neutrino oscillation can be found in any system of coupled harmonic oscillators. A simple example is a system of two pendulums connected by a weak spring (a spring with a small spring co ...
... Time evolution of the pendulums Lower frequency normal mode Higher frequency normal mode The basic physics behind neutrino oscillation can be found in any system of coupled harmonic oscillators. A simple example is a system of two pendulums connected by a weak spring (a spring with a small spring co ...
Quantum electrodynamics

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it ""the jewel of physics"" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen.