2. Misconceptions about Psychological Disorders
... others? People may not want to seek help. When determining if ones behavior is “normal” or “abnormal” practice thinking of things that should be considered before labeling a disorder. ...
... others? People may not want to seek help. When determining if ones behavior is “normal” or “abnormal” practice thinking of things that should be considered before labeling a disorder. ...
Chapter 3 CLASSIFICATION OF MENTAL DISORDERS This chapter
... see themselves in a mirror, they frequently “see” themselves as fat, a phenomenon which suggests mistakes of perception. This condition is often disabling (although, some people with anorexia nervosa can perform rewarding work and maintain stable relationships). In spite of apparent “delusions” and ...
... see themselves in a mirror, they frequently “see” themselves as fat, a phenomenon which suggests mistakes of perception. This condition is often disabling (although, some people with anorexia nervosa can perform rewarding work and maintain stable relationships). In spite of apparent “delusions” and ...
DSM-5 Changes In Intellectual Disabilities And Mental Health
... – Explain the process of diagnosing mental illnesses and developmental disabilities without the traditional five-axis format – List at least three changes in specific diagnostic categories listed in the DSM-5 • Change in name and criteria for intellectual disability, including shift away from primar ...
... – Explain the process of diagnosing mental illnesses and developmental disabilities without the traditional five-axis format – List at least three changes in specific diagnostic categories listed in the DSM-5 • Change in name and criteria for intellectual disability, including shift away from primar ...
CHAPTER 31 for wiki
... in which an individual experiences two or more distinct and alternating personalities • Formerly called multiple personalities – Before the 1970s fewer than 100 cases had ever been reported. – In the 1980s alone, reports of more than 20,000 diagnosed cases appeared, almost all of them in North Ameri ...
... in which an individual experiences two or more distinct and alternating personalities • Formerly called multiple personalities – Before the 1970s fewer than 100 cases had ever been reported. – In the 1980s alone, reports of more than 20,000 diagnosed cases appeared, almost all of them in North Ameri ...
Unit 12 Abnormal Reading Guide 2017 - Bullis Haiku
... 1. Discuss how we draw the line between normality and disorder. 2. Discuss the controversy over the attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. 3. Contrast the medical model with the biopsychosocial approach to psychological disorders. 4. Describe how and why clinicians classify psychological disorder ...
... 1. Discuss how we draw the line between normality and disorder. 2. Discuss the controversy over the attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. 3. Contrast the medical model with the biopsychosocial approach to psychological disorders. 4. Describe how and why clinicians classify psychological disorder ...
Illness Summaries from DSM 5
... Paranoid Personality Disorder – Characterized by paranoia and a pervasive, long-standing suspiciousness and generalized mistrust of others. Schizoid Personality Disorder – Characterized by a lack of interest in social relationships, a tendency towards a solitary lifestyle, secretiveness, emotion ...
... Paranoid Personality Disorder – Characterized by paranoia and a pervasive, long-standing suspiciousness and generalized mistrust of others. Schizoid Personality Disorder – Characterized by a lack of interest in social relationships, a tendency towards a solitary lifestyle, secretiveness, emotion ...
Unit XII Textbook PowerPoint questions and answers
... later in life. b. People born in densely populated areas are less likely to develop schizophrenia later in life. c. Fetuses exposed to flu virus are more likely to develop schizophrenia later in life. d. Maternal influenza during pregnancy does not affect brain development in monkeys. e. The retrovi ...
... later in life. b. People born in densely populated areas are less likely to develop schizophrenia later in life. c. Fetuses exposed to flu virus are more likely to develop schizophrenia later in life. d. Maternal influenza during pregnancy does not affect brain development in monkeys. e. The retrovi ...
chapter 29-1
... • A “harmful dysfunction” in which behaviors are maladaptive, unjustifiable, disturbing, and atypical ...
... • A “harmful dysfunction” in which behaviors are maladaptive, unjustifiable, disturbing, and atypical ...
Personality Disorder
... Critics argue that the diagnosis of DID increased in the late 20th century. DID has not been found in other countries. Critics’ Arguments 1. Role-playing by people open to a therapist’s suggestion. 2. Learned response that reinforces reductions in anxiety. ...
... Critics argue that the diagnosis of DID increased in the late 20th century. DID has not been found in other countries. Critics’ Arguments 1. Role-playing by people open to a therapist’s suggestion. 2. Learned response that reinforces reductions in anxiety. ...
Module 29 Power Point
... • A “harmful dysfunction” in which behaviors are maladaptive, unjustifiable, disturbing, and atypical ...
... • A “harmful dysfunction” in which behaviors are maladaptive, unjustifiable, disturbing, and atypical ...
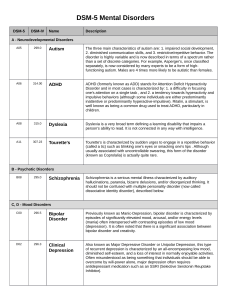
DSM V Mental Disorders
... (compulsions) aimed at relieving the anxiety brought on by those thoughts. Common compulsions include excessive handwashing, repeated checking, nervous rituals, or extreme hoarding. Unlike those with ObsessiveCompulsive Personality Disorder (OCPD), individuals with OCD often recognize that their obs ...
... (compulsions) aimed at relieving the anxiety brought on by those thoughts. Common compulsions include excessive handwashing, repeated checking, nervous rituals, or extreme hoarding. Unlike those with ObsessiveCompulsive Personality Disorder (OCPD), individuals with OCD often recognize that their obs ...
Anxiety, Somatoform, Dissociative Disorders and Stress
... trying to identify what behaviors Mr. Udall shows that are part of his obsessive compulsive disorder and which behaviors are part of his personality and if there are any other behaviors which might indicate ...
... trying to identify what behaviors Mr. Udall shows that are part of his obsessive compulsive disorder and which behaviors are part of his personality and if there are any other behaviors which might indicate ...
Chpt.14 & 15 Psychological Disorders & Treatment
... 1) Depressive Disorders *most common disorders” a mood disorder in which a person, for no apparent reason, experiences two or more weeks of depressed moods, feelings of worthlessness, and diminished interest or pleasure in most activities ...
... 1) Depressive Disorders *most common disorders” a mood disorder in which a person, for no apparent reason, experiences two or more weeks of depressed moods, feelings of worthlessness, and diminished interest or pleasure in most activities ...
Mood & Disruptive Behavior Disorders in Children & Adolescents
... Some did well at 1 year follow-up Some do not maintain Tx gains Lowered recidivism rates 6 - 18 months out Number of serious criminal offenses stayed the same These may be more difficult cases May require higher level of treatment ...
... Some did well at 1 year follow-up Some do not maintain Tx gains Lowered recidivism rates 6 - 18 months out Number of serious criminal offenses stayed the same These may be more difficult cases May require higher level of treatment ...
Psychological Disorders
... Can you see how social stigmas associated with psychological disorders and labels could effect others? People may not want to seek help. When determining if ones behavior is “normal” or “abnormal” practice thinking of things that should be considered before labeling a disorder. ...
... Can you see how social stigmas associated with psychological disorders and labels could effect others? People may not want to seek help. When determining if ones behavior is “normal” or “abnormal” practice thinking of things that should be considered before labeling a disorder. ...
abnormal psychology - Oxford University Press
... youngest child in the family are cleansed by bathing with a herb concoction as recommended by the traditional healer or a traditional community counsellor after the death of her husband. A person who is menstruating or who had sex that day is also regarded as having ‘sefifi’. Such people are not all ...
... youngest child in the family are cleansed by bathing with a herb concoction as recommended by the traditional healer or a traditional community counsellor after the death of her husband. A person who is menstruating or who had sex that day is also regarded as having ‘sefifi’. Such people are not all ...
Personality Disorder
... Critics argue that the diagnosis of DID increased in the late 20th century. DID has not been found in other countries. Critics’ Arguments 1. Role-playing by people open to a therapist’s suggestion. 2. Learned response that reinforces reductions in anxiety. ...
... Critics argue that the diagnosis of DID increased in the late 20th century. DID has not been found in other countries. Critics’ Arguments 1. Role-playing by people open to a therapist’s suggestion. 2. Learned response that reinforces reductions in anxiety. ...
doc - HCC Learning Web
... 1. Match each term with its definition. (1) _____ phobia (2) _____ specific phobia (3) _____ social phobia (A) fear of a certain object or situation (B) persistent, irrational fear and avoidance of an object or situation (C) irrational fear of embarrassment 2. Which of the following is suffering fro ...
... 1. Match each term with its definition. (1) _____ phobia (2) _____ specific phobia (3) _____ social phobia (A) fear of a certain object or situation (B) persistent, irrational fear and avoidance of an object or situation (C) irrational fear of embarrassment 2. Which of the following is suffering fro ...
Psychological Disorders - BowkerPsych
... choosy about picking friends, since they believe that not just anyone is worthy of being their friend. They are generally uninterested in the feelings of others and may take advantage of them. ...
... choosy about picking friends, since they believe that not just anyone is worthy of being their friend. They are generally uninterested in the feelings of others and may take advantage of them. ...
Somatic Symptom Disorder - DSM-5
... medically unexplained symptoms, DSM-5 criteria instead emphasize the degree to which a patient’s thoughts, feelings and behaviors about their somatic symptoms are disproportionate or excessive. The new narrative text for SSD notes that some patients with physical conditions such as heart disease or ...
... medically unexplained symptoms, DSM-5 criteria instead emphasize the degree to which a patient’s thoughts, feelings and behaviors about their somatic symptoms are disproportionate or excessive. The new narrative text for SSD notes that some patients with physical conditions such as heart disease or ...
DSM5, ICD10, PDM, 2013 - Mmpi
... • Elimination of the special attribution of bizarre delusions and Schneiderian first-rank auditory hallucinations (e.g., two or more voices conversing). • The second change is the addition of a requirement in Criterion A that the individual must have at least one of these three symptoms: delusions, ...
... • Elimination of the special attribution of bizarre delusions and Schneiderian first-rank auditory hallucinations (e.g., two or more voices conversing). • The second change is the addition of a requirement in Criterion A that the individual must have at least one of these three symptoms: delusions, ...
Psychopathology
... – The social circumstances lead to increased stress, and thus these people are more at risk. – Alternatively, those who have the disorder will be less successful and drift to the bottom of the social hierarchy, downward drift theory. ...
... – The social circumstances lead to increased stress, and thus these people are more at risk. – Alternatively, those who have the disorder will be less successful and drift to the bottom of the social hierarchy, downward drift theory. ...