AD/HD, bipolar Disorder, and Effective treatment
... The consequence of not treating either disorder is usually some measure of compromised function for the affected individual. Both disorders can have lifelong consequences. Many AD/HD adults tell of not having reached their potential in their academic work, hence impairing their life’s choice of work ...
... The consequence of not treating either disorder is usually some measure of compromised function for the affected individual. Both disorders can have lifelong consequences. Many AD/HD adults tell of not having reached their potential in their academic work, hence impairing their life’s choice of work ...
Document
... Narcissus rejected the Nymph Echo He was cursed to fall in love with his own reflection. ...
... Narcissus rejected the Nymph Echo He was cursed to fall in love with his own reflection. ...
Borderline Personality Disorder
... Diagnostic Interview for Borderline Personality Disorders-Revised, ...
... Diagnostic Interview for Borderline Personality Disorders-Revised, ...
Mental Disorders
... There is no known single cause of schizophrenia. It appears that genetic factors produce a vulnerability to schizophrenia, with environmental factors contributing to different degrees in ...
... There is no known single cause of schizophrenia. It appears that genetic factors produce a vulnerability to schizophrenia, with environmental factors contributing to different degrees in ...
Abnormal Psych
... the tic must be expressed (against their will). Tics in response to an environmental trigger can appear to be voluntary or purposeful but are not. ...
... the tic must be expressed (against their will). Tics in response to an environmental trigger can appear to be voluntary or purposeful but are not. ...
DSM-IV
... • Existence in one individual of two or more distinct identities or personality states that each has its own pattern of perceiving, relating to, and thinking about the environment and self. • At least 2 of the personalities take control of the person’s behavior in sequence, with gaps in recent & pas ...
... • Existence in one individual of two or more distinct identities or personality states that each has its own pattern of perceiving, relating to, and thinking about the environment and self. • At least 2 of the personalities take control of the person’s behavior in sequence, with gaps in recent & pas ...
Mental Disorders Powerpoint
... An illness of the mind that can affect the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of a person, preventing him or her from leading a happy, healthful, and productive life. ...
... An illness of the mind that can affect the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of a person, preventing him or her from leading a happy, healthful, and productive life. ...
ABNORMAL BEHAVIOR Theories and Diagnoses of Psychopathology
... Individuals suffering from psychological disorders may meet some or all of these criteria. It is important to keep in mind, though, that what is abnormal is defined by the society in which the behavior occurs—what some societies consider abnormal is perfectly average in other societies. ...
... Individuals suffering from psychological disorders may meet some or all of these criteria. It is important to keep in mind, though, that what is abnormal is defined by the society in which the behavior occurs—what some societies consider abnormal is perfectly average in other societies. ...
Ch 12
... Classifying Emotional Disorders Five axes, or dimensions Axis I: classifies current symptoms into explicitly defined categories Axis II: describes developmental disorders and long-standing personality disorders or maladaptive traits (compulssiveness, over-dependency, etc.) Axis III: physical disord ...
... Classifying Emotional Disorders Five axes, or dimensions Axis I: classifies current symptoms into explicitly defined categories Axis II: describes developmental disorders and long-standing personality disorders or maladaptive traits (compulssiveness, over-dependency, etc.) Axis III: physical disord ...
chapter 23 mental health
... converting the anxious feelings into physical symptoms that have no organic basis, but are perceived to be real by the individual ...
... converting the anxious feelings into physical symptoms that have no organic basis, but are perceived to be real by the individual ...
Chapter 16 Part I Intro to Abnormal Psychology,
... Please utilize Barron’s Book for this chapter! 4/3 Chapter 16 quiz – Intro to abnormal, anxiety, OCD, PTSD, and mood disorders quiz (25 MC questions) ...
... Please utilize Barron’s Book for this chapter! 4/3 Chapter 16 quiz – Intro to abnormal, anxiety, OCD, PTSD, and mood disorders quiz (25 MC questions) ...
Navigating the Kraepelinian Vortex2
... Developmental Coordination Disorder Stereotypic Movement Disorder Tourette’s Disorder Tic disorders (criteria for a “tic” have been standardized across all disorders) ...
... Developmental Coordination Disorder Stereotypic Movement Disorder Tourette’s Disorder Tic disorders (criteria for a “tic” have been standardized across all disorders) ...
Panic Disorder
... book published by the American Psychiatric Association that describes the specific symptoms and diagnostic guidelines for different psychological disorders ...
... book published by the American Psychiatric Association that describes the specific symptoms and diagnostic guidelines for different psychological disorders ...
Dissociative Disorders - Mood Disorders Association of Manitoba
... person literally dissociates him/herself from a situation or experience too traumatic to integrate with his/her conscious self. Symptoms of these disorders, or even one or more of the disorders themselves, are also seen in a number of other mental illnesses, including post-traumatic stress disorder, ...
... person literally dissociates him/herself from a situation or experience too traumatic to integrate with his/her conscious self. Symptoms of these disorders, or even one or more of the disorders themselves, are also seen in a number of other mental illnesses, including post-traumatic stress disorder, ...
Chpt_13_Psychologica..
... How do we decide when a set of symptoms are severe enough to be called a disorder that needs treatment? Can we define specific disorders clearly enough so that we can know that we’re all referring to the same behavior/mental state? Can we use our diagnostic labels to guide treatment rather than to s ...
... How do we decide when a set of symptoms are severe enough to be called a disorder that needs treatment? Can we define specific disorders clearly enough so that we can know that we’re all referring to the same behavior/mental state? Can we use our diagnostic labels to guide treatment rather than to s ...
CHAPTER 5 PERSONALITY DISORDERS
... What Are Personality Disorders? Personality disorders cause enduring patterns ...
... What Are Personality Disorders? Personality disorders cause enduring patterns ...
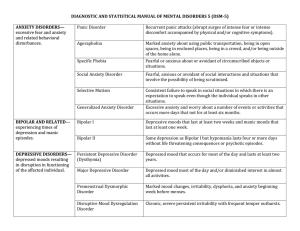
Major Disorders as Defined by DSM-5
... and behavior that deviates markedly from expectations of individual’s culture. ...
... and behavior that deviates markedly from expectations of individual’s culture. ...
Brochure - Lifestyle Intervention Conference
... and mental health, will describe the new diagnostic criteria and compare the DSM –IV and the new DSM5. Emphasis will be placed on the new diagnostic category of Substance Use and Addictive Disorders and mental health disorders including those most likely to be found in co-occurring with substance us ...
... and mental health, will describe the new diagnostic criteria and compare the DSM –IV and the new DSM5. Emphasis will be placed on the new diagnostic category of Substance Use and Addictive Disorders and mental health disorders including those most likely to be found in co-occurring with substance us ...
part 2 - University of Sussex
... 2) Have a severe personality disorder as defined by a high PCL-R score and/or a number of different personality disorder diagnoses 3) There should be a functional link between the personality disorder & the offending. ...
... 2) Have a severe personality disorder as defined by a high PCL-R score and/or a number of different personality disorder diagnoses 3) There should be a functional link between the personality disorder & the offending. ...
Somatoform disorders
... consciousness, alternative medical care common – High comorbidity with depression and anxiety disorders ...
... consciousness, alternative medical care common – High comorbidity with depression and anxiety disorders ...