THE WORLD OF ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY
... ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY COLLEGE COURSE PSYCH 219 Dr. Mary Ann Woodman Rogue Community College ...
... ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY COLLEGE COURSE PSYCH 219 Dr. Mary Ann Woodman Rogue Community College ...
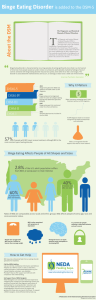
Binge Eating Disorder is added to the DSM-5
... the criteria established by the APA to diagnose them. For a particular mental disorder to be diagnosed in an individual, the individual must exhibit the symptoms listed in the criteria for that disorder. ...
... the criteria established by the APA to diagnose them. For a particular mental disorder to be diagnosed in an individual, the individual must exhibit the symptoms listed in the criteria for that disorder. ...
Cluster A Personality Disorders 301.0 Paranoid Personality Disorder
... Other Personality Disorders may be confused with Paranoid Personality Disorder because they have certain features in common. It is, therefore, important to distinguish among these disorders based on differences in their characteristic features. However, if an individual has personality features that ...
... Other Personality Disorders may be confused with Paranoid Personality Disorder because they have certain features in common. It is, therefore, important to distinguish among these disorders based on differences in their characteristic features. However, if an individual has personality features that ...
Chapter 15 pt. 1: Perspectives on Psychological Disorders and Anxiety
... Freud saw the neurotic disorders as ways of dealing with anxiety Psychotic disorder person loses contact with reality experiences irrational ideas and distorted perceptions ...
... Freud saw the neurotic disorders as ways of dealing with anxiety Psychotic disorder person loses contact with reality experiences irrational ideas and distorted perceptions ...
Pharmacological Issues in Treatment of Co
... Five (or more) of the following symptoms have been present during the same 2-week period and represent a change from previous functioning; at least one of the symptoms is either (1) depressed mood or (2) loss of interest or pleasure. Note: Do not include symptoms that are clearly due to a general me ...
... Five (or more) of the following symptoms have been present during the same 2-week period and represent a change from previous functioning; at least one of the symptoms is either (1) depressed mood or (2) loss of interest or pleasure. Note: Do not include symptoms that are clearly due to a general me ...
Chapter 12
... an enduring pattern of inner experience and behavior that deviates markedly from the expectations of the individual's culture. This pattern is manifested in two (or more) of the following areas: cognition (i.e., ways of perceiving and interpreting self, other people, and events); affectivity (i.e., ...
... an enduring pattern of inner experience and behavior that deviates markedly from the expectations of the individual's culture. This pattern is manifested in two (or more) of the following areas: cognition (i.e., ways of perceiving and interpreting self, other people, and events); affectivity (i.e., ...
has
... _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
... _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
Nov 22_BC_Psych disorders lecture.SOSC 103
... Mental health workers view psychological disorders as ongoing patterns of thoughts, feelings, and actions that are deviant, distressful, and dysfunctional (Comer, 2004). ...
... Mental health workers view psychological disorders as ongoing patterns of thoughts, feelings, and actions that are deviant, distressful, and dysfunctional (Comer, 2004). ...
Abnormal Psychology
... of people who suffer from psychological disorders Behavior and or thoughts From depression, substance abuse, learning difficulties to schizophrenia and bipolar disorder ...
... of people who suffer from psychological disorders Behavior and or thoughts From depression, substance abuse, learning difficulties to schizophrenia and bipolar disorder ...
Module32
... operates differently than the normal brain. • The frontal lobes show less activity. • Those with schizophrenia have a larger number of receptor sites for the neurotransmitter dopamine. ...
... operates differently than the normal brain. • The frontal lobes show less activity. • Those with schizophrenia have a larger number of receptor sites for the neurotransmitter dopamine. ...
Attention Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder
... the hyperactivity and impulsivity criteria, while older adolescents and adults (over age 17 years) must present with five. While the criteria have not changed from DSM-IV, examples have been included to illustrate the types of behavior children, older adolescents, and adults with ADHD might exhibit. ...
... the hyperactivity and impulsivity criteria, while older adolescents and adults (over age 17 years) must present with five. While the criteria have not changed from DSM-IV, examples have been included to illustrate the types of behavior children, older adolescents, and adults with ADHD might exhibit. ...
ICD-10: F60-62 Personality Disorders (F62.0
... (b)the abnormal behaviour pattern is enduring, of long standing, and not limited to episodes of mental illness; (c)the abnormal behaviour pattern is pervasive and clearly maladaptive to a broad range of personal and social situations; (d)the above manifestations always appear during childhood or ado ...
... (b)the abnormal behaviour pattern is enduring, of long standing, and not limited to episodes of mental illness; (c)the abnormal behaviour pattern is pervasive and clearly maladaptive to a broad range of personal and social situations; (d)the above manifestations always appear during childhood or ado ...
TAP3_LecturePowerPointSlides_Module32
... operates differently than the normal brain. • The frontal lobes show less activity. • Those with schizophrenia have a larger number of receptor sites for the neurotransmitter dopamine. ...
... operates differently than the normal brain. • The frontal lobes show less activity. • Those with schizophrenia have a larger number of receptor sites for the neurotransmitter dopamine. ...
Abnormal Psychology - West Morris Mendham High School
... -inability to behave in ways that further the well being of the individual and society *Discomfort- Psychological/Physiological *Deviance-Bizarre, unusual behavior *Dysfunction-inability to complete tasks or take responsibility -any behavior that interferes with personal growth ...
... -inability to behave in ways that further the well being of the individual and society *Discomfort- Psychological/Physiological *Deviance-Bizarre, unusual behavior *Dysfunction-inability to complete tasks or take responsibility -any behavior that interferes with personal growth ...
Psychologie Anglophone
... The DSM is controversial and some mental health professionals and others question the utility of this classification system. C/ Understanding the DSM Over the years, mental health professionals decided Freud’s emphasis on unconscious processes was too limiting and the category of neurosis was too la ...
... The DSM is controversial and some mental health professionals and others question the utility of this classification system. C/ Understanding the DSM Over the years, mental health professionals decided Freud’s emphasis on unconscious processes was too limiting and the category of neurosis was too la ...
Mental Health Nursing II NURS 2310
... toward authority figures that occurs more frequently than is usually observed in individuals of same age/developmental level Typically begins by age 8, and usually not later than early adolescence May precede a conduct disorder “Normal” oppositional phases occur in older infancy, toddlerhood, ...
... toward authority figures that occurs more frequently than is usually observed in individuals of same age/developmental level Typically begins by age 8, and usually not later than early adolescence May precede a conduct disorder “Normal” oppositional phases occur in older infancy, toddlerhood, ...
Personality Disorders - American Academy of Family Physicians
... well as cognitive or perceptual distortions and behavioral eccentricities), and paranoid (pervasive distrust and suspiciousness of others).7 The prevalence of schizoid personality disorder ranges from 0.5 to 7 percent in the general population to as high as 14 percent in the homeless population.5,14 ...
... well as cognitive or perceptual distortions and behavioral eccentricities), and paranoid (pervasive distrust and suspiciousness of others).7 The prevalence of schizoid personality disorder ranges from 0.5 to 7 percent in the general population to as high as 14 percent in the homeless population.5,14 ...
Review Questions - Bremen High School District 228
... 4) How is our behavior affected by the presence of others or by being part of a group? 5) What are group polarization and groupthink? 6) How do cultural norms affect our behavior? 7) How much power do we have as individuals? Can a minority sway a majority? 8) What is prejudice? 9) What are the socia ...
... 4) How is our behavior affected by the presence of others or by being part of a group? 5) What are group polarization and groupthink? 6) How do cultural norms affect our behavior? 7) How much power do we have as individuals? Can a minority sway a majority? 8) What is prejudice? 9) What are the socia ...
1. Joe has an intense, irrational fear of snakes. He is suffering from a
... A) reactive; process B) acute; reactive C) chronic; acute D) chronic; process 8. The early warning signs of schizophrenia, based on studies of high-risk children, include all but which of the following? A) having a severely schizophrenic mother B) having matured physically at a very early age C) hav ...
... A) reactive; process B) acute; reactive C) chronic; acute D) chronic; process 8. The early warning signs of schizophrenia, based on studies of high-risk children, include all but which of the following? A) having a severely schizophrenic mother B) having matured physically at a very early age C) hav ...
Abnormal Behavior What is Normal Behavior? What is Abnormal
... Diagnosis schizophrenia. • Why does the patient have delusions and hallucinations? • Because they are schizophrenic • Is a circular explanation ...
... Diagnosis schizophrenia. • Why does the patient have delusions and hallucinations? • Because they are schizophrenic • Is a circular explanation ...
Clinical Syndromes Scales
... the symptoms and attitudes characteristic of the phenomenology of depression rather than to adhere to any particular theory (Beck et al., 1996). • Additionally, although the BDI-II’s items are congruent with the DSM-IV, the BDIII is intended to identify the severity of symptoms and not nosological d ...
... the symptoms and attitudes characteristic of the phenomenology of depression rather than to adhere to any particular theory (Beck et al., 1996). • Additionally, although the BDI-II’s items are congruent with the DSM-IV, the BDIII is intended to identify the severity of symptoms and not nosological d ...
Abnormal Psychology
... of people who suffer from psychological disorders Behavior and or thoughts From depression, substance abuse, learning difficulties to schizophrenia and bipolar disorder ...
... of people who suffer from psychological disorders Behavior and or thoughts From depression, substance abuse, learning difficulties to schizophrenia and bipolar disorder ...
Ch 12
... 26. How can depression be a vicious cycle? In your discussion incorporate Martin Seligman’s concept of “learned helplessness.” 27. What does the cognitive approach to depression suggest as being an appropriate therapy for depression? 28. Why do depression rates tend to be higher in men than in women ...
... 26. How can depression be a vicious cycle? In your discussion incorporate Martin Seligman’s concept of “learned helplessness.” 27. What does the cognitive approach to depression suggest as being an appropriate therapy for depression? 28. Why do depression rates tend to be higher in men than in women ...
ADHD vs. Mood Disorders - Columbia Associates in Psychiatry
... looking for symptoms or diagnosis of either disorder among blood relatives can be useful. If Bipolar Disorder is revealed, the childhood history of those family members should be explored looking for similarities and differences. Many parents tell me that these possibilities were never considered. ...
... looking for symptoms or diagnosis of either disorder among blood relatives can be useful. If Bipolar Disorder is revealed, the childhood history of those family members should be explored looking for similarities and differences. Many parents tell me that these possibilities were never considered. ...
Borderline Personality Disorder: Podcast Script #1 A personality
... A personality disorder can best be described as behavior that is very different from what is considered “normal” for one’s culture (American Psychiatric Association [DSM-IV-TR], 2000). Personality disorders are stable over time, usually cause great distress or impairment to those affected, and typi ...
... A personality disorder can best be described as behavior that is very different from what is considered “normal” for one’s culture (American Psychiatric Association [DSM-IV-TR], 2000). Personality disorders are stable over time, usually cause great distress or impairment to those affected, and typi ...